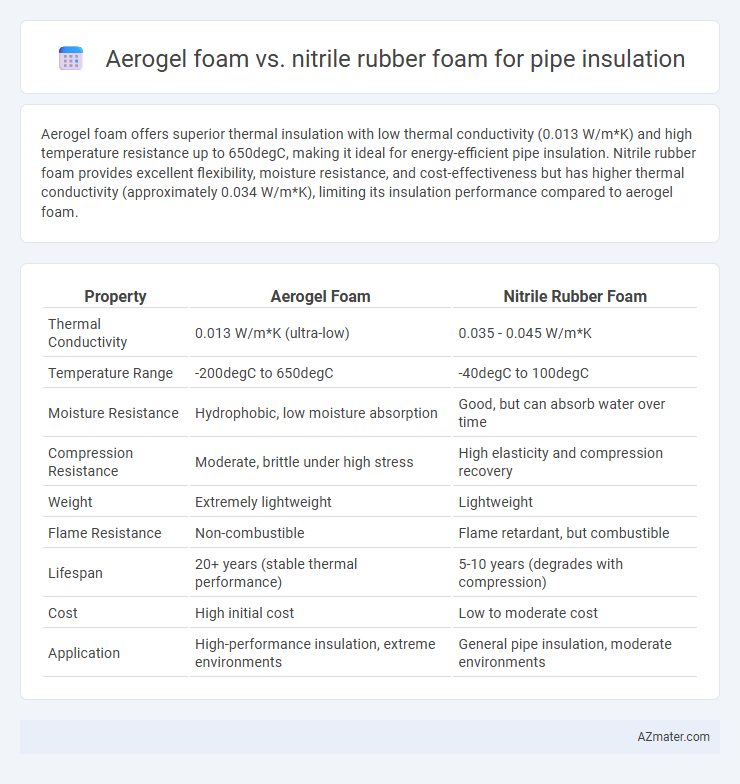
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation with low thermal conductivity (0.013 W/m*K) and high temperature resistance up to 650degC, making it ideal for energy-efficient pipe insulation. Nitrile rubber foam provides excellent flexibility, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness but has higher thermal conductivity (approximately 0.034 W/m*K), limiting its insulation performance compared to aerogel foam.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aerogel Foam | Nitrile Rubber Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.013 W/m*K (ultra-low) | 0.035 - 0.045 W/m*K |
| Temperature Range | -200degC to 650degC | -40degC to 100degC |
| Moisture Resistance | Hydrophobic, low moisture absorption | Good, but can absorb water over time |
| Compression Resistance | Moderate, brittle under high stress | High elasticity and compression recovery |
| Weight | Extremely lightweight | Lightweight |
| Flame Resistance | Non-combustible | Flame retardant, but combustible |
| Lifespan | 20+ years (stable thermal performance) | 5-10 years (degrades with compression) |
| Cost | High initial cost | Low to moderate cost |
| Application | High-performance insulation, extreme environments | General pipe insulation, moderate environments |
Introduction to Pipe Insulation Materials
Aerogel foam and nitrile rubber foam are widely used materials for pipe insulation, each offering distinct thermal properties and application benefits. Aerogel foam provides superior thermal resistance with extremely low thermal conductivity, making it ideal for high-performance insulation in industrial and cryogenic pipelines. Nitrile rubber foam offers flexibility, moisture resistance, and good thermal insulation, often preferred for HVAC systems and pipes requiring vibration damping.
Understanding Aerogel Foam: Properties and Composition
Aerogel foam, known for its ultra-low thermal conductivity ranging from 0.013 to 0.021 W/m*K, is primarily composed of silica-based nanoparticles creating a highly porous, lightweight structure that makes it one of the best insulating materials available. Its hydrophobic nature and low density, often below 150 kg/m3, enhance its efficiency in minimizing heat transfer and moisture penetration compared to conventional nitrile rubber foam, which typically exhibits thermal conductivity around 0.035 to 0.060 W/m*K. The rigid, mesoporous network of aerogel foam provides superior thermal resistance and durability in high-temperature environments, making it highly effective for pipe insulation applications where space savings and energy efficiency are critical.
