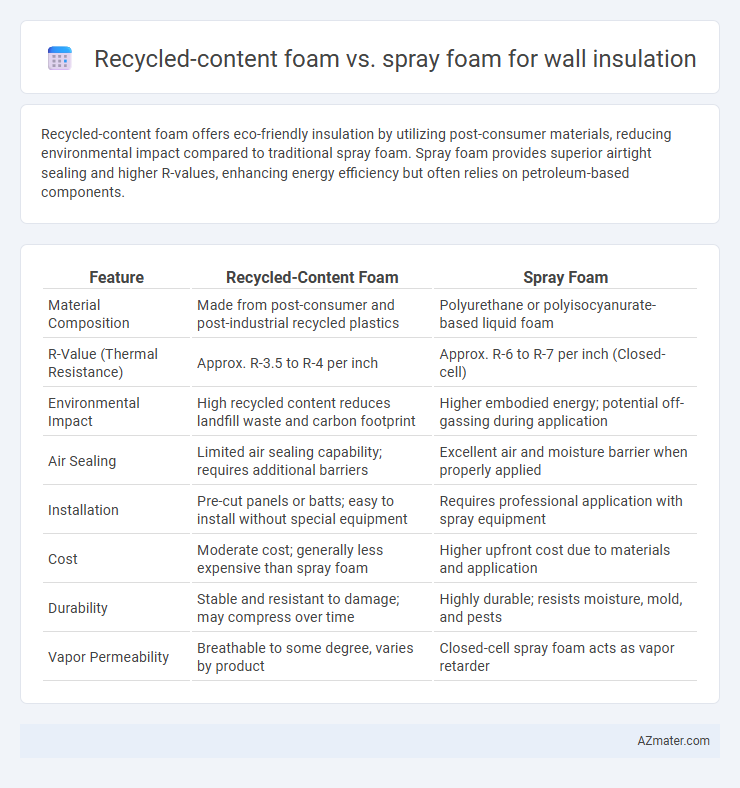
Recycled-content foam offers eco-friendly insulation by utilizing post-consumer materials, reducing environmental impact compared to traditional spray foam. Spray foam provides superior airtight sealing and higher R-values, enhancing energy efficiency but often relies on petroleum-based components.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled-Content Foam | Spray Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Made from post-consumer and post-industrial recycled plastics | Polyurethane or polyisocyanurate-based liquid foam |
| R-Value (Thermal Resistance) | Approx. R-3.5 to R-4 per inch | Approx. R-6 to R-7 per inch (Closed-cell) |
| Environmental Impact | High recycled content reduces landfill waste and carbon footprint | Higher embodied energy; potential off-gassing during application |
| Air Sealing | Limited air sealing capability; requires additional barriers | Excellent air and moisture barrier when properly applied |
| Installation | Pre-cut panels or batts; easy to install without special equipment | Requires professional application with spray equipment |
| Cost | Moderate cost; generally less expensive than spray foam | Higher upfront cost due to materials and application |
| Durability | Stable and resistant to damage; may compress over time | Highly durable; resists moisture, mold, and pests |
| Vapor Permeability | Breathable to some degree, varies by product | Closed-cell spray foam acts as vapor retarder |
Introduction to Wall Insulation Options
Recycled-content foam insulation offers an eco-friendly alternative by utilizing post-consumer or industrial waste materials, reducing environmental impact while maintaining thermal efficiency for walls. Spray foam insulation, known for its superior air-sealing properties and high R-values per inch, provides excellent moisture resistance and structural reinforcement in wall cavities. Choosing between recycled-content foam and spray foam depends on factors such as budget, environmental priorities, and desired insulation performance in residential or commercial wall applications.
What Is Recycled-Content Foam Insulation?
Recycled-content foam insulation is made from materials such as recycled plastics and industrial byproducts, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional spray foam. This type of insulation provides comparable thermal performance while reducing environmental impact by diverting waste from landfills. Its composition enhances sustainability without compromising on energy efficiency or moisture resistance in wall applications.
