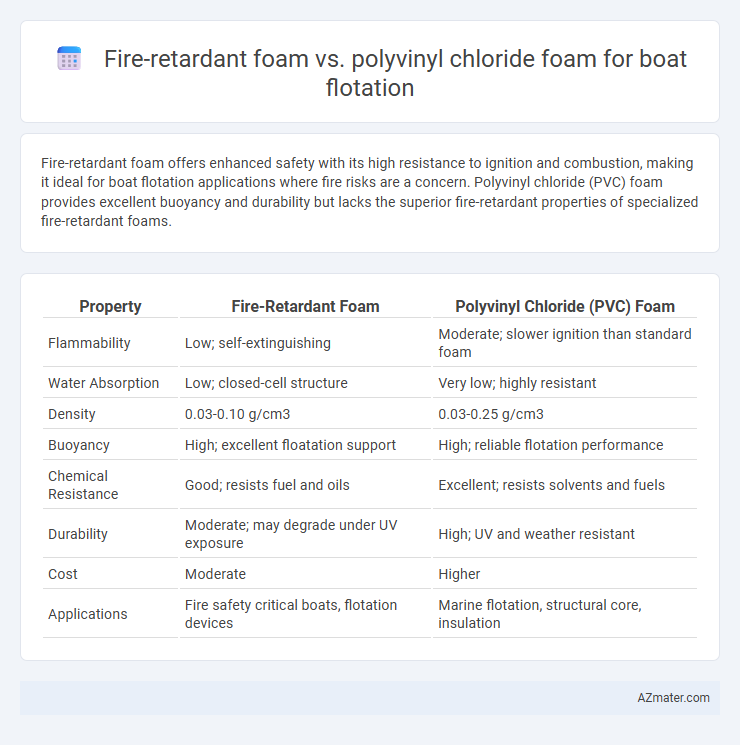
Fire-retardant foam offers enhanced safety with its high resistance to ignition and combustion, making it ideal for boat flotation applications where fire risks are a concern. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides excellent buoyancy and durability but lacks the superior fire-retardant properties of specialized fire-retardant foams.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fire-Retardant Foam | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Flammability | Low; self-extinguishing | Moderate; slower ignition than standard foam |
| Water Absorption | Low; closed-cell structure | Very low; highly resistant |
| Density | 0.03-0.10 g/cm3 | 0.03-0.25 g/cm3 |
| Buoyancy | High; excellent floatation support | High; reliable flotation performance |
| Chemical Resistance | Good; resists fuel and oils | Excellent; resists solvents and fuels |
| Durability | Moderate; may degrade under UV exposure | High; UV and weather resistant |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Applications | Fire safety critical boats, flotation devices | Marine flotation, structural core, insulation |
Introduction to Boat Flotation Materials
Fire-retardant foam and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam are two prominent materials used for boat flotation, each offering distinct advantages in buoyancy and safety. Fire-retardant foam is engineered to resist ignition and slow the spread of flames, enhancing onboard fire safety, while PVC foam provides durable, closed-cell properties that ensure excellent water resistance and structural support. Choosing between these materials depends on factors such as fire protection requirements, weight considerations, and environmental exposure in marine applications.
Overview of Fire-Retardant Foam
Fire-retardant foam used in boat flotation is specifically engineered to resist ignition and slow the spread of flames, enhancing onboard safety during fire incidents. It typically consists of closed-cell polyurethane or polyethylene infused with fire-resistant additives that maintain buoyancy and structural integrity under high temperatures. Compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, fire-retardant foam offers superior thermal stability and complies with strict marine safety regulations such as ASTM F1487.
Properties of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers high durability, excellent resistance to moisture, and superior buoyancy, making it ideal for boat flotation applications. Its closed-cell structure ensures minimal water absorption and enhanced fire-retardant properties compared to other foam materials. PVC foam exhibits strong chemical resistance, UV stability, and mechanical strength, contributing to long-lasting performance in marine environments.
Buoyancy Performance Comparison
Fire-retardant foam offers superior buoyancy performance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam due to its higher closed-cell content, which enhances water resistance and prevents foam saturation. PVC foam, while lightweight and resistant to chemicals, tends to absorb more water over time, reducing its overall buoyant capacity in marine environments. Selecting fire-retardant foam ensures consistent flotation and improved safety by maintaining optimal buoyancy under prolonged exposure to water.
Fire Safety and Thermal Resistance
Fire-retardant foam offers superior fire safety by significantly reducing flame spread and smoke production compared to standard foams, making it crucial for boat flotation in preventing onboard fire hazards. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides moderate fire resistance but tends to melt and release toxic fumes under high heat, posing risks in emergency situations. Thermal resistance of fire-retardant foam maintains structural integrity in elevated temperatures, whereas PVC foam can degrade faster, compromising flotation reliability and safety.
Water Absorption and Durability
Fire-retardant foam exhibits superior water absorption resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, maintaining buoyancy and structural integrity in marine environments. PVC foam offers excellent durability with high impact resistance and chemical stability, but it may absorb more water over time, potentially compromising flotation. Selecting fire-retardant foam enhances long-term performance and safety by minimizing water ingress and ensuring sustained flotation under harsh conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fire-retardant foam used for boat flotation typically contains chemical additives that can release toxic substances during degradation, posing environmental risks when disposed of improperly. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, while durable and resistant to water, is derived from petroleum and produces harmful chlorinated compounds during manufacturing and incineration, raising concerns over its sustainability. Sustainable alternatives emphasize materials with lower ecological footprints, favoring foams that minimize toxic emissions and support recycling or biodegradability in marine environments.
Cost Effectiveness for Boat Builders
Fire-retardant foam offers superior safety compliance but typically comes at a higher cost compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, impacting the overall budget for boat builders. PVC foam provides excellent buoyancy and durability at a lower price point, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale production. Evaluating long-term benefits, PVC foam reduces material expenses while fire-retardant foam may increase insurance savings and regulatory adherence costs.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Fire-retardant foam offers superior resistance to heat and combustion, making it a safer choice for boat flotation where fire hazards exist, while polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides excellent durability and water resistance with a lightweight structure. Installation of fire-retardant foam may require specialized handling to maintain its fire-resistant properties, whereas PVC foam is easier to cut and shape, facilitating straightforward integration into hulls and compartments. Maintenance for fire-retardant foam involves regular inspection for heat damage and ensuring foam integrity, while PVC foam typically requires less frequent servicing due to its robust chemical and moisture resistance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam for Your Boat
Fire-retardant foam offers superior safety by reducing the risk of ignition and slowing flame spread, making it ideal for boats where fire hazards are a primary concern. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides excellent durability, water resistance, and buoyancy, ensuring long-lasting flotation performance in marine environments. Selecting the right foam depends on prioritizing fire safety with fire-retardant foam or opting for the robust, moisture-resistant qualities of PVC foam to maximize flotation reliability.
Infographic: Fire-retardant foam vs Polyvinyl chloride foam for Boat flotation
 azmater.com
azmater.com