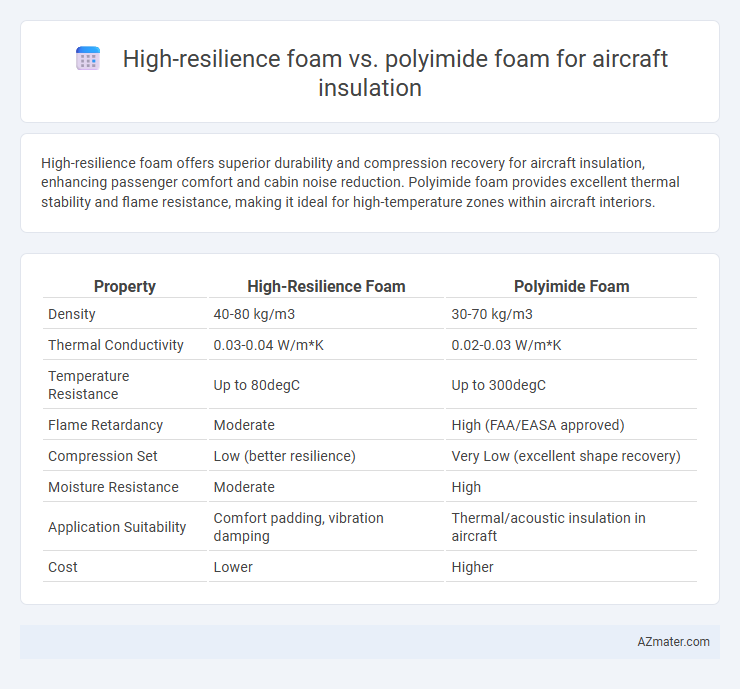
High-resilience foam offers superior durability and compression recovery for aircraft insulation, enhancing passenger comfort and cabin noise reduction. Polyimide foam provides excellent thermal stability and flame resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature zones within aircraft interiors.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High-Resilience Foam | Polyimide Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 40-80 kg/m3 | 30-70 kg/m3 |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.03-0.04 W/m*K | 0.02-0.03 W/m*K |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 80degC | Up to 300degC |
| Flame Retardancy | Moderate | High (FAA/EASA approved) |
| Compression Set | Low (better resilience) | Very Low (excellent shape recovery) |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Application Suitability | Comfort padding, vibration damping | Thermal/acoustic insulation in aircraft |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Aircraft Insulation Materials
High-resilience foam offers excellent cushioning and energy absorption properties, making it ideal for aircraft seats and interior panels where passenger comfort and vibration dampening are critical. Polyimide foam excels in thermal insulation and fire resistance, essential for maintaining cabin temperature control and meeting stringent aviation safety standards. Both materials provide lightweight solutions, but polyimide foam's superior flame retardancy and low smoke emission make it the preferred choice for critical aircraft insulation applications.
Overview of High-Resilience Foam
High-resilience foam, characterized by its superior elasticity and durability, is widely used in aircraft insulation for its excellent energy absorption and structural integrity. This type of foam maintains consistent thermal resistance while offering resistance to compression and fatigue, making it ideal for long-term performance in demanding aerospace environments. Compared to polyimide foam, high-resilience foam provides enhanced cushioning properties and is effective in vibration damping, ensuring occupant comfort and component protection.
Overview of Polyimide Foam
Polyimide foam offers superior thermal stability and flame resistance compared to traditional high-resilience foam, making it ideal for aircraft insulation applications requiring stringent fire safety standards. Its low density and excellent acoustic damping properties contribute to weight savings and noise reduction in aerospace environments. The material's chemical inertness and resistance to harsh environmental conditions ensure long-term durability and performance in demanding flight operations.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
High-resilience foam exhibits excellent thermal insulation properties due to its dense cell structure, effectively reducing heat transfer in aircraft cabins. Polyimide foam outperforms high-resilience foam with a lower thermal conductivity, offering superior temperature resistance and enhanced fire retardancy critical for aerospace standards. The choice between these materials hinges on specific insulation efficiency requirements and the thermal stress tolerance needed in different aircraft sections.
Weight and Density Considerations
High-resilience foam offers lower density and lighter weight compared to polyimide foam, making it ideal for aircraft insulation where weight reduction is critical for fuel efficiency and performance. Polyimide foam, though denser, provides superior thermal resistance and structural integrity under extreme temperatures. Selecting between these materials requires balancing weight constraints with insulation effectiveness to optimize aircraft operational efficiency.
Fire Resistance and Safety Properties
High-resilience foam exhibits excellent fire resistance with low smoke emission and self-extinguishing properties, making it a reliable choice for aircraft insulation where safety is critical. Polyimide foam offers superior thermal stability and can endure extreme temperatures without degrading, enhancing fire safety in demanding aviation environments. Both materials comply with FAA fire safety standards, but polyimide foam provides higher resistance to toxic gas release during combustion, improving overall occupant protection.
Durability and Longevity in Aircraft Environments
High-resilience foam exhibits superior durability and longevity in aircraft insulation due to its excellent resistance to compression set and repeated mechanical stress, maintaining structural integrity over extended flight cycles. Polyimide foam offers high-temperature stability and chemical resistance but may degrade faster under continuous mechanical strain typical in aviation environments. Therefore, high-resilience foam is preferred for applications demanding long-term resilience against vibration, impact, and dynamic loads experienced during aircraft operation.
Installation and Maintenance Factors
High-resilience foam offers easier installation due to its flexibility and compressibility, allowing it to conform tightly to aircraft contours and reduce labor time. Polyimide foam, while more rigid, provides superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, resulting in less frequent maintenance and longer service intervals. Maintenance of high-resilience foam may require more regular inspections and replacements due to potential compression set, whereas polyimide foam maintains structural integrity under extreme conditions, minimizing repair needs.
Cost Analysis of High-Resilience vs Polyimide Foam
High-resilience foam offers a more cost-effective solution compared to polyimide foam for aircraft insulation, with significantly lower material and manufacturing expenses. Although polyimide foam provides superior thermal stability and fire resistance, its high production costs and complex processing make it less economical for large-scale use. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses, including maintenance and replacement, high-resilience foam demonstrates favorable cost benefits for standard insulation applications.
Application Suitability and Industry Recommendations
High-resilience foam offers superior cushioning and energy absorption, making it ideal for applications requiring vibration damping and passenger comfort in aircraft cabins. Polyimide foam is preferred for thermal insulation and fire resistance due to its excellent high-temperature stability and low smoke toxicity, aligning with stringent aerospace safety standards. Industry recommendations favor polyimide foam for critical thermal barriers and high-resilience foam for ergonomic seating and padding solutions.
Infographic: High-resilience foam vs Polyimide foam for Aircraft insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com