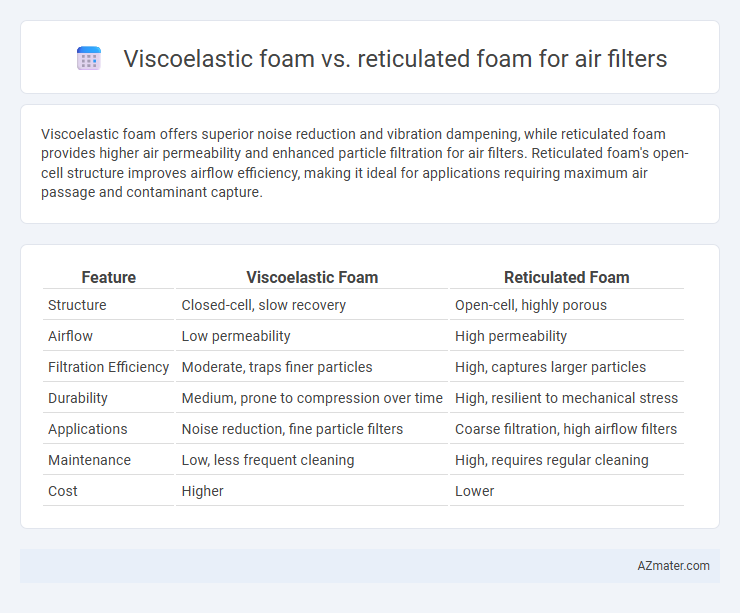
Viscoelastic foam offers superior noise reduction and vibration dampening, while reticulated foam provides higher air permeability and enhanced particle filtration for air filters. Reticulated foam's open-cell structure improves airflow efficiency, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum air passage and contaminant capture.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Viscoelastic Foam | Reticulated Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Closed-cell, slow recovery | Open-cell, highly porous |
| Airflow | Low permeability | High permeability |
| Filtration Efficiency | Moderate, traps finer particles | High, captures larger particles |
| Durability | Medium, prone to compression over time | High, resilient to mechanical stress |
| Applications | Noise reduction, fine particle filters | Coarse filtration, high airflow filters |
| Maintenance | Low, less frequent cleaning | High, requires regular cleaning |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Foam Types for Air Filters
Viscoelastic foam, known for its pressure-sensitive and memory-like properties, offers superior dust and allergen trapping capabilities in air filters due to its dense cellular structure. Reticulated foam, characterized by its open-cell network, enables enhanced airflow and faster particle filtration, making it ideal for applications requiring high breathability. Selecting between viscoelastic and reticulated foam types depends on balancing filtration efficiency with airflow requirements in air filtration systems.
What is Viscoelastic Foam?
Viscoelastic foam, also known as memory foam, is a type of polyurethane foam characterized by its high density and slow recovery properties, making it ideal for air filters requiring excellent dust and particulate capture. Its unique cell structure conforms to airflow patterns, enhancing filtration efficiency while absorbing vibrations and noise. In contrast, reticulated foam features an open-cell structure that promotes airflow but offers less filtration precision, making viscoelastic foam preferable for applications demanding both filtration performance and acoustic comfort.
What is Reticulated Foam?
Reticulated foam is an open-cell polyurethane foam characterized by its porous, net-like structure, which maximizes airflow and filtration efficiency in air filters. Unlike viscoelastic foam, which is dense and compressible for cushioning applications, reticulated foam provides minimal resistance to air, making it ideal for trapping particles while maintaining optimal ventilation. Its high porosity and durability ensure effective removal of dust, pollen, and other contaminants in HVAC and industrial air filtration systems.
Structural Differences: Viscoelastic vs Reticulated Foam
Viscoelastic foam features a closed-cell structure with high density and slow recovery, providing superior particle trapping through its viscoelastic properties, whereas reticulated foam consists of an open-cell, highly porous network designed for maximum airflow and minimal resistance. The reticulated foam's interconnected pores enhance air permeability and filtration efficiency by allowing larger volumes of air to pass through, while viscoelastic foam's dense matrix excels at capturing finer particulate matter. Structural differences between these foams directly influence their applications in air filters, with viscoelastic foam favoring contaminant absorption and reticulated foam optimizing air circulation and dust capture.
Filtration Efficiency Comparison
Viscoelastic foam and reticulated foam differ significantly in filtration efficiency for air filters due to their structural properties. Viscoelastic foam has a dense, closed-cell structure that traps smaller particles effectively but may reduce airflow, while reticulated foam features an open-cell network allowing higher air permeability with moderate particle capture. Reticulated foam generally offers better balance between filtration efficiency and airflow, making it more suitable for applications requiring both particle removal and ventilation.
Airflow Performance Analysis
Viscoelastic foam exhibits lower airflow permeability due to its dense cellular structure, resulting in higher resistance and reduced ventilation efficiency in air filters. Reticulated foam features an open-cell framework with interconnected pores, significantly enhancing airflow performance and minimizing pressure drop across the filter media. Comparative airflow tests indicate reticulated foam achieves up to 50% greater volumetric flow rates than viscoelastic foam under identical operating conditions.
Durability and Lifespan
Viscoelastic foam offers moderate durability with excellent compression recovery but tends to degrade faster under prolonged airflow exposure, reducing its lifespan in air filters. Reticulated foam exhibits superior durability due to its open-cell structure, allowing for enhanced airflow and resistance to clogging, which extends its functional lifespan significantly. The higher mechanical strength and resistance to environmental factors make reticulated foam the preferred choice for long-lasting air filtration applications.
Maintenance Requirements
Viscoelastic foam in air filters requires infrequent maintenance due to its dense structure that traps finer particles but may accumulate dust more quickly, necessitating occasional cleaning to maintain airflow. Reticulated foam, characterized by its open-cell structure, allows for easier cleaning and quicker drying, significantly reducing maintenance time and extending filter lifespan. Selecting between the two depends on balancing particle filtration efficiency against the frequency and ease of maintenance needed for optimal air filter performance.
Application Suitability in Air Filtration
Viscoelastic foam offers superior noise reduction and particle capture due to its dense, slow-recovery structure, making it suitable for applications requiring fine filtration and sound dampening in HVAC systems. Reticulated foam provides excellent airflow and quick moisture drainage due to its open-cell structure, ideal for coarse filtration and environments with high humidity or particulate load. Choosing between viscoelastic and reticulated foam depends on balancing filtration efficiency, airflow resistance, and moisture management specific to air filter requirements.
Summary: Which Foam is Better for Air Filters?
Viscoelastic foam offers superior sound absorption and vibration dampening in air filters due to its slow recovery and high-density properties, making it ideal for noise-sensitive environments. Reticulated foam provides excellent airflow and particulate filtration with its open-cell structure, enhancing air circulation and dust capture efficiency. Reticulated foam is generally better for air filters requiring high breathability and dust removal, while viscoelastic foam suits applications prioritizing noise reduction and vibration control.
Infographic: Viscoelastic foam vs Reticulated foam for Air filter
 azmater.com
azmater.com