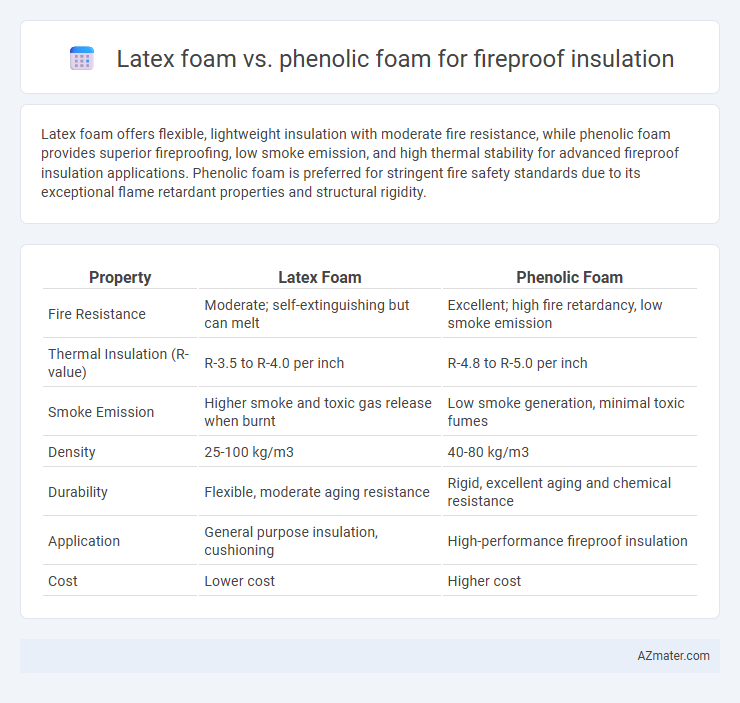
Latex foam offers flexible, lightweight insulation with moderate fire resistance, while phenolic foam provides superior fireproofing, low smoke emission, and high thermal stability for advanced fireproof insulation applications. Phenolic foam is preferred for stringent fire safety standards due to its exceptional flame retardant properties and structural rigidity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Latex Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Moderate; self-extinguishing but can melt | Excellent; high fire retardancy, low smoke emission |
| Thermal Insulation (R-value) | R-3.5 to R-4.0 per inch | R-4.8 to R-5.0 per inch |
| Smoke Emission | Higher smoke and toxic gas release when burnt | Low smoke generation, minimal toxic fumes |
| Density | 25-100 kg/m3 | 40-80 kg/m3 |
| Durability | Flexible, moderate aging resistance | Rigid, excellent aging and chemical resistance |
| Application | General purpose insulation, cushioning | High-performance fireproof insulation |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Fireproof Insulation Materials
Latex foam and phenolic foam are prominent fireproof insulation materials used for enhancing safety and thermal efficiency in buildings. Phenolic foam exhibits superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and excellent thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for fireproofing applications. Latex foam, while offering good elasticity and cushioning, generally lacks the high fire retardancy and thermal stability required for stringent fireproof insulation standards.
What is Latex Foam Insulation?
Latex foam insulation is a flexible, resilient material derived from natural or synthetic latex, renowned for its superior thermal insulation and fire-resistant properties. It exhibits excellent breathability and durability, making it effective in preventing heat transfer while resisting ignition and flame spread. Compared to phenolic foam, latex foam offers enhanced elasticity and environmentally friendly characteristics, often preferred in applications requiring both fire retardancy and comfort.
Understanding Phenolic Foam Insulation
Phenolic foam insulation offers superior fire resistance compared to latex foam, characterized by its low smoke emission and excellent thermal stability at high temperatures. This rigid, closed-cell foam is chemically formulated with phenol and formaldehyde resins, providing exceptional flame retardancy and dimensional stability in fireproofing applications. Its lightweight structure, combined with a high R-value per inch, makes phenolic foam an efficient choice for insulation systems requiring stringent fire safety standards.
Fire Resistance Properties: Latex Foam vs Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam exhibits superior fire resistance compared to latex foam due to its inherently low flammability and ability to form a carbonaceous char that slows heat release and flame spread. Latex foam, primarily composed of organic polymers, tends to ignite more readily and produce higher smoke emissions during combustion. Fireproof insulation projects requiring stringent fire safety standards often prefer phenolic foam for its excellent thermal stability and compliance with fire retardant regulations.
Thermal Insulation Efficiency Comparison
Latex foam exhibits a lower thermal conductivity, typically around 0.035 W/m*K, providing superior thermal insulation compared to phenolic foam, which averages 0.040 W/m*K. Phenolic foam offers enhanced fire resistance with a higher Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) of approximately 30%, but Latex foam can achieve comparable fireproofing when treated with fire-retardant additives. For applications prioritizing thermal insulation efficiency, Latex foam's lower heat transfer rate makes it more effective, while phenolic foam excels in fireproofing performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Latex foam, derived from natural rubber, offers greater biodegradability and lower carbon emissions during production compared to phenolic foam, which relies on synthetic resins and formaldehyde-based chemicals. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance and thermal insulation but poses environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradable nature and potential release of toxic gases during disposal. Choosing latex foam enhances sustainability by reducing ecological footprint and promoting renewable resource use, while phenolic foam remains preferable for high-performance fireproofing despite environmental trade-offs.
Installation Process and Practical Considerations
Latex foam offers easy handling and flexibility during installation, allowing for seamless fitting into irregular spaces, while phenolic foam requires precise cutting and protective gear due to its brittle nature and potential irritants. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance with a higher Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) of around 40%, making it ideal for strict fire codes, whereas latex foam typically has a lower LOI near 20-25%. Practical considerations include latex foam's moisture sensitivity and lower thermal stability compared to the chemically stable, moisture-resistant phenolic foam favored in high-temperature, high-safety environments.
Cost Analysis: Latex Foam vs Phenolic Foam
Latex foam typically has a higher upfront cost compared to phenolic foam due to its complex manufacturing process and material properties. Phenolic foam offers a more cost-effective solution for fireproof insulation, providing excellent fire resistance and thermal performance at a lower price point. When evaluating long-term expenses, phenolic foam also reduces maintenance and replacement costs due to its superior durability in fire safety applications.
Health and Safety Implications
Latex foam for fireproof insulation offers better breathability and lower toxicity, reducing the risk of harmful off-gassing and smoke inhalation during a fire event. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance and low smoke emission but may release formaldehyde and other hazardous compounds under high temperatures, posing respiratory risks. Choosing insulation requires balancing phenolic foam's enhanced flame retardancy against latex foam's safer chemical profile for healthier indoor air quality.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Fireproof Insulation
Latex foam offers excellent flexibility and moderate fire resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring comfort and thermal insulation, whereas phenolic foam provides superior fireproofing due to its inherent low flame spread and smoke emission properties. Phenolic foam's high char yield and low heat release rate make it the preferred choice for stringent fire safety standards in building insulation. Selecting the best fireproof insulation depends on balancing fire resistance requirements with thermal performance and mechanical properties, with phenolic foam often favored for critical fireproof applications.
Infographic: Latex foam vs Phenolic foam for Fireproof Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com