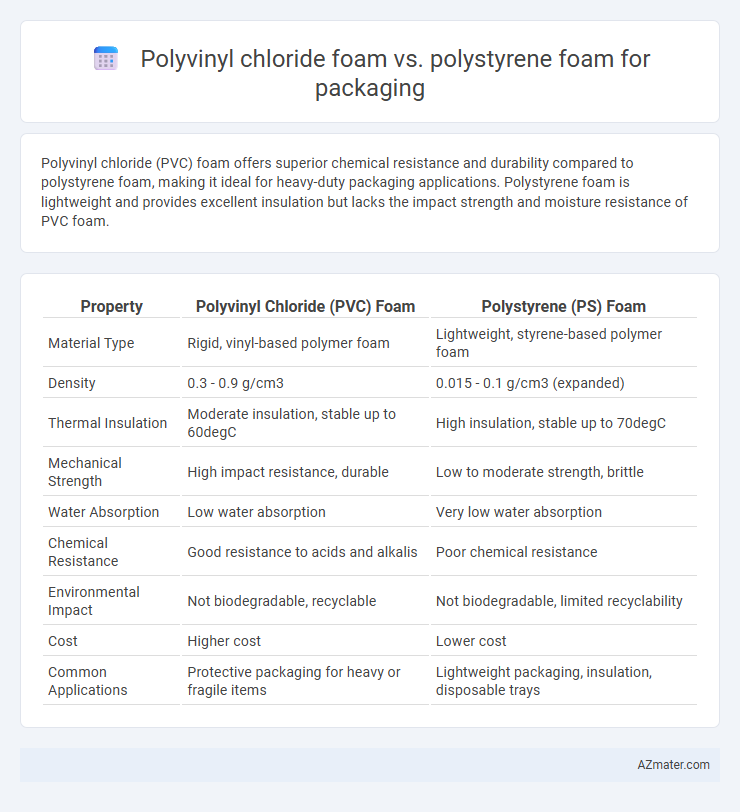
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior chemical resistance and durability compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging applications. Polystyrene foam is lightweight and provides excellent insulation but lacks the impact strength and moisture resistance of PVC foam.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam | Polystyrene (PS) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Rigid, vinyl-based polymer foam | Lightweight, styrene-based polymer foam |
| Density | 0.3 - 0.9 g/cm3 | 0.015 - 0.1 g/cm3 (expanded) |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation, stable up to 60degC | High insulation, stable up to 70degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High impact resistance, durable | Low to moderate strength, brittle |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption | Very low water absorption |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Poor chemical resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Not biodegradable, recyclable | Not biodegradable, limited recyclability |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Common Applications | Protective packaging for heavy or fragile items | Lightweight packaging, insulation, disposable trays |
Introduction to Foam Packaging Materials
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam and polystyrene foam are widely used packaging materials characterized by lightweight, durability, and cushioning properties. PVC foam offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility compared to polystyrene, which excels in rigidity and thermal insulation. The choice between these foams depends on specific packaging requirements such as protection level, environmental exposure, and cost efficiency.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is a rigid, closed-cell material known for its excellent impact resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for protective packaging applications that require durability and cushioning. Its lightweight yet strong structure offers superior resistance to moisture, oils, and solvents compared to polystyrene foam, enhancing protection during transportation and storage. PVC foam's customizable density and thickness provide flexibility in packaging design, catering to sensitive electronic components and delicate items needing high-performance shock absorption.
Overview of Polystyrene (PS) Foam
Polystyrene (PS) foam is a lightweight, rigid material widely used in packaging for its excellent cushioning and impact resistance properties. It offers superior insulation, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam. PS foam's closed-cell structure ensures strong protection of fragile items during shipping and handling, making it a preferred choice in the packaging industry.
Material Properties: PVC Foam vs Polystyrene Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers greater durability and chemical resistance compared to polystyrene foam, making it suitable for packaging fragile or sensitive items. PVC foam exhibits higher impact strength and better moisture resistance, while polystyrene foam is lighter and provides excellent thermal insulation with superior cushioning. Both materials vary significantly in density and compressive strength, with PVC foam generally providing a tougher and more resilient packaging solution.
Insulation and Protective Performance Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior insulation properties with higher thermal resistance compared to polystyrene foam, making it more effective in maintaining temperature stability during packaging. PVC foam demonstrates enhanced impact absorption and durability, providing better protective performance against mechanical shocks and vibrations. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, typically exhibits lower compressive strength and thermal insulation capacity, limiting its protective effectiveness in demanding shipping conditions.
Environmental Impact and Recycling Considerations
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam presents significant environmental challenges due to the release of toxic chlorine-based compounds during its production and disposal, complicating recycling efforts and posing health risks. Polystyrene (PS) foam, while easier to recycle in certain facilities, often accumulates in landfills and aquatic environments, contributing to persistent plastic pollution owing to its low biodegradability. Both materials have limited recycling infrastructure, but PS foam's widespread use in single-use packaging exacerbates environmental impact compared to the more durable PVC foam applications.
Cost Analysis: PVC Foam vs Polystyrene Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam generally incurs higher production costs than polystyrene foam due to its more complex polymer structure and processing requirements. Polystyrene foam benefits from lower raw material expenses and energy consumption, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale packaging applications. Cost analysis reveals that despite PVC foam's superior durability and chemical resistance, polystyrene foam offers significant savings for companies prioritizing budget efficiency in packaging solutions.
Applications in Packaging: Industry Use Cases
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is widely used in packaging for its durability, chemical resistance, and cushioning properties, making it ideal for protecting electronics, medical devices, and automotive parts during transit. Polystyrene foam excels in lightweight applications such as food packaging, insulation, and disposable containers due to its excellent thermal insulation and shock absorption. Industries like electronics, aerospace, and food & beverage leverage PVC foam for robust, reusable protection, while polystyrene is preferred for cost-effective, single-use packaging solutions.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior chemical resistance and flame retardancy compared to polystyrene foam, making it a safer option for packaging sensitive or hazardous materials. PVC foam often complies with stringent safety regulations such as RoHS and REACH, ensuring lower hazardous substance content. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cushioning, is more flammable and may release toxic fumes during combustion, posing higher safety risks and stricter regulatory scrutiny in certain regions.
Choosing the Right Foam for Packaging Needs
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior durability, chemical resistance, and excellent cushioning for heavy or sensitive items, making it ideal for long-term storage and transportation. Polystyrene (PS) foam provides lightweight, cost-effective protection with good insulation properties, suitable for disposable packaging and short-term shipping. Selecting the right foam depends on factors like product fragility, environmental exposure, budget constraints, and desired reusability.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride foam vs Polystyrene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com