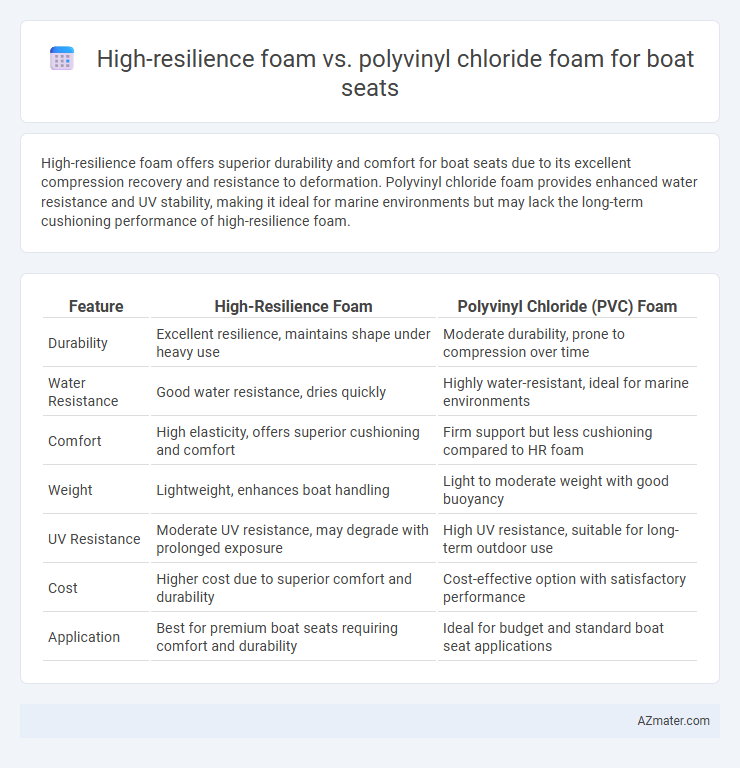
High-resilience foam offers superior durability and comfort for boat seats due to its excellent compression recovery and resistance to deformation. Polyvinyl chloride foam provides enhanced water resistance and UV stability, making it ideal for marine environments but may lack the long-term cushioning performance of high-resilience foam.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | High-Resilience Foam | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Excellent resilience, maintains shape under heavy use | Moderate durability, prone to compression over time |
| Water Resistance | Good water resistance, dries quickly | Highly water-resistant, ideal for marine environments |
| Comfort | High elasticity, offers superior cushioning and comfort | Firm support but less cushioning compared to HR foam |
| Weight | Lightweight, enhances boat handling | Light to moderate weight with good buoyancy |
| UV Resistance | Moderate UV resistance, may degrade with prolonged exposure | High UV resistance, suitable for long-term outdoor use |
| Cost | Higher cost due to superior comfort and durability | Cost-effective option with satisfactory performance |
| Application | Best for premium boat seats requiring comfort and durability | Ideal for budget and standard boat seat applications |
Introduction to Marine Foam Materials
High-resilience foam offers superior support and durability compared to polyvinyl chloride foam, making it ideal for boat seats exposed to varying marine conditions. Polyvinyl chloride foam provides excellent water resistance and mold prevention but tends to compress over time under constant pressure. Choosing marine foam materials depends on balancing cushioning comfort, weather resistance, and longevity for optimal boating experiences.
What is High-Resilience Foam?
High-resilience foam, characterized by its superior elasticity and durability, provides excellent support and comfort for boat seats by quickly regaining its shape after compression. This open-cell polyurethane foam offers enhanced airflow, moisture resistance, and long-lasting resilience in marine environments compared to polyvinyl chloride foam, which is denser and less breathable. High-resilience foam's ability to withstand repeated stress and harsh conditions makes it a preferred choice for boat seating applications prioritizing comfort and longevity.
Understanding Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) foam is a durable, closed-cell material widely used in boat seat cushioning due to its excellent resistance to water absorption, chemicals, and UV rays, ensuring long-lasting comfort and structural integrity. Its rigid yet lightweight nature provides superior support and shape retention compared to high-resilience foam, making it ideal for marine environments where exposure to moisture and harsh conditions is constant. PVC foam also offers enhanced fire resistance and ease of fabrication, contributing to its preference in premium boat seating applications.
Comfort and Support: HR Foam vs PVC Foam
High-resilience (HR) foam offers superior comfort and support for boat seats due to its excellent durability and ability to retain shape under prolonged pressure, providing consistent cushioning and reducing fatigue during long rides. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is less resilient, often compressing faster and offering firmer, less adaptive support, which can lead to discomfort over extended use. HR foam's open-cell structure enhances breathability and moisture resistance, making it a preferred choice for maintaining comfort in marine environments compared to the denser, less breathable PVC foam.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
High-resilience foam offers superior durability for boat seats due to its excellent compression set and quick rebound properties, maintaining shape and comfort over extended use. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, while resistant to water and chemicals, tends to degrade faster under constant marine exposure, leading to reduced lifespan compared to high-resilience foam. The lifespan of high-resilience foam typically exceeds 10 years in marine environments, whereas PVC foam often lasts around 5 to 7 years before significant deterioration occurs.
Water Resistance and Moisture Management
High-resilience foam offers superior water resistance due to its closed-cell structure, which limits water absorption and helps maintain buoyancy and comfort in marine environments. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, while also water-resistant, tends to absorb more moisture over time, which can lead to degradation and decreased support in boat seats. Efficient moisture management in high-resilience foam prolongs the life of boat upholstery by preventing mold and mildew growth, unlike PVC foam that often requires additional protective treatments to achieve similar performance.
UV Resistance and Weather Performance
High-resilience foam offers superior UV resistance and weather performance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, making it ideal for prolonged exposure to sunlight and harsh marine environments. Its open-cell structure enhances breathability and resists deformation under fluctuating temperatures, while PVC foam can degrade, crack, and lose structural integrity when exposed to UV rays and moisture over time. Choosing high-resilience foam ensures longer durability and comfort for boat seats, maintaining form and cushioning in variable weather conditions.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
High-resilience foam used in boat seats offers excellent durability and resistance to water absorption, making it easier to maintain with simple cleaning using mild soap and water, preventing mold and mildew buildup. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam requires regular wiping and occasional use of specialized cleaners to avoid surface degradation and maintain its waterproof properties, though it may be more susceptible to UV damage over time. Both materials benefit from quick drying and prompt removal of dirt and salt residue to extend seat lifespan and ensure consistent comfort.
Environmental Impact of Boat Seat Foams
High-resilience foam, known for its superior durability and cushioning, generally has a lower environmental impact compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam due to its biodegradability and reduced chemical emissions during production. In contrast, PVC foam, widely used in boat seats, poses significant environmental challenges owing to its reliance on chlorine-based chemicals and the release of hazardous dioxins during manufacturing and disposal. Choosing high-resilience foam can contribute to more sustainable boating practices by minimizing toxic waste and promoting eco-friendly material lifecycle management.
Which Foam is Best for Boat Seats?
High-resilience foam excels in boat seats due to its superior durability, resilience, and quick recovery after compression, offering long-lasting comfort even in wet environments. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides excellent water resistance and is lightweight, but it tends to compress over time, reducing cushioning effectiveness. For optimal marine seating, high-resilience foam is generally the best choice due to its balance of comfort, support, and moisture resistance.
Infographic: High-resilience foam vs Polyvinyl chloride foam for Boat seat
 azmater.com
azmater.com