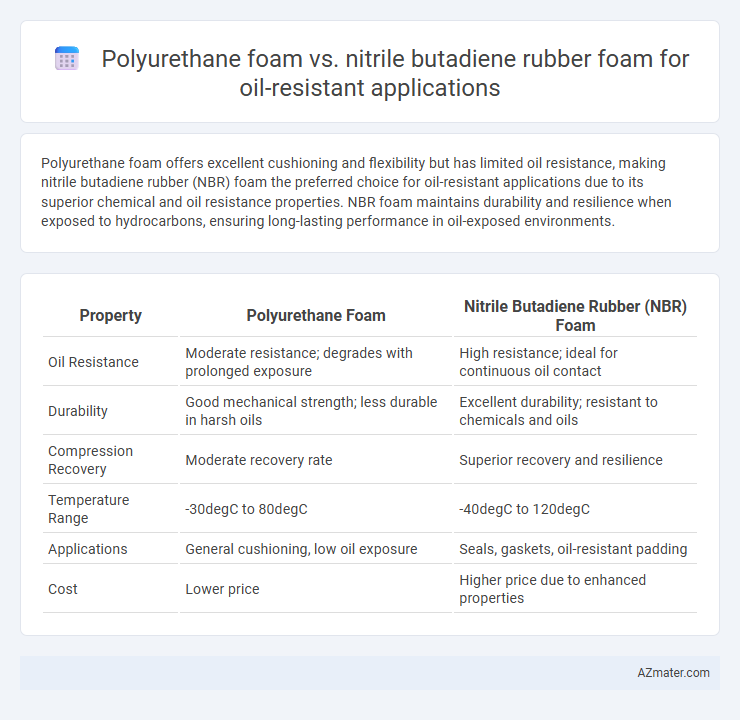
Polyurethane foam offers excellent cushioning and flexibility but has limited oil resistance, making nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam the preferred choice for oil-resistant applications due to its superior chemical and oil resistance properties. NBR foam maintains durability and resilience when exposed to hydrocarbons, ensuring long-lasting performance in oil-exposed environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane Foam | Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Resistance | Moderate resistance; degrades with prolonged exposure | High resistance; ideal for continuous oil contact |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength; less durable in harsh oils | Excellent durability; resistant to chemicals and oils |
| Compression Recovery | Moderate recovery rate | Superior recovery and resilience |
| Temperature Range | -30degC to 80degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Applications | General cushioning, low oil exposure | Seals, gaskets, oil-resistant padding |
| Cost | Lower price | Higher price due to enhanced properties |
Introduction to Oil-Resistant Foams
Oil-resistant foams such as polyurethane foam and nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam are engineered to withstand exposure to hydrocarbons, oils, and fuels without significant degradation. Polyurethane foam offers excellent cushioning and abrasion resistance but can have limited oil resistance depending on its formulation. Nitrile butadiene rubber foam exhibits superior oil and chemical resistance, making it ideal for sealing, gasketing, and insulation in oil-exposed environments.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane foam is a versatile polymer material known for its excellent cushioning, flexibility, and abrasion resistance, widely used in oil-resistant applications. Its cellular structure helps provide effective sealing and insulation properties, making it suitable for gaskets and seals exposed to oils and chemicals. Compared to nitrile butadiene rubber foam, polyurethane foam typically offers better mechanical strength and durability in environments with oil exposure.
What is Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) Foam?
Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) foam is a synthetic rubber material known for its excellent oil and chemical resistance, making it ideal for oil-resistant applications. Unlike polyurethane foam, which offers moderate oil resistance and better cushioning, NBR foam maintains structural integrity and durability when exposed to fuels, oils, and solvents. Its closed-cell structure provides high resistance to swelling and degradation in harsh environments, ensuring long-lasting performance in automotive, industrial, and marine sealing and gasketing applications.
Chemical Resistance: Polyurethane vs NBR Foam
Polyurethane foam offers moderate chemical resistance but tends to degrade faster in environments with oils and solvents compared to Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) foam. NBR foam excels in oil-resistant applications due to its superior resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and greases, maintaining elasticity and structural integrity over prolonged exposure. The molecular structure of NBR foam provides enhanced durability against chemical breakdown, making it the preferred choice for sealing, gaskets, and cushioning in oil-exposed conditions.
Mechanical Properties and Durability
Polyurethane foam offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it highly effective for oil-resistant applications requiring durability under mechanical stress. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam excels in oil and chemical resistance due to its molecular structure, providing excellent resilience and flexibility in harsh environments. While polyurethane foam maintains mechanical integrity over extended periods, NBR foam demonstrates better resistance to swelling and degradation from prolonged oil exposure, ensuring longevity in dynamic sealing and cushioning uses.
Temperature Stability and Environmental Performance
Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam outperforms polyurethane foam in oil-resistant applications due to its superior temperature stability, maintaining integrity between -40degC and 120degC compared to polyurethane's narrower range of -30degC to 80degC. NBR foam resists degradation from hydrocarbons and oils, ensuring prolonged durability in harsh environments, whereas polyurethane foam can swell and deteriorate when exposed to oils. Environmentally, NBR foam offers better recyclability and lower volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, aligning with stricter environmental regulations in oil-resistant sealing solutions.
Oil Absorption and Swelling Rates
Polyurethane foam exhibits higher oil absorption due to its open-cell structure, but it tends to swell significantly when exposed to oil, reducing dimensional stability in oil-resistant applications. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam, characterized by a closed-cell structure, demonstrates lower oil absorption and minimal swelling, maintaining integrity and performance in aggressive oil environments. For applications requiring long-term oil resistance with minimal volume change, NBR foam provides superior resistance compared to polyurethane foam.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Polyurethane foam generally offers a lower cost compared to nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam, making it a budget-friendly option for oil-resistant applications. NBR foam provides superior oil resistance and durability but tends to be more expensive and less widely available than polyurethane foam. Availability of polyurethane foam is higher due to its widespread use in various industries, whereas NBR foam may require specialized suppliers, affecting lead times and overall cost.
Industry Applications: Choosing the Right Foam
Polyurethane foam exhibits excellent oil resistance and cushioning properties, making it ideal for automotive gaskets, seals, and filtration systems where durability under oil exposure is critical. Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility, commonly used in oil seals, fuel system components, and industrial hose liners within the oil and gas, aerospace, and manufacturing sectors. Selecting the right foam depends on application-specific factors such as temperature range, mechanical stress, and exposure to petroleum-based fluids, ensuring optimal performance and longevity in demanding industrial environments.
Conclusion: Which Foam is Best for Oil Resistance?
Nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) foam outperforms polyurethane foam in oil-resistant applications due to its superior chemical resistance and durability against petroleum-based oils and solvents. Polyurethane foam tends to degrade faster when exposed to oils, making NBR foam the preferred choice for sealing, gaskets, and cushioning in automotive, industrial, and marine environments. For long-lasting oil resistance and mechanical integrity, NBR foam provides optimal performance.
Infographic: Polyurethane foam vs Nitrile butadiene rubber foam for Oil-resistant application
 azmater.com
azmater.com