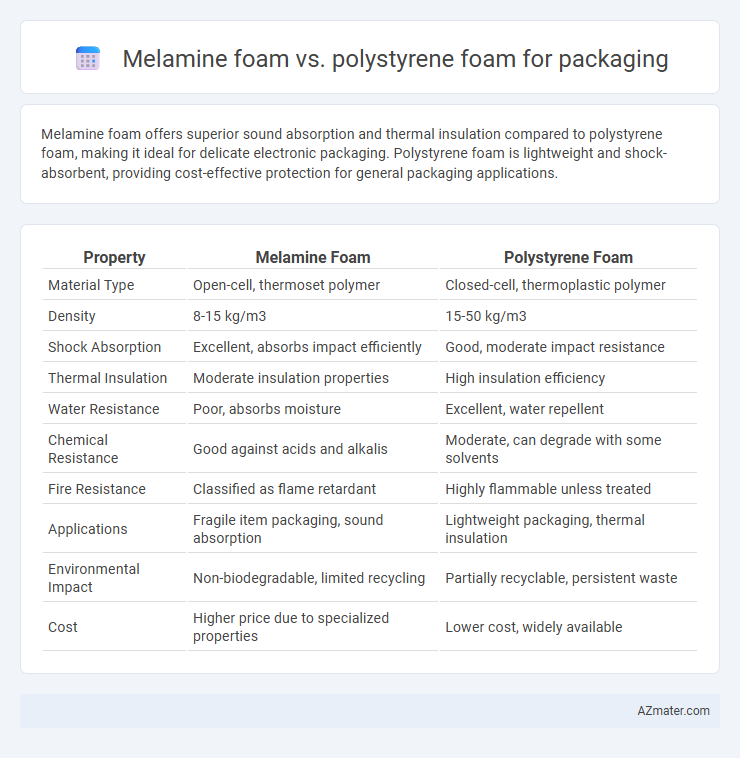
Melamine foam offers superior sound absorption and thermal insulation compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for delicate electronic packaging. Polystyrene foam is lightweight and shock-absorbent, providing cost-effective protection for general packaging applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Melamine Foam | Polystyrene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Open-cell, thermoset polymer | Closed-cell, thermoplastic polymer |
| Density | 8-15 kg/m3 | 15-50 kg/m3 |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent, absorbs impact efficiently | Good, moderate impact resistance |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation properties | High insulation efficiency |
| Water Resistance | Poor, absorbs moisture | Excellent, water repellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against acids and alkalis | Moderate, can degrade with some solvents |
| Fire Resistance | Classified as flame retardant | Highly flammable unless treated |
| Applications | Fragile item packaging, sound absorption | Lightweight packaging, thermal insulation |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, limited recycling | Partially recyclable, persistent waste |
| Cost | Higher price due to specialized properties | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Melamine and Polystyrene Foams
Melamine foam is a lightweight, open-cell foam known for its exceptional sound absorption and thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for protective packaging in sensitive environments. Polystyrene foam, commonly available as expanded (EPS) or extruded (XPS), offers high impact resistance and excellent cushioning, widely used for packaging electronics, appliances, and fragile goods. Both foams provide effective protection, but their distinct structural characteristics influence factors such as durability, moisture resistance, and environmental impact in packaging applications.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Melamine foam consists of a thermosetting polymer made from melamine-formaldehyde resin, featuring a unique open-cell structure that provides excellent sound absorption and fire resistance. Polystyrene foam is composed of polystyrene polymer beads, typically expanded into closed-cell, lightweight structures offering high cushioning and moisture resistance. The chemical composition of melamine foam delivers superior thermal stability and flame retardancy, while polystyrene foam prioritizes compressive strength and economical bulk protection in packaging applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Melamine foam exhibits a unique open-cell structure offering superior sound absorption and high thermal resistance up to 240degC, while polystyrene foam features a closed-cell structure that provides excellent insulation and lightweight properties with lower thermal resistance around 70-100degC. Melamine foam's density ranges from 9-24 kg/m3, making it softer and more flexible, whereas polystyrene foam commonly has densities between 10-50 kg/m3, resulting in higher rigidity and impact resistance. The compressive strength of melamine foam is significantly lower than polystyrene foam, which offers better mechanical protection for packaging fragile items.
Insulation and Cushioning Performance
Melamine foam offers superior thermal insulation with low thermal conductivity around 0.035 W/m*K, making it ideal for temperature-sensitive packaging. Polystyrene foam, especially expanded polystyrene (EPS), provides excellent cushioning due to its high impact absorption and compressive strength, protecting fragile items during transit. Melamine foam's open-cell structure ensures sound absorption and fire resistance, whereas polystyrene's closed-cell design excels in lightweight shock protection.
Weight and Density Differences
Melamine foam features a lower density, typically around 9 to 45 kg/m3, compared to polystyrene foam, which ranges from 10 to 30 kg/m3 depending on type and formulation. Despite its lower density, melamine foam's open-cell structure results in a lightweight yet durable material, offering superior cushioning and impact absorption for packaging applications. Polystyrene foam, especially expanded polystyrene (EPS), is lightweight and stiff but generally less effective than melamine foam in vibration damping due to its closed-cell structure and higher density.
Durability and Lifespan
Melamine foam offers superior durability compared to polystyrene foam, maintaining structural integrity under compression and resisting deformation over prolonged use. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, is more prone to cracking and crumbling, reducing its effective lifespan in packaging applications. The enhanced resilience and longer lifespan of melamine foam make it ideal for protective packaging requiring repeated handling and impact resistance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Melamine foam offers improved environmental benefits over polystyrene foam due to its superior biodegradability and lower carbon footprint during production. Polystyrene foam is notorious for its persistence in landfills and contribution to microplastic pollution, posing significant challenges for waste management and marine ecosystems. Sustainable packaging choices favor melamine foam for its reduced environmental impact and enhanced recyclability compared to conventional polystyrene foam.
Cost Considerations for Packaging
Melamine foam typically incurs higher costs than polystyrene foam due to its advanced sound-absorbing and heat-resistant properties, making it suitable for premium packaging applications requiring durability and insulation. Polystyrene foam is a cost-effective choice favored for lightweight, bulk packaging, providing sufficient protection at a lower price point for mass distribution. Budget constraints often drive the selection between these materials, with polystyrene offering economical scalability and melamine foam delivering specialized benefits that justify its premium cost.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Melamine foam offers superior flame retardant properties and low toxicity, making it compliant with stringent fire safety standards such as UL 94 V-0, while polystyrene foam often requires additional fire retardants to meet similar regulations. Melamine foam's formaldehyde-based composition demands careful handling, but it typically emits fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to expanded or extruded polystyrene foams, enhancing indoor air quality safety. Regulatory bodies like the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) closely monitor both materials for chemical safety, with melamine foam generally favored in environments requiring higher fire safety and lower toxic emissions.
Best Use Cases for Each Foam Type
Melamine foam excels in packaging fragile electronics and high-value items due to its superior shock absorption and flame-retardant properties. Polystyrene foam is ideal for lightweight packaging of consumer goods, offering excellent insulation and cost-effectiveness for bulk shipping and cushioning. Choosing the right foam depends on the balance between protection requirements and budget constraints in the packaging application.
Infographic: Melamine foam vs Polystyrene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com