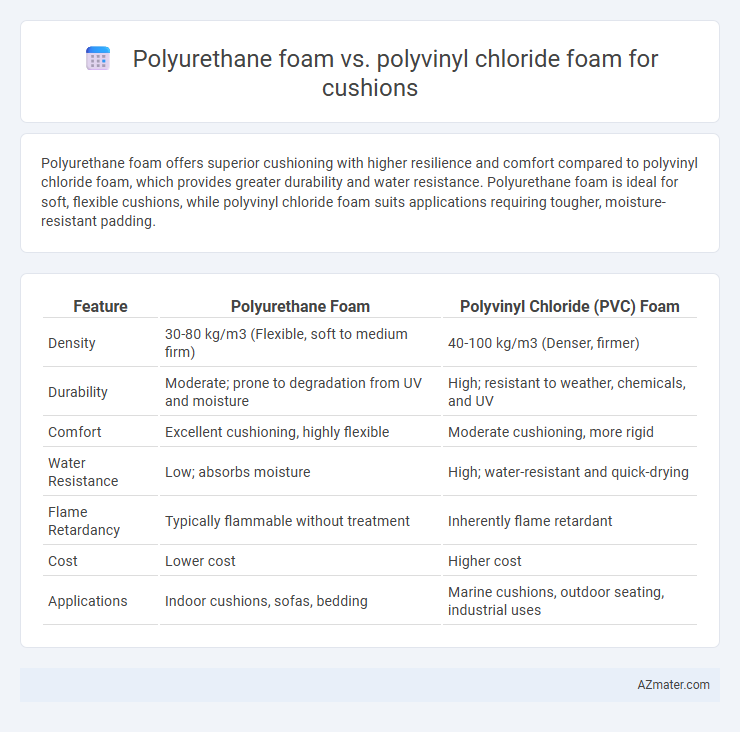
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning with higher resilience and comfort compared to polyvinyl chloride foam, which provides greater durability and water resistance. Polyurethane foam is ideal for soft, flexible cushions, while polyvinyl chloride foam suits applications requiring tougher, moisture-resistant padding.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyurethane Foam | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 30-80 kg/m3 (Flexible, soft to medium firm) | 40-100 kg/m3 (Denser, firmer) |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to degradation from UV and moisture | High; resistant to weather, chemicals, and UV |
| Comfort | Excellent cushioning, highly flexible | Moderate cushioning, more rigid |
| Water Resistance | Low; absorbs moisture | High; water-resistant and quick-drying |
| Flame Retardancy | Typically flammable without treatment | Inherently flame retardant |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Applications | Indoor cushions, sofas, bedding | Marine cushions, outdoor seating, industrial uses |
Overview: Polyurethane Foam vs. Polyvinyl Chloride Foam
Polyurethane foam provides superior cushioning with high resilience and excellent comfort, making it ideal for furniture and automotive seats. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers greater chemical resistance and durability, suitable for outdoor and marine cushion applications. Both materials vary in density, flexibility, and moisture resistance, influencing their performance in different cushioning contexts.
Material Composition and Structure
Polyurethane foam consists of a polymer matrix formed by reacting polyols with isocyanates, creating a flexible, open-cell structure ideal for cushioning due to its excellent resilience and energy absorption. In contrast, Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is a closed-cell material made from vinyl chloride monomers, offering higher density, rigidity, and superior resistance to moisture and chemicals. The open-cell polyurethane foam provides better breathability and softness, while PVC foam's closed-cell structure ensures enhanced durability and structural integrity in cushion applications.
Comfort and Cushioning Performance
Polyurethane foam offers superior comfort and cushioning performance due to its high resilience, excellent pressure distribution, and ability to conform to body contours, making it ideal for cushions requiring long-lasting support. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides moderate cushioning with a firmer feel and enhanced durability against moisture and chemicals, suitable for outdoor or industrial cushion applications. Polyurethane foam generally outperforms PVC foam in softness and rebound, directly impacting comfort levels in seating and bedding products.
Durability and Longevity
Polyurethane foam offers superior durability and resilience for cushions, maintaining its shape and comfort over extended use compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam. Polyvinyl chloride foam tends to degrade faster under continual pressure and environmental exposure, making it less ideal for long-term applications. For longevity-focused cushions, polyurethane foam provides enhanced structural integrity and resistance to wear and tear.
Weight and Density Comparison
Polyurethane foam typically weighs less than polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, offering a lighter cushioning option ideal for applications requiring mobility and ease of handling. In terms of density, polyurethane foam ranges from 16 to 80 kg/m3, providing flexible support, while PVC foam density usually spans 30 to 200 kg/m3, delivering firmer, more rigid cushioning performance. The lower density and weight of polyurethane foam make it preferable for comfort-focused cushions, whereas PVC foam suits areas needing greater durability and structural integrity.
Flexibility and Resilience
Polyurethane foam exhibits superior flexibility and resilience compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, making it ideal for cushions requiring long-lasting comfort and shape retention. Polyurethane's open-cell structure allows for excellent compression recovery, while PVC foam's closed-cell composition offers less elasticity and can become stiff over time. For applications demanding high durability and bounce-back performance, polyurethane foam remains the preferred choice in cushion manufacturing.
Airflow and Breathability
Polyurethane foam offers superior airflow and breathability compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, thanks to its open-cell structure that allows air to pass through easily, reducing heat retention and moisture buildup. In contrast, PVC foam has a closed-cell composition that restricts airflow, resulting in less breathability and potential discomfort during prolonged use. These characteristics make polyurethane foam a preferred choice for cushions requiring enhanced ventilation and moisture management.
Cost-Effectiveness and Affordability
Polyurethane foam offers greater cost-effectiveness and affordability compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam for cushions due to its lower production costs and wider availability. While PVC foam provides durability and water resistance, its higher manufacturing expenses make it less budget-friendly for large-scale cushioning applications. Polyurethane foam's balance of comfort, resilience, and price efficiency makes it the preferred choice for economical cushion solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane foam, widely used in cushions, poses environmental challenges due to its petroleum-based origin and slow biodegradability, contributing to landfill waste and toxic emissions during production. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam releases harmful dioxins and phthalates throughout its lifecycle, raising concerns about soil and water contamination along with human health risks. Sustainable alternatives prioritize bio-based polyurethane foams and recycled PVC options, aiming to reduce carbon footprint and improve recyclability within the cushioning industry.
Application Suitability: Best Uses for Each Foam Type
Polyurethane foam excels in cushioning applications requiring high resilience, comfort, and impact absorption, making it ideal for furniture, automotive seats, and mattress cores. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior rigidity, chemical resistance, and weather durability, suited for outdoor cushions, marine seating, and industrial padding. Choosing polyurethane foam ensures softness and elasticity, whereas PVC foam provides structural support and longevity under harsh environmental conditions.
Infographic: Polyurethane foam vs Polyvinyl chloride foam for Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com