Nitrile Rubber Foam: Features and Advantages
Nitrile Rubber Foam offers exceptional thermal insulation properties with a low thermal conductivity of around 0.035 W/m*K, making it highly efficient for pipe insulation. Its outstanding resistance to oil, chemicals, and moisture ensures durability and longevity in industrial environments, while its flexibility and closed-cell structure provide excellent vibration dampening and prevent water absorption. Compared to Aerogel foam, Nitrile Rubber Foam is easier to install, cost-effective, and performs exceptionally well in applications requiring robust mechanical strength and resistance to harsh conditions.
Thermal Insulation Performance: Aerogel vs Nitrile Rubber
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation performance compared to nitrile rubber foam due to its extremely low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.013 W/m*K, which significantly reduces heat transfer in pipe insulation applications. Nitrile rubber foam has higher thermal conductivity values, generally ranging from 0.035 to 0.045 W/m*K, making it less effective for minimizing energy loss. The high porosity and nanostructure of aerogel foam provide exceptional resistance to heat flow, outperforming nitrile rubber foam in maintaining temperature stability in insulated pipes.
Moisture Resistance and Water Vapor Permeability
Aerogel foam offers superior moisture resistance and extremely low water vapor permeability, making it highly effective for pipe insulation in damp or wet environments by preventing condensation and minimizing thermal bridging. Nitrile rubber foam, while flexible and resilient, exhibits higher water vapor permeability and can absorb moisture over time, reducing its insulating performance in humid conditions. For long-term protection against moisture-related damage and maintaining insulation efficiency, aerogel foam outperforms nitrile rubber foam in pipe insulation applications.
Fire Safety Comparison: Aerogel Foam vs Nitrile Rubber Foam
Aerogel foam exhibits superior fire resistance compared to nitrile rubber foam, with a higher ignition temperature and lower flame spread rating, making it a safer choice for pipe insulation in fire-sensitive environments. Nitrile rubber foam tends to melt and produce toxic smoke when exposed to flames, whereas aerogel foam is non-combustible and maintains structural integrity under extreme heat. Fire safety standards, such as ASTM E84, often rate aerogel foam significantly better, reducing fire hazards and improving overall safety in industrial and commercial piping applications.
Durability and Longevity in Real-World Applications
Aerogel foam exhibits superior durability and longevity in pipe insulation due to its exceptional thermal stability and resistance to moisture absorption, maintaining performance over extended periods in harsh environments. Nitrile rubber foam offers good flexibility and resistance to oils and chemicals but tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and mechanical stress, reducing its lifespan in outdoor or industrial settings. Real-world applications favor aerogel foam for long-term insulation needs where sustained thermal performance and minimal maintenance are critical.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation with a lightweight, rigid structure but requires careful handling during installation to avoid damage and often needs adhesive bonding or mechanical fasteners to secure it around pipes. Nitrile rubber foam provides excellent flexibility and ease of installation, allowing it to conform easily to pipe shapes, minimizing seams and reducing installation time. The flexibility of nitrile rubber foam makes it ideal for applications involving vibration or movement, whereas aerogel foam's brittleness demands precise installation techniques to maintain insulation integrity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation with a lower environmental footprint due to its minimal material density and longer lifespan, reducing energy consumption and waste over time. Nitrile rubber foam, while effective for moisture resistance and flexibility, typically relies on petroleum-based components and involves higher emissions during production, posing greater sustainability challenges. Choosing aerogel foam supports eco-friendly insulation projects by minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing energy efficiency in pipe insulation systems.
Cost Analysis and Final Recommendations
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation with higher R-values, significantly reducing energy losses in pipe insulation but comes at a premium cost ranging from $20 to $30 per square foot. Nitrile rubber foam, while less efficient thermally with R-values around 3 to 4, is more budget-friendly, typically priced between $5 and $8 per square foot, making it suitable for standard applications and moderate temperature ranges. For projects prioritizing long-term energy savings and high-performance insulation, aerogel foam is recommended despite upfront expenses, whereas nitrile rubber foam is ideal for cost-sensitive installations needing flexibility and moisture resistance.
Infographic: Aerogel foam vs Nitrile rubber foam for Pipe insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com