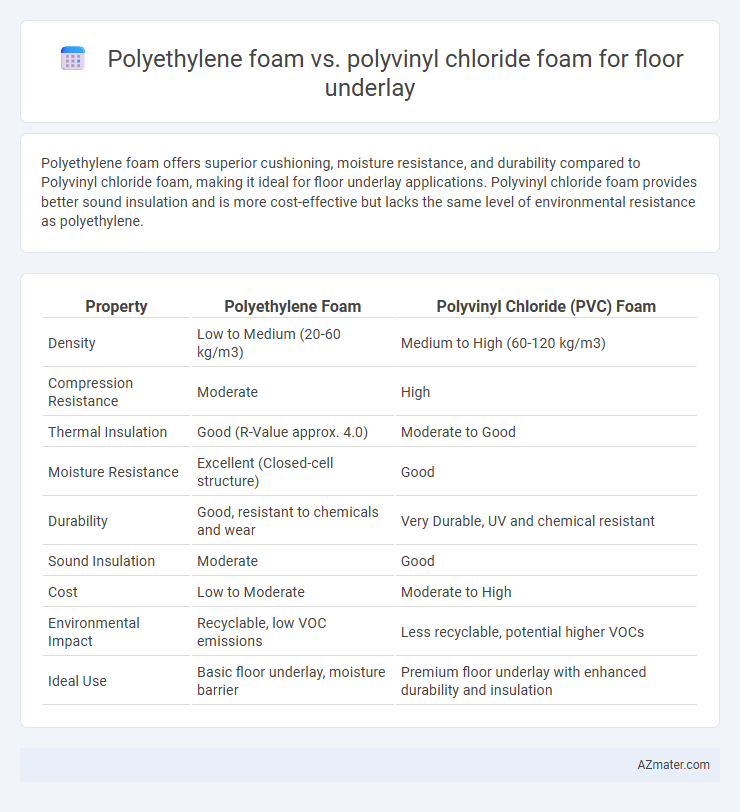
Polyethylene foam offers superior cushioning, moisture resistance, and durability compared to Polyvinyl chloride foam, making it ideal for floor underlay applications. Polyvinyl chloride foam provides better sound insulation and is more cost-effective but lacks the same level of environmental resistance as polyethylene.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Foam | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low to Medium (20-60 kg/m3) | Medium to High (60-120 kg/m3) |
| Compression Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Thermal Insulation | Good (R-Value approx. 4.0) | Moderate to Good |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent (Closed-cell structure) | Good |
| Durability | Good, resistant to chemicals and wear | Very Durable, UV and chemical resistant |
| Sound Insulation | Moderate | Good |
| Cost | Low to Moderate | Moderate to High |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, low VOC emissions | Less recyclable, potential higher VOCs |
| Ideal Use | Basic floor underlay, moisture barrier | Premium floor underlay with enhanced durability and insulation |
Introduction to Floor Underlay Materials
Polyethylene foam and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam are common materials used for floor underlay due to their cushioning and insulation properties. Polyethylene foam offers excellent moisture resistance and compressive strength, making it ideal for subfloor protection and soundproofing. PVC foam provides greater durability and fire resistance, suitable for high-traffic areas requiring enhanced stability and longevity.
What is Polyethylene Foam?
Polyethylene foam is a lightweight, closed-cell foam known for its excellent cushioning, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for floor underlay applications. This foam provides effective sound absorption and shock resistance, enhancing floor durability and comfort by reducing impact noise and wear. Compared to polyvinyl chloride foam, polyethylene foam offers superior water resistance and flexibility, which ensures long-lasting performance in various indoor environments.
What is Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) foam is a closed-cell, rigid foam known for its excellent durability, water resistance, and thermal insulation properties, making it an ideal floor underlay material. Unlike polyethylene foam, PVC foam offers superior impact absorption and increased resistance to chemicals and abrasion, which enhances the lifespan of flooring installations. Its dense structure also provides improved sound insulation and dimensional stability, contributing to overall floor comfort and performance.
Key Properties of Polyethylene Foam for Underlay
Polyethylene foam offers superior moisture resistance, excellent thermal insulation, and high durability, making it an ideal choice for floor underlay. Its closed-cell structure provides outstanding cushioning and sound absorption, enhancing comfort and noise reduction in residential and commercial flooring applications. Lightweight and easy to install, polyethylene foam also resists mold and mildew, ensuring long-term performance in varying humidity conditions.
Key Properties of PVC Foam for Underlay
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam used for floor underlay possesses excellent durability, high resistance to moisture, and superior compressive strength compared to polyethylene foam. Its closed-cell structure enhances sound insulation and provides effective thermal insulation, making it ideal for subfloor applications in both residential and commercial settings. PVC foam's fire retardant properties and chemical resistance further ensure long-lasting performance and safety in various flooring installations.
Durability Comparison: Polyethylene vs PVC Foam
Polyethylene foam offers superior durability for floor underlays due to its high resistance to compression, moisture, and chemical degradation, making it ideal for long-term performance in high-traffic areas. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam underlays provide good cushioning but are more susceptible to wear and tear, UV exposure, and plasticizer migration, which can reduce their lifespan under heavy use. Polyethylene's closed-cell structure ensures better resilience and stability compared to the more flexible and less dense PVC foam, resulting in a longer-lasting floor underlay solution.
Acoustic and Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Polyethylene foam offers excellent thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity around 0.035 W/m*K, providing effective heat retention beneath flooring. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, while slightly less efficient thermally, excels in acoustic insulation due to its higher density and cellular structure that dampens sound transmission effectively. For floor underlay applications prioritizing noise reduction, PVC foam outperforms polyethylene foam, whereas polyethylene foam delivers superior performance in minimizing heat loss.
Installation and Maintenance Differences
Polyethylene foam offers lightweight, flexible properties that make installation quick and simple, often requiring minimal cutting and fitting for floor underlay applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, being denser and more rigid, demands precise handling and careful installation to prevent damage or deformation. Maintenance-wise, polyethylene foam is water-resistant and resists mold, leading to low upkeep, while PVC foam requires regular checks for potential cracking or wear, especially in high-traffic areas.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene foam offers a lower environmental footprint compared to polyvinyl chloride foam due to its recyclability and lower toxic emissions during production and disposal. Polyvinyl chloride foam releases harmful dioxins and heavy metals, raising concerns about long-term environmental pollution and health hazards. Choosing polyethylene foam for floor underlay supports sustainability by reducing landfill waste and minimizing ecological toxicity.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Flooring Needs
Polyethylene foam offers excellent moisture resistance and cushioning, making it ideal for laminate or hardwood floors where durability and sound insulation are priorities. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides superior fire resistance and higher density, which benefits commercial or high-traffic areas requiring enhanced impact absorption and long-term performance. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing factors like moisture exposure, foot traffic, insulation needs, and budget to ensure optimal flooring protection and comfort.
Infographic: Polyethylene foam vs Polyvinyl chloride foam for Floor underlay
 azmater.com
azmater.com