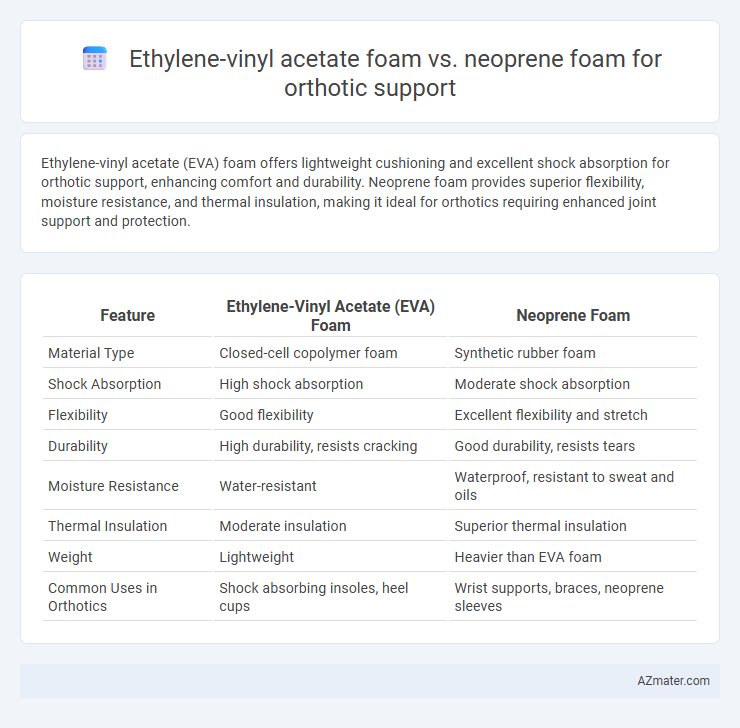
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers lightweight cushioning and excellent shock absorption for orthotic support, enhancing comfort and durability. Neoprene foam provides superior flexibility, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation, making it ideal for orthotics requiring enhanced joint support and protection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam | Neoprene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Closed-cell copolymer foam | Synthetic rubber foam |
| Shock Absorption | High shock absorption | Moderate shock absorption |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility | Excellent flexibility and stretch |
| Durability | High durability, resists cracking | Good durability, resists tears |
| Moisture Resistance | Water-resistant | Waterproof, resistant to sweat and oils |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation | Superior thermal insulation |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than EVA foam |
| Common Uses in Orthotics | Shock absorbing insoles, heel cups | Wrist supports, braces, neoprene sleeves |
Introduction to Orthotic Support Materials
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam and neoprene foam are prominent materials used in orthotic support due to their unique properties. EVA foam provides lightweight cushioning, excellent shock absorption, and durability, making it ideal for custom insoles and foot orthoses. Neoprene foam offers superior flexibility, resistance to moisture, and thermal insulation, which benefits orthotic braces and supports requiring both comfort and structural stability.
Overview of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam
Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) foam offers exceptional cushioning and shock absorption, making it a preferred material for orthotic support due to its lightweight and flexible properties. Its closed-cell structure resists moisture and compression set, ensuring durability and sustained performance over time. EVA foam's ability to mold to foot contours enhances comfort and stability, reducing strain and improving gait efficiency compared to neoprene foam.
Key Properties of Neoprene Foam
Neoprene foam offers superior durability, flexibility, and excellent resistance to oils, chemicals, and weathering, making it ideal for orthotic support requiring long-lasting wear and environmental resilience. Its closed-cell structure provides enhanced cushioning, shock absorption, and moisture resistance, which ensures patient comfort and reduces skin irritation. Neoprene's high elasticity and thermal insulation help maintain joint warmth and support during extended use.
Cushioning and Shock Absorption Comparison
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides superior cushioning with a softer, more flexible structure ideal for distributing pressure evenly in orthotic support. Neoprene foam excels in shock absorption due to its higher density and resilience, effectively reducing impact forces during dynamic activities. While EVA foam offers enhanced comfort for prolonged wear, neoprene's durability and compression recovery make it better suited for high-impact orthotic applications.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam exhibits superior durability and longevity for orthotic support due to its excellent resilience and resistance to compression set, maintaining structural integrity over extended periods. Neoprene foam offers moderate durability with good flexibility but tends to degrade faster under continuous stress and exposure to moisture, reducing its effective lifespan. EVA's ability to withstand repetitive impacts and maintain cushioning properties makes it a preferred material for long-term orthotic applications compared to neoprene foam.
Comfort and Fit for Orthotic Applications
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers excellent cushioning and shock absorption, enhancing comfort and reducing pressure points in orthotic applications, while its lightweight flexibility ensures a snug fit. Neoprene foam provides superior elasticity and durability, conforming closely to foot contours to maintain support and comfort during prolonged wear. Both materials optimize orthotic fit, but EVA excels in softness and impact resistance, whereas neoprene is favored for dynamic support and moisture resistance.
Moisture Resistance and Breathability
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior moisture resistance compared to neoprene foam, making it ideal for orthotic support in environments prone to sweat and humidity. Neoprene foam provides better breathability due to its open-cell structure, which enhances airflow and reduces heat buildup during prolonged wear. Choosing between EVA and neoprene foam for orthotic applications depends on balancing the need for moisture resistance against the importance of ventilation and comfort.
Weight and Flexibility Considerations
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior lightweight properties compared to neoprene foam, making it ideal for orthotic support that requires minimal bulk and reduced fatigue. EVA's high flexibility allows it to conform closely to foot contours, enhancing comfort and shock absorption during prolonged use. In contrast, neoprene foam, while slightly heavier, provides greater durability and moderate flexibility, which can be beneficial for orthotics needing more structural support.
Cost-Effectiveness for Orthotic Support
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior cost-effectiveness for orthotic support due to its lightweight nature, durability, and cushioning properties, making it ideal for mass production and long-term use. Neoprene foam, while providing excellent flexibility and moisture resistance, generally incurs higher material and manufacturing costs, impacting overall affordability. Choosing EVA foam reduces expenses without compromising comfort and support, making it a preferred option in budget-conscious orthotic applications.
Choosing the Best Foam: EVA vs Neoprene
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior shock absorption and firmness, making it ideal for orthotic support requiring high impact resistance and structural stability. Neoprene foam provides excellent flexibility and water resistance, beneficial for orthotics used in moist or active environments where durability and comfort are essential. Selecting between EVA and Neoprene depends on balancing the need for cushioning and durability against flexibility and moisture protection in orthotic applications.
Infographic: Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam vs Neoprene foam for Orthotic support
 azmater.com
azmater.com