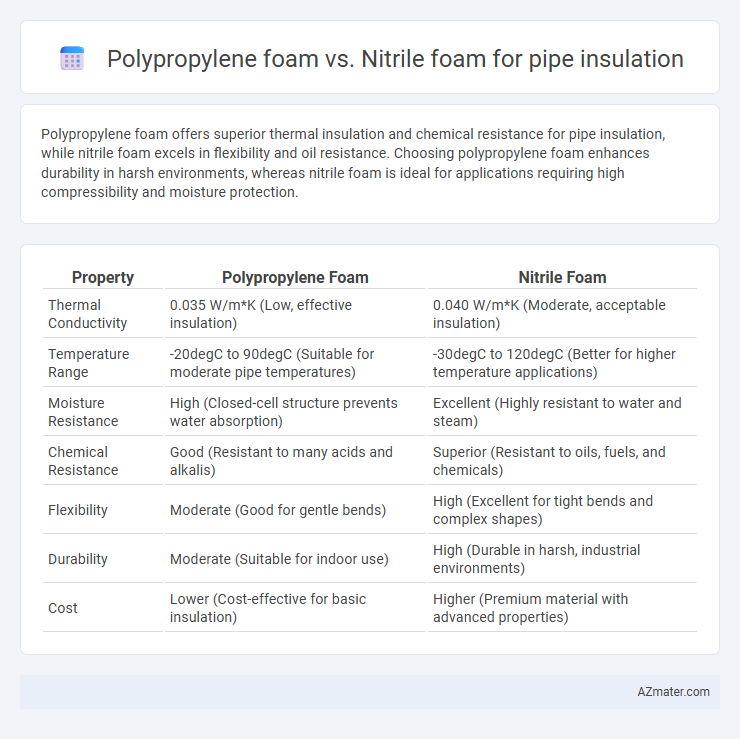
Polypropylene foam offers superior thermal insulation and chemical resistance for pipe insulation, while nitrile foam excels in flexibility and oil resistance. Choosing polypropylene foam enhances durability in harsh environments, whereas nitrile foam is ideal for applications requiring high compressibility and moisture protection.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene Foam | Nitrile Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.035 W/m*K (Low, effective insulation) | 0.040 W/m*K (Moderate, acceptable insulation) |
| Temperature Range | -20degC to 90degC (Suitable for moderate pipe temperatures) | -30degC to 120degC (Better for higher temperature applications) |
| Moisture Resistance | High (Closed-cell structure prevents water absorption) | Excellent (Highly resistant to water and steam) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (Resistant to many acids and alkalis) | Superior (Resistant to oils, fuels, and chemicals) |
| Flexibility | Moderate (Good for gentle bends) | High (Excellent for tight bends and complex shapes) |
| Durability | Moderate (Suitable for indoor use) | High (Durable in harsh, industrial environments) |
| Cost | Lower (Cost-effective for basic insulation) | Higher (Premium material with advanced properties) |
Introduction to Pipe Insulation Materials
Polypropylene foam and nitrile foam are commonly used materials for pipe insulation due to their thermal resistance and durability. Polypropylene foam offers excellent chemical resistance, low water absorption, and a lightweight structure, making it suitable for various industrial applications. Nitrile foam provides superior flexibility, high resistance to oils and fuels, and effective thermal insulation properties, ideal for mechanical and automotive piping systems exposed to harsh environments.
What is Polypropylene Foam?
Polypropylene foam is a lightweight, closed-cell insulation material known for its excellent thermal resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for pipe insulation applications. Its low moisture absorption and high compressive strength provide durable protection against temperature fluctuations and mechanical stress. Compared to nitrile foam, polypropylene foam offers superior resistance to oils and chemicals, enhancing its suitability for industrial environments.
What is Nitrile Foam?
Nitrile foam is a synthetic rubber material known for its excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and temperature variations, making it ideal for pipe insulation in industrial environments. Its closed-cell structure provides superior thermal insulation and moisture resistance compared to polypropylene foam, which is less effective against oil exposure. Nitrile foam's durability and flexibility ensure long-lasting insulation performance in harsh conditions.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Polypropylene foam offers excellent thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity typically around 0.035 to 0.040 W/m*K, providing effective resistance to heat transfer in pipe insulation applications. Nitrile foam, also known as NBR foam, exhibits slightly higher thermal conductivity values, generally ranging from 0.040 to 0.045 W/m*K, which results in marginally lower insulation efficiency compared to polypropylene foam. Both materials provide good thermal performance, but polypropylene foam has an edge in maintaining lower heat loss and better energy efficiency in pipe insulation systems.
Moisture Resistance: Polypropylene vs Nitrile Foam
Polypropylene foam offers excellent moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, preventing water absorption and maintaining insulation efficiency in damp environments. Nitrile foam also provides good moisture resistance, with its rubber-based composition acting as a barrier against water vapor and condensation. For pipe insulation applications where consistent moisture control is critical, polypropylene foam typically outperforms nitrile foam in long-term durability and resistance to mold growth.
Fire Resistance and Safety Ratings
Polypropylene foam offers high fire resistance with a UL94 V-0 rating, ensuring minimal flame spread and low smoke emission, making it highly suitable for pipe insulation in fire-critical environments. Nitrile foam, while providing excellent thermal insulation and chemical resistance, typically achieves a UL94 V-1 or V-2 rating, indicating a lower fire retardancy compared to polypropylene foam. Safety standards such as ASTM E84 often favor polypropylene foam for applications requiring superior flame retardancy and low smoke toxicity.
Durability and Longevity
Polypropylene foam offers excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV degradation, resulting in superior durability for pipe insulation in various environmental conditions. Nitrile foam provides strong resistance to oils, fuels, and temperature fluctuations but may degrade faster when exposed to prolonged UV light and ozone. For long-term insulation performance, polypropylene foam generally ensures greater longevity, especially in outdoor or humid environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polypropylene foam offers superior environmental benefits due to its recyclability and low carbon footprint during production compared to nitrile foam, which involves more energy-intensive manufacturing processes and generates higher emissions. Polypropylene foam's ability to be recycled multiple times reduces landfill waste and supports circular economy principles, whereas nitrile foam is less commonly recycled and often ends up as non-biodegradable waste. The sustainable attributes of polypropylene foam make it a preferred choice for eco-conscious pipe insulation projects aiming to minimize environmental impact.
Cost Analysis: Polypropylene Foam vs Nitrile Foam
Polypropylene foam offers a cost-effective solution for pipe insulation with lower material and installation expenses compared to nitrile foam. Nitrile foam, while more expensive upfront, provides superior durability and thermal resistance that can reduce long-term maintenance and energy costs. Choosing polypropylene foam is advantageous for budget-sensitive projects, whereas nitrile foam delivers better value in applications requiring enhanced performance and longevity.
Best Applications and Recommendations
Polypropylene foam excels in pipe insulation for low to medium temperature applications due to its excellent thermal insulation properties and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for HVAC systems and chilled water lines. Nitrile foam offers superior oil and chemical resistance, making it the preferred choice for industrial pipe insulation exposed to oils, fuels, and corrosive substances. For applications requiring flexibility and durability in harsh chemical environments, nitrile foam is recommended, while polypropylene foam suits environments where cost-effectiveness and moisture resistance are primary concerns.
Infographic: Polypropylene foam vs Nitrile foam for Pipe insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com