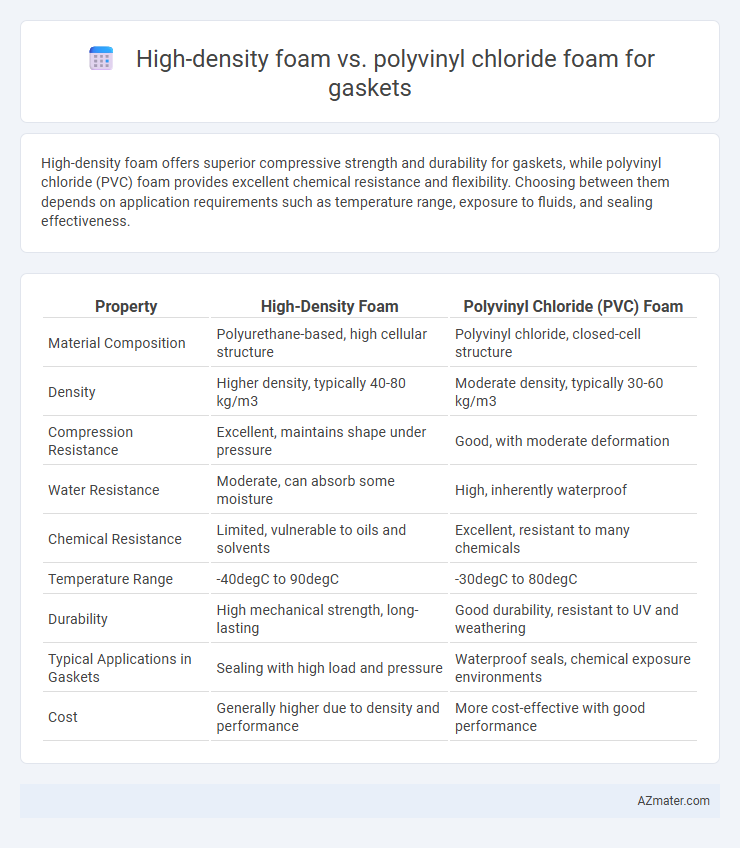
High-density foam offers superior compressive strength and durability for gaskets, while polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides excellent chemical resistance and flexibility. Choosing between them depends on application requirements such as temperature range, exposure to fluids, and sealing effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High-Density Foam | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polyurethane-based, high cellular structure | Polyvinyl chloride, closed-cell structure |
| Density | Higher density, typically 40-80 kg/m3 | Moderate density, typically 30-60 kg/m3 |
| Compression Resistance | Excellent, maintains shape under pressure | Good, with moderate deformation |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, can absorb some moisture | High, inherently waterproof |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited, vulnerable to oils and solvents | Excellent, resistant to many chemicals |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 90degC | -30degC to 80degC |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, long-lasting | Good durability, resistant to UV and weathering |
| Typical Applications in Gaskets | Sealing with high load and pressure | Waterproof seals, chemical exposure environments |
| Cost | Generally higher due to density and performance | More cost-effective with good performance |
Introduction to Gasket Materials
High-density foam and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam are common gasket materials chosen for their distinct physical and chemical properties. High-density foam offers superior compressibility and excellent sealing capabilities in high-pressure environments, whereas PVC foam is favored for its chemical resistance and durability in various industrial applications. Selecting the appropriate gasket material depends on factors like temperature tolerance, exposure to chemicals, and mechanical stress to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Overview of High-Density Foam
High-density foam offers superior compression strength and excellent resistance to deformation, making it ideal for gaskets that require durable sealing under heavy pressure. Its closed-cell structure provides outstanding moisture resistance and thermal insulation, enhancing gasket performance in harsh environments. This foam type typically outperforms polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam in terms of longevity and resilience, especially in industrial sealing applications.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits exceptional durability, chemical resistance, and flexibility, making it a preferred material for gasket applications in automotive, marine, and industrial environments. This closed-cell foam provides excellent compression set resistance and moisture resistance, ensuring long-term sealing performance under varying temperature and pressure conditions. Compared to high-density foam, PVC foam offers superior resistance to oils, solvents, and weathering, promoting extended gasket lifespan in demanding sealing tasks.
Key Differences Between High-Density Foam and PVC Foam
High-density foam offers superior compressive strength and durability, making it ideal for gaskets exposed to heavy mechanical stress and repeated compression cycles. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is more resistant to chemicals, moisture, and UV exposure, providing excellent environmental resistance for gaskets used in outdoor or corrosive settings. While high-density foam excels in cushioning and load-bearing applications, PVC foam is preferred for sealing and insulation where chemical and weather resistance are critical.
Performance and Durability Comparison
High-density foam offers superior compression resistance and better energy absorption, making it ideal for gaskets requiring long-lasting performance under dynamic loads. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides excellent chemical resistance and weatherability, yet tends to exhibit lower tensile strength and may degrade faster under UV exposure compared to high-density foam. Overall, high-density foam demonstrates enhanced durability and resilience in demanding sealing applications, while PVC foam is advantageous in environments requiring chemical and environmental resistance.
Applications in Gasket Manufacturing
High-density foam offers superior compressibility and resilience, making it ideal for gaskets requiring excellent sealing performance under dynamic pressure conditions, such as automotive and industrial machinery applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides enhanced chemical resistance and durability, which suits gaskets used in chemical processing, HVAC systems, and water-resistant seals. Selecting between high-density foam and PVC foam in gasket manufacturing depends on factors like environmental exposure, required flexibility, and resistance to temperature and chemicals.
Chemical and Weather Resistance
High-density foam offers superior chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, making it ideal for gaskets exposed to aggressive solvents and oils. PVC foam provides moderate weather resistance but tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and extreme temperature fluctuations than high-density foam. For applications requiring long-term durability against harsh environmental conditions, high-density foam gaskets maintain integrity better than PVC counterparts.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
High-density foam offers superior durability and cushioning at a moderate cost, making it cost-effective for long-term gasket applications, but its availability can be limited in specialized grades. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is widely available and generally lower in initial cost, providing an economical choice for mass-produced gaskets, though it may lack the longevity of high-density alternatives. Manufacturers must weigh the balance between PVC foam's accessibility and upfront savings against the higher performance and potentially lower replacement frequency of high-density foam.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
High-density foam gaskets offer improved durability and thermal insulation but often derive from petrochemical sources, leading to moderate environmental concerns due to non-biodegradability and energy-intensive production. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, while lightweight and versatile, presents significant environmental challenges, including toxic chlorine content, difficulty in recycling, and potential release of harmful dioxins during degradation or incineration. Sustainable gasket solutions increasingly favor bio-based or recyclable foam materials to minimize ecological footprint and comply with stringent environmental regulations.
Choosing the Right Foam for Gasket Applications
High-density foam offers superior compressibility and excellent sealing properties ideal for gasketing applications requiring durability and resistance to oils and chemicals. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides good weather resistance, UV stability, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for outdoor and general-purpose gaskets. Selecting the right foam depends on factors like temperature range, environmental exposure, and mechanical stress to ensure optimal gasket performance.
Infographic: High-density foam vs Polyvinyl chloride foam for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com