Understanding Spray Foam Insulation
Spray foam insulation offers superior air-sealing capabilities compared to recycled-content foam, significantly reducing thermal bridging and enhancing energy efficiency. It expands upon application to fill gaps and cracks, providing a continuous barrier that minimizes air infiltration and moisture buildup. Understanding spray foam's closed-cell and open-cell variants helps optimize insulation performance based on thermal resistance (R-value) and vapor permeability requirements.
Environmental Impact: Recycled vs. Spray Foam
Recycled-content foam insulation significantly reduces environmental impact by utilizing post-consumer or post-industrial materials, thereby diverting waste from landfills and lowering the demand for virgin resources. Spray foam, while excellent for air sealing and energy efficiency, often contains petrochemicals and blowing agents with high global warming potential, contributing to a larger carbon footprint. Choosing recycled-content foam promotes sustainability through material reuse and reduced embodied energy compared to the higher emissions associated with spray foam manufacturing and application.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Recycled-content foam insulation offers moderate thermal resistance with R-values typically ranging from R-3.5 to R-4.5 per inch, providing effective energy savings while promoting environmental sustainability. Spray foam insulation, especially closed-cell variants, delivers superior thermal performance with R-values around R-6 to R-7 per inch, ensuring airtight sealing and minimizing heat loss for optimal wall insulation. Evaluating both options, spray foam generally outperforms recycled-content foam in thermal efficiency but at a higher cost and environmental impact.
Installation Processes and Techniques
Recycled-content foam insulation relies on pre-manufactured panels or blocks that are cut and fitted into wall cavities, offering a straightforward installation with minimal on-site preparation and reduced environmental impact. Spray foam insulation requires specialized equipment to mix and apply the foam directly onto wall surfaces, expanding to fill gaps and creating an airtight seal, which demands skilled technicians for precise application and curing control. Both methods enhance thermal performance and moisture resistance, but recycled-content foam emphasizes easier, cleaner installation, while spray foam prioritizes seamless coverage and superior air barrier properties.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term
Recycled-content foam typically offers lower initial costs due to the use of sustainable materials and simpler manufacturing processes, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. Spray foam insulation, while having higher upfront expenses, provides superior air sealing and energy efficiency, resulting in significant long-term savings on heating and cooling bills. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, spray foam's durability and performance often offset the premium initial price through reduced energy consumption and maintenance costs over time.
Health and Indoor Air Quality Considerations
Recycled-content foam insulation typically emits fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contributing to better indoor air quality and a healthier living environment. Spray foam insulation, especially closed-cell varieties, can off-gas chemicals during and shortly after application, requiring proper ventilation and curing time to minimize health risks. Selecting recycled-content foam can reduce exposure to harmful toxins, making it a preferred option for sensitive individuals concerned with long-term indoor air quality.
Durability and Maintenance Factors
Recycled-content foam insulation offers moderate durability but may degrade more quickly under moisture exposure compared to spray foam, which provides superior long-term structural integrity and moisture resistance. Spray foam's closed-cell structure enhances insulation performance and minimizes air leaks, resulting in less frequent maintenance and reduced risk of mold growth. Maintenance for recycled-content foam often involves periodic inspections for compression or water damage, while spray foam typically requires minimal upkeep due to its resilient and adhesive properties.
Choosing the Best Foam Insulation for Your Walls
Recycled-content foam offers environmental benefits by incorporating post-consumer materials while providing good thermal resistance, typically with R-values between 3.5 to 4 per inch. Spray foam insulation, especially closed-cell types, delivers higher R-values up to 6.5 per inch and superior air sealing, making it ideal for energy efficiency and moisture control in walls. When choosing the best foam insulation, consider factors like insulation performance, budget, environmental impact, and installation requirements to ensure optimal wall thermal protection and sustainability.
Infographic: Recycled-content foam vs Spray foam for Wall insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com