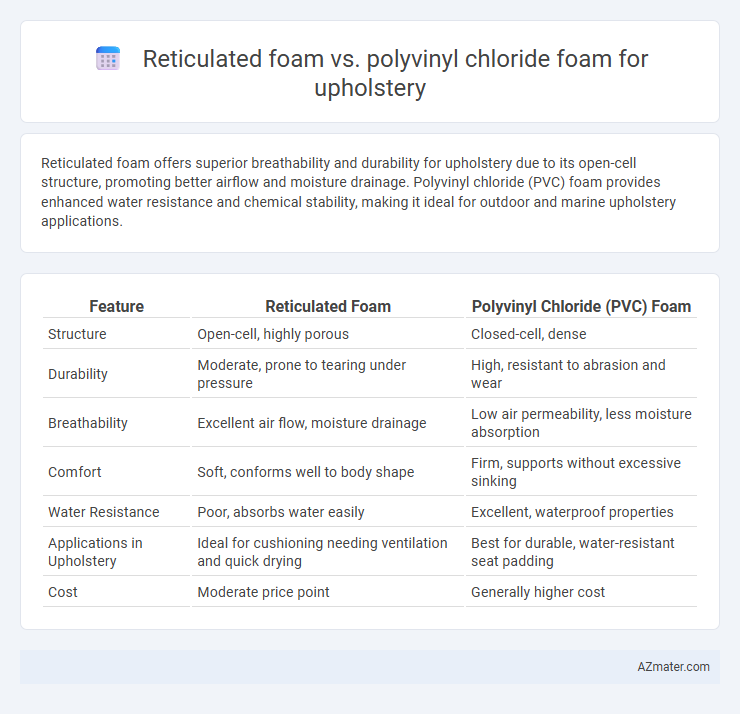
Reticulated foam offers superior breathability and durability for upholstery due to its open-cell structure, promoting better airflow and moisture drainage. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides enhanced water resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for outdoor and marine upholstery applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Reticulated Foam | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Open-cell, highly porous | Closed-cell, dense |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to tearing under pressure | High, resistant to abrasion and wear |
| Breathability | Excellent air flow, moisture drainage | Low air permeability, less moisture absorption |
| Comfort | Soft, conforms well to body shape | Firm, supports without excessive sinking |
| Water Resistance | Poor, absorbs water easily | Excellent, waterproof properties |
| Applications in Upholstery | Ideal for cushioning needing ventilation and quick drying | Best for durable, water-resistant seat padding |
| Cost | Moderate price point | Generally higher cost |
Introduction to Reticulated Foam and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Reticulated foam consists of a highly porous, open-cell structure that enhances breathability and moisture drainage, making it ideal for upholstery applications requiring ventilation and quick drying. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is a closed-cell material with excellent durability, chemical resistance, and structural integrity, often used in upholstery where firmness and water resistance are prioritized. Comparing reticulated foam to PVC foam highlights differences in breathability, resilience, and moisture management crucial for selecting appropriate upholstery materials.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Reticulated foam is produced by removing cell membranes from polyurethane foam, creating an open-cell structure ideal for breathability and durability in upholstery applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is made through the polymerization of vinyl chloride monomers, resulting in a closed-cell, resilient material with excellent chemical and moisture resistance. Manufacturing reticulated foam involves a thermal or chemical reticulation process, whereas PVC foam is typically created via a foaming agent in an extrusion or molding process, influencing their respective physical properties and suitability for different upholstery needs.
Structural Properties and Cell Architecture
Reticulated foam features an open-cell structure with interconnected pores, providing superior breathability and water drainage, making it ideal for upholstery requiring moisture management. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits a closed-cell architecture, offering higher density and enhanced structural rigidity, which contributes to durability and resistance to compression. The choice between reticulated foam and PVC foam depends on desired flexibility, cushioning, and environmental exposure for upholstery applications.
Comfort and Support Characteristics
Reticulated foam offers superior breathability and moisture dissipation, enhancing comfort by maintaining a cooler seating surface ideal for upholstery. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides firmer support with excellent resilience and durability, making it suitable for structural applications requiring long-lasting performance. The open-cell structure of reticulated foam contributes to softer cushioning, while PVC foam's closed-cell design ensures consistent support and resistance to compression over time.
Durability and Longevity in Upholstery Applications
Reticulated foam offers superior breathability and moisture resistance, making it highly durable for upholstery applications exposed to frequent use and humidity. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides excellent structural integrity and resists wear, but it tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and heavy mechanical stress. Overall, reticulated foam outperforms PVC foam in longevity due to its enhanced airflow and resistance to environmental factors, ensuring sustained comfort and support in upholstered furniture.
Moisture Resistance and Breathability
Reticulated foam offers superior moisture resistance due to its open-cell structure, allowing efficient water drainage and faster drying, making it ideal for upholstered furniture in humid environments. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, while providing moderate moisture resistance, has a closed-cell design that traps moisture, reducing breathability and potentially leading to mold growth. The enhanced breathability of reticulated foam improves air circulation, increasing comfort and durability in upholstery applications compared to PVC foam.
Weight, Density, and Flexibility Comparison
Reticulated foam offers a lower density and lighter weight compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, making it advantageous for upholstery applications requiring enhanced breathability and comfort. PVC foam typically exhibits higher density and weight, providing superior durability and support but with less flexibility than reticulated foam. The increased flexibility and open-cell structure of reticulated foam promote better air circulation, while PVC foam's closed-cell design emphasizes resilience and moisture resistance.
Safety, Toxicity, and Environmental Considerations
Reticulated foam offers superior breathability and low chemical emissions, making it safer and less toxic for upholstery applications compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, which can release harmful phthalates and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). PVC foam production involves chlorine and other hazardous substances, contributing to environmental pollution and challenges in biodegradability, whereas reticulated foam is typically made from polyurethane or polyester, which are more environmentally friendly and easier to recycle. Choosing reticulated foam reduces indoor air quality risks and supports sustainability goals by minimizing toxic exposure and environmental impact.
Cost-Efficiency and Market Availability
Reticulated foam offers superior breathability and durability at a higher cost, making it ideal for premium upholstery applications where longevity justifies the investment. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides a more cost-efficient option with widespread market availability, favored for budget-conscious projects requiring basic comfort and moisture resistance. The choice depends on balancing long-term performance with upfront expenses, as reticulated foam commands a niche market while PVC foam dominates due to versatile pricing and accessibility.
Choosing the Right Foam for Upholstery: Key Considerations
Reticulated foam offers superior breathability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for outdoor upholstery or high-humidity environments, while polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides excellent durability, chemical resistance, and structural support suitable for indoor furniture. Consider factors such as intended use, comfort level, environmental exposure, and longevity when selecting between reticulated foam and PVC foam for upholstery applications. Understanding the foam's density, resilience, and maintenance requirements ensures optimal performance and customer satisfaction in upholstery projects.
Infographic: Reticulated foam vs Polyvinyl chloride foam for Upholstery
 azmater.com
azmater.com