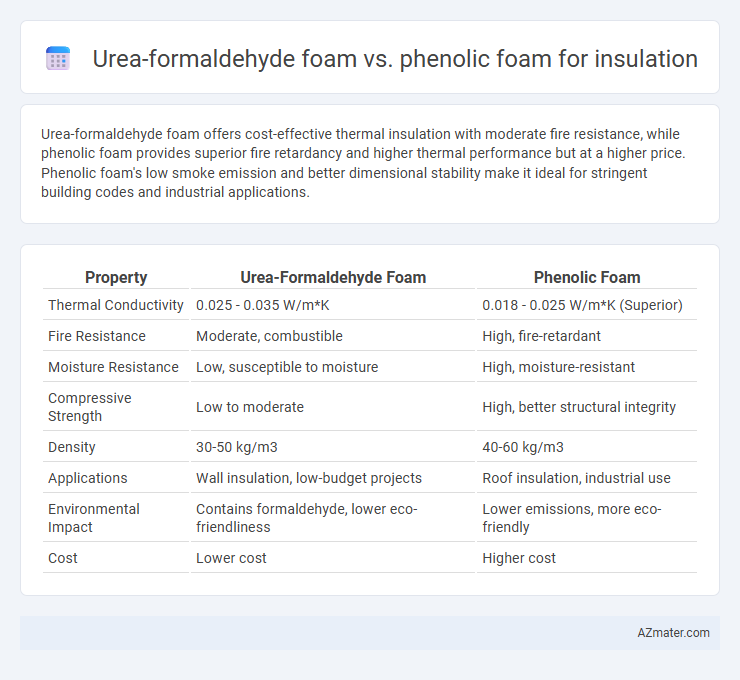
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers cost-effective thermal insulation with moderate fire resistance, while phenolic foam provides superior fire retardancy and higher thermal performance but at a higher price. Phenolic foam's low smoke emission and better dimensional stability make it ideal for stringent building codes and industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Urea-Formaldehyde Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.025 - 0.035 W/m*K | 0.018 - 0.025 W/m*K (Superior) |
| Fire Resistance | Moderate, combustible | High, fire-retardant |
| Moisture Resistance | Low, susceptible to moisture | High, moisture-resistant |
| Compressive Strength | Low to moderate | High, better structural integrity |
| Density | 30-50 kg/m3 | 40-60 kg/m3 |
| Applications | Wall insulation, low-budget projects | Roof insulation, industrial use |
| Environmental Impact | Contains formaldehyde, lower eco-friendliness | Lower emissions, more eco-friendly |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Insulation Materials
Urea-formaldehyde foam and phenolic foam are both popular insulation materials known for their thermal efficiency and fire-resistant properties. Urea-formaldehyde foam is valued for its cost-effectiveness and ease of application in wall cavities, while phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and lower smoke emission levels due to its unique chemical structure. Selecting between these foams depends on specific construction needs, thermal performance requirements, and regulatory standards for building insulation.
Urea-Formaldehyde Foam: Properties and Applications
Urea-formaldehyde foam insulation is a lightweight, cost-effective material known for its excellent thermal resistance and soundproofing capabilities, making it suitable for wall cavity and floor insulation. It exhibits low thermal conductivity and good fire-retardant properties due to its chemical composition, but it emits formaldehyde gas, requiring careful ventilation during installation. Commonly used in residential applications, Urea-formaldehyde foam provides a durable, moisture-resistant barrier that reduces energy consumption and enhances indoor comfort.
Phenolic Foam: Properties and Applications
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and low smoke emission compared to urea-formaldehyde foam, making it an excellent choice for high-risk environments. Its closed-cell structure provides outstanding thermal insulation with low thermal conductivity values, commonly around 0.020 W/m*K. Widely used in commercial buildings, cold storage, and offshore applications, phenolic foam ensures durability and enhanced safety standards.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Urea-formaldehyde foam insulation offers moderate thermal resistance with an R-value typically ranging from 3.6 to 4.0 per inch, making it effective for residential applications but less efficient in extreme temperatures. Phenolic foam insulation provides superior thermal performance, achieving R-values around 4.5 to 5.0 per inch, which translates to better energy efficiency and enhanced fire resistance in both commercial and industrial settings. Phenolic foam's low thermal conductivity and stability under high temperatures make it a preferred choice where maximum insulation and safety standards are critical.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Phenolic foam exhibits superior fire resistance compared to urea-formaldehyde foam, offering lower smoke emission and a higher limiting oxygen index (LOI), which enhances overall safety in insulation applications. Urea-formaldehyde foam tends to release more toxic gases and has a lower ignition point, making it less favorable in fire-sensitive environments. Phenolic foam's thermal stability and self-extinguishing properties make it a preferred choice for construction projects prioritizing stringent fire safety standards.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Phenolic foam offers superior moisture resistance compared to urea-formaldehyde foam, making it less prone to water absorption and degradation in humid environments. This enhanced resistance contributes to phenolic foam's greater long-term durability, maintaining its insulating properties and structural integrity over time. Urea-formaldehyde foam, while effective as an insulator, tends to be more susceptible to moisture-related issues, reducing its lifespan and performance in damp conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Urea-formaldehyde foam releases low levels of formaldehyde but raises concerns due to potential off-gassing and reliance on fossil fuel-based chemicals, impacting indoor air quality and environmental health. Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with lower global warming potential (GWP) and reduced smoke toxicity during combustion, making it more sustainable in long-term applications. Both materials require careful consideration of life cycle assessments, with phenolic foam generally favored for its enhanced fire resistance and lower environmental footprint.
Health and Safety Considerations
Urea-formaldehyde foam insulation releases formaldehyde gas, which poses respiratory risks and potential carcinogenic effects, necessitating proper ventilation during and after installation. Phenolic foam offers lower formaldehyde emissions and improved fire resistance, reducing indoor air quality concerns and enhancing occupant safety. Both materials require adherence to safety guidelines, but phenolic foam is generally preferred for minimizing health hazards associated with volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Cost and Installation Differences
Urea-formaldehyde foam insulation typically costs less per board foot compared to phenolic foam, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale or residential projects. Installation of urea-formaldehyde foam is generally easier due to its spray-foam application method, which expands to fill cavities effectively, reducing gaps and air leaks. Phenolic foam, despite its higher cost, offers superior fire resistance and lower thermal conductivity, but requires more specialized handling and longer curing times during installation.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Insulation Needs
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers cost-effective insulation with good thermal performance and soundproofing properties, making it suitable for residential applications, especially in older homes. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance, higher R-values, and excellent moisture resistance, ideal for commercial or industrial settings requiring stringent safety standards. Selecting the right foam depends on factors such as budget, fire safety requirements, moisture exposure, and desired insulation efficiency.
Infographic: Urea-formaldehyde foam vs Phenolic foam for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com