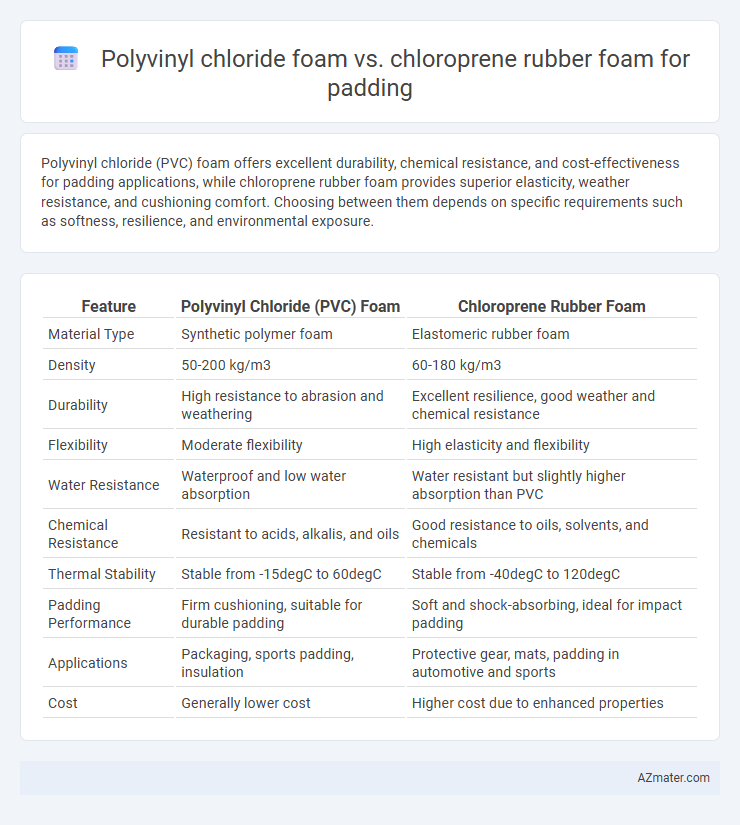
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers excellent durability, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness for padding applications, while chloroprene rubber foam provides superior elasticity, weather resistance, and cushioning comfort. Choosing between them depends on specific requirements such as softness, resilience, and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam | Chloroprene Rubber Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic polymer foam | Elastomeric rubber foam |
| Density | 50-200 kg/m3 | 60-180 kg/m3 |
| Durability | High resistance to abrasion and weathering | Excellent resilience, good weather and chemical resistance |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High elasticity and flexibility |
| Water Resistance | Waterproof and low water absorption | Water resistant but slightly higher absorption than PVC |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids, alkalis, and oils | Good resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals |
| Thermal Stability | Stable from -15degC to 60degC | Stable from -40degC to 120degC |
| Padding Performance | Firm cushioning, suitable for durable padding | Soft and shock-absorbing, ideal for impact padding |
| Applications | Packaging, sports padding, insulation | Protective gear, mats, padding in automotive and sports |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to enhanced properties |
Introduction to Polyvinyl Chloride Foam and Chloroprene Rubber Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is a lightweight, closed-cell material known for its excellent cushioning, water resistance, and chemical stability, making it ideal for padding in various industrial and consumer applications. Chloroprene rubber foam, commonly referred to as neoprene, offers superior elasticity, thermal insulation, and resistance to oils and weathering, which enhances padding durability in dynamic environments. Both materials provide effective padding solutions, but PVC foam excels in structural rigidity and moisture resistance, while chloroprene rubber foam delivers enhanced flexibility and environmental resilience.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam consists of a polymer matrix with vinyl chloride monomers polymerized into a rigid, yet flexible cellular structure, providing excellent resistance to moisture and chemicals. Chloroprene rubber (CR) foam is made from polychloroprene, a synthetic rubber with a highly elastic, porous, and closed-cell structure that offers superior abrasion resistance and flexibility. The chemical stability of PVC foam derives from its thermoplastic vinyl chloride backbone, whereas CR foam's unique chlorinated polymer network grants enhanced elasticity and resilience under dynamic stress.
