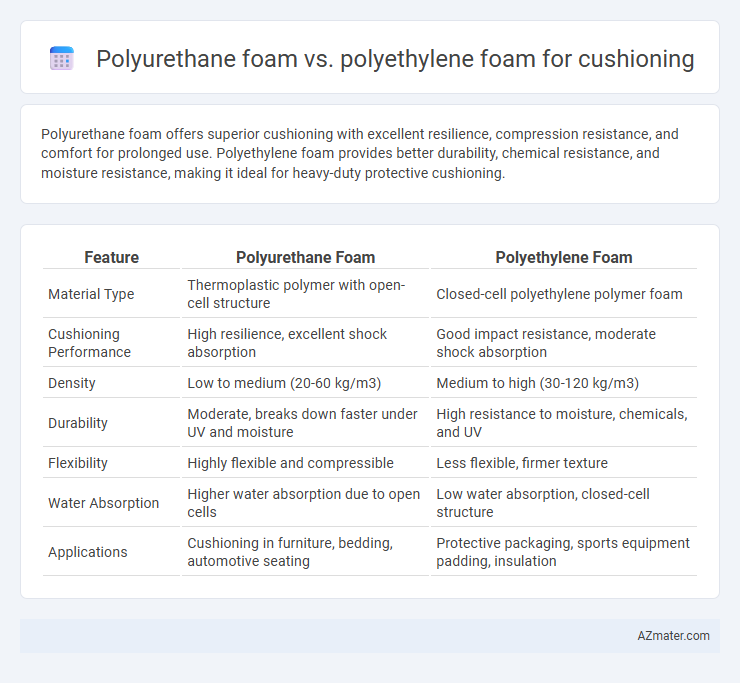
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning with excellent resilience, compression resistance, and comfort for prolonged use. Polyethylene foam provides better durability, chemical resistance, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty protective cushioning.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyurethane Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer with open-cell structure | Closed-cell polyethylene polymer foam |
| Cushioning Performance | High resilience, excellent shock absorption | Good impact resistance, moderate shock absorption |
| Density | Low to medium (20-60 kg/m3) | Medium to high (30-120 kg/m3) |
| Durability | Moderate, breaks down faster under UV and moisture | High resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and compressible | Less flexible, firmer texture |
| Water Absorption | Higher water absorption due to open cells | Low water absorption, closed-cell structure |
| Applications | Cushioning in furniture, bedding, automotive seating | Protective packaging, sports equipment padding, insulation |
Introduction to Foam Cushioning Materials
Polyurethane foam and polyethylene foam are widely used in cushioning applications due to their distinct properties and performance characteristics. Polyurethane foam offers excellent flexibility, shock absorption, and comfort, making it ideal for seating and bedding. Polyethylene foam provides superior durability, water resistance, and impact protection, often utilized in packaging and sports equipment cushioning.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane foam is a versatile, open-cell material known for its excellent cushioning and shock absorption properties, commonly used in furniture, packaging, and automotive applications. Its ability to compress and recover makes it ideal for providing comfort and protection by evenly distributing pressure and reducing impact forces. Compared to polyethylene foam, polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility and softness, making it more suitable for applications requiring enhanced ergonomic support.
What is Polyethylene Foam?
Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell, lightweight, and durable material known for its excellent cushioning and impact absorption properties, making it ideal for protective packaging and padding applications. Unlike polyurethane foam, polyethylene foam offers superior resistance to moisture, chemicals, and abrasion, enhancing its longevity in various environments. Its high tear strength and low compression set contribute to effective shock absorption and reusable cushioning solutions.
Key Differences Between Polyurethane and Polyethylene Foam
Polyurethane foam offers superior flexibility and cushioning with excellent rebound and resilience, making it ideal for applications requiring comfort and shock absorption. Polyethylene foam is denser, providing higher durability, moisture resistance, and structural support, suited for protective packaging and heavy-duty cushioning. The key differences lie in polyurethane's open-cell structure for softness and breathability versus polyethylene's closed-cell structure for rigidity and water resistance.
Cushioning Performance: Which Foam Protects Better?
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning performance due to its high resilience and ability to absorb impact effectively, making it ideal for applications requiring shock absorption and comfort. Polyethylene foam provides excellent compression resistance and durability but tends to be less effective than polyurethane in dissipating dynamic forces. For optimal product protection and comfort, polyurethane foam typically outperforms polyethylene foam in cushioning applications.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Polyurethane foam offers superior durability and long-lasting cushioning due to its higher resilience and ability to retain shape under repeated pressure, making it ideal for heavy-use applications. Polyethylene foam provides good cushioning with excellent moisture resistance and chemical stability but tends to compress faster, reducing its lifespan in high-impact environments. When comparing longevity, polyurethane foam generally outperforms polyethylene foam by maintaining structural integrity and comfort over extended periods.
Comfort and Support: Polyurethane vs Polyethylene
Polyurethane foam offers superior comfort and support due to its higher density and excellent energy absorption, making it ideal for cushioning that requires pressure relief and long-lasting resilience. Polyethylene foam provides firmer support with greater rigidity and impact resistance but lacks the same softness and contouring ability as polyurethane. Choosing between the two depends on the desired balance of cushioning softness and structural support for specific applications.
Cost Analysis of Polyurethane and Polyethylene Foams
Polyurethane foam generally offers a lower initial cost compared to polyethylene foam, making it a more budget-friendly option for cushioning applications. Polyethylene foam, while more expensive upfront, provides superior durability and resistance to moisture, which can reduce long-term replacement and maintenance costs. Evaluating both material costs and lifespan benefits is essential for accurate cost analysis in cushioning solutions.
Environmental Impact and Recycling Options
Polyurethane foam, widely used in cushioning, poses greater environmental challenges due to its reliance on petrochemicals and limited recycling options, often ending up in landfills where it can take decades to degrade. Polyethylene foam, while also petroleum-based, offers better recyclability through established processes like grinding and remelting, reducing its ecological footprint. Both materials contribute to microplastic pollution, but advancements in recycling technologies for polyethylene foam make it a relatively more sustainable choice in cushioning applications.
Which Foam is Best for Your Cushioning Needs?
Polyurethane foam offers superior comfort and flexibility, making it ideal for cushioning applications requiring softness and pressure relief, while polyethylene foam excels in durability, impact resistance, and moisture resistance, suited for heavy-duty protection and insulation. Choosing the best foam depends on your cushioning needs: opt for polyurethane foam for enhanced cushioning performance and comfort or select polyethylene foam for long-lasting, resilient cushioning in demanding environments. Understanding the specific use-case factors like load-bearing, environmental exposure, and desired softness ensures the right foam selection.
Infographic: Polyurethane foam vs Polyethylene foam for Cushioning
 azmater.com
azmater.com