Physical Properties and Durability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers excellent resistance to water, chemicals, and abrasion, making it highly durable for padding applications where moisture exposure occurs. Chloroprene rubber foam provides superior elasticity, impact absorption, and resistance to oils and UV light, enhancing comfort and longevity under dynamic conditions. PVC foam typically has higher compressive strength, while chloroprene rubber foam excels in flexibility and resilience, influencing the choice based on specific durability and physical property requirements.
Cushioning Performance and Comfort
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers high density and firmness, providing excellent impact resistance but limited elasticity, which may reduce cushioning comfort over prolonged use. Chloroprene rubber foam exhibits superior resilience and flexibility, delivering enhanced energy absorption and consistent cushioning that adapts well to body contours for optimal comfort. The closed-cell structure of PVC foam ensures moisture resistance, while the open-cell nature of chloroprene rubber foam allows better breathability and softness, making it preferable for comfort-focused padding applications.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, effectively preventing water absorption and making it ideal for damp environments. Chloroprene rubber foam offers notable chemical resistance, particularly against oils, solvents, and some acids, but may absorb more moisture compared to PVC foam. For applications requiring both high moisture and chemical resistance, PVC foam provides enhanced durability against water, while chloroprene foam excels in resistance to a broader range of chemicals.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits superior thermal insulation due to its closed-cell structure, which minimizes heat transfer and enhances energy efficiency in padding applications. Chloroprene rubber foam, while offering good flexibility and durability, has higher thermal conductivity, resulting in comparatively lower insulating properties. For applications prioritizing thermal insulation, PVC foam provides better performance by effectively reducing heat flow and maintaining consistent temperature control.
Weight and Flexibility Analysis
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers lower density, typically around 0.5 g/cm3, making it lighter than Chloroprene rubber foam, which ranges from 0.9 to 1.2 g/cm3, impacting overall product weight and transport costs. In terms of flexibility, Chloroprene rubber foam exhibits superior elastic recovery and elongation at break, often exceeding 400%, compared to PVC foam's lower flexibility and brittleness under stress. These properties make Chloroprene rubber foam preferable for applications requiring high pliability and cushioning, whereas PVC foam suits uses prioritizing lightweight padding.
Common Applications in Padding
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is commonly used in padding applications requiring durability and resistance to water, such as sports equipment padding, protective cases, and automotive seat cushioning. Chloroprene rubber foam, known for its excellent flexibility and chemical resistance, is frequently utilized in padding for wetsuits, medical cushions, and gasketing in machinery to absorb vibrations. Both materials offer distinct advantages, with PVC foam excelling in structural support and Chloroprene rubber foam providing superior comfort and resilience under varying environmental conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam presents significant environmental concerns due to its production process that releases toxic chemicals such as dioxins and its difficulty in recycling, leading to long-term landfill accumulation. Chloroprene rubber foam, often marketed as neoprene, offers better environmental sustainability owing to its higher durability and potential for partial reclamation, but it still relies on synthetic, petroleum-based inputs that pose challenges for biodegradability. Choosing between the two for padding applications requires balancing PVC's problematic ecological footprint against chloroprene's moderate sustainability benefits and environmental trade-offs.
Cost Effectiveness and Market Availability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior cost effectiveness due to its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses compared to chloroprene rubber foam, making it a preferred choice in budget-sensitive padding applications. PVC foam also boasts widespread market availability with extensive production capacity and global distribution networks, ensuring easy procurement and consistent supply. Chloroprene rubber foam, while providing better elasticity and chemical resistance, tends to be costlier and less readily available, limiting its use in mass-market padding solutions.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride foam vs Chloroprene rubber foam for Padding
 azmater.com
azmater.com