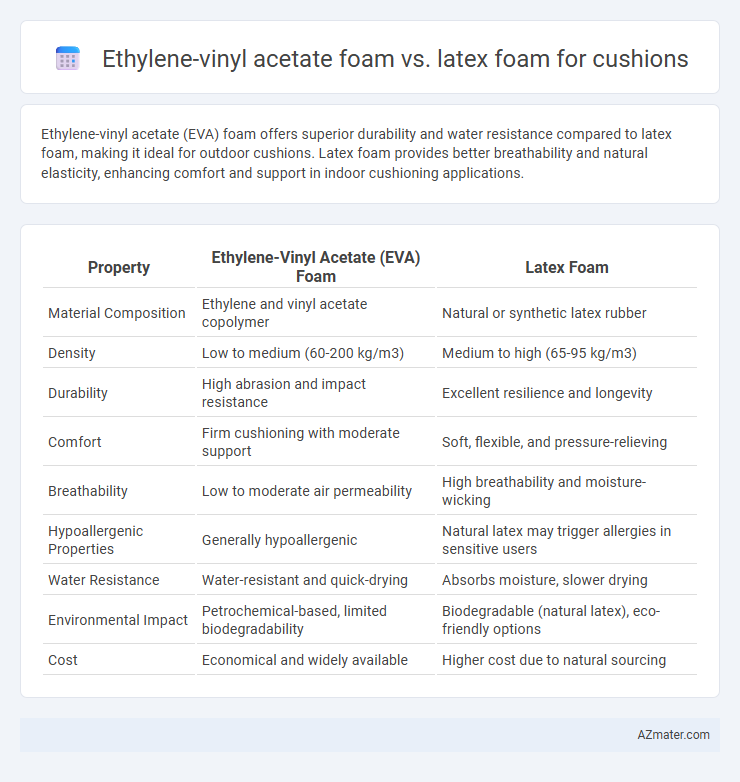
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior durability and water resistance compared to latex foam, making it ideal for outdoor cushions. Latex foam provides better breathability and natural elasticity, enhancing comfort and support in indoor cushioning applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam | Latex Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Ethylene and vinyl acetate copolymer | Natural or synthetic latex rubber |
| Density | Low to medium (60-200 kg/m3) | Medium to high (65-95 kg/m3) |
| Durability | High abrasion and impact resistance | Excellent resilience and longevity |
| Comfort | Firm cushioning with moderate support | Soft, flexible, and pressure-relieving |
| Breathability | Low to moderate air permeability | High breathability and moisture-wicking |
| Hypoallergenic Properties | Generally hypoallergenic | Natural latex may trigger allergies in sensitive users |
| Water Resistance | Water-resistant and quick-drying | Absorbs moisture, slower drying |
| Environmental Impact | Petrochemical-based, limited biodegradability | Biodegradable (natural latex), eco-friendly options |
| Cost | Economical and widely available | Higher cost due to natural sourcing |
Introduction to Cushion Foam Materials
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers lightweight durability, excellent shock absorption, and high resilience, making it ideal for cushioning applications requiring flexibility and moisture resistance. Latex foam, derived from natural or synthetic rubber, provides superior elasticity, breathability, and pressure relief, enhancing comfort and support in cushions. Both materials serve distinct purposes, with EVA excelling in impact protection and latex foam optimizing ergonomics and airflow.
What is Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam?
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is a soft, flexible material made from ethylene and vinyl acetate copolymers, known for its excellent shock absorption and resilience. Compared to latex foam, EVA foam offers superior water resistance, making it ideal for outdoor cushions and applications requiring durability against moisture. The closed-cell structure of EVA foam provides enhanced cushioning and insulation properties, distinguishing it from the natural elasticity and breathability found in latex foam.
What is Latex Foam?
Latex foam is a natural or synthetic material made from latex sap, known for its elasticity, durability, and breathability, making it a popular choice for cushions. It offers superior pressure relief and support due to its open-cell structure, promoting airflow and temperature regulation. Compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, latex foam provides enhanced comfort and resilience, ideal for premium cushioning applications.
Comfort and Support Comparison
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers excellent shock absorption and durability, providing firm yet flexible support ideal for cushions requiring long-term resilience. Latex foam excels in breathability and responsiveness, delivering superior comfort with its natural elasticity and pressure-relieving properties. Comparing both, EVA foam tends to be denser and more supportive for structured cushioning, while latex foam emphasizes plush comfort and enhanced airflow for cooler seating experiences.
Durability and Longevity
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior durability and resistance to compression set compared to latex foam, making it ideal for cushions requiring long-lasting support and shape retention. Latex foam, while providing excellent comfort and natural elasticity, tends to wear down faster under high-use conditions due to its lower resistance to moisture and microbial degradation. EVA foam's enhanced wear resistance and ability to maintain cushioning properties over time make it the preferred choice for applications prioritizing longevity and sustained performance.
Allergen and Health Considerations
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is hypoallergenic and resistant to dust mites and mold, making it suitable for individuals with allergies or asthma. Latex foam, while naturally antimicrobial and breathable, may trigger allergic reactions in people sensitive to natural latex proteins. Choosing EVA foam minimizes allergen exposure, whereas latex foam offers health benefits only if the user has no latex allergy concerns.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is a petroleum-based material with limited biodegradability, contributing to long-term environmental pollution. Latex foam, derived from natural rubber, is biodegradable and renewable, offering a more sustainable option for cushioning with reduced carbon footprint. Choosing latex foam supports eco-friendly manufacturing practices and waste reduction compared to EVA foam's higher reliance on non-renewable resources and complex recycling processes.
Cost Differences and Affordability
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam generally offers a more affordable option for cushions compared to latex foam due to lower production costs and widespread availability. Latex foam, known for its natural origin and durability, typically commands a higher price because of its complex manufacturing process and eco-friendly properties. Choosing EVA foam can reduce upfront expenses while latex foam represents a long-term investment with enhanced comfort and longevity.
Common Applications in Cushions
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is widely used in cushions for sports equipment, footwear insoles, and outdoor seating due to its excellent shock absorption, water resistance, and durability. Latex foam is favored in high-end mattresses, ergonomic chairs, and premium pillows because of its natural elasticity, breathability, and hypoallergenic properties. Both materials serve specialized roles in cushioning, with EVA providing robust support and latex foam delivering superior comfort and resilience.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Needs
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers excellent durability and water resistance, making it ideal for outdoor cushions and high-traffic areas, while latex foam provides superior breathability and natural elasticity, perfect for indoor cushions requiring enhanced comfort and hypoallergenic properties. EVA foam's dense structure ensures long-lasting support but may lack the softness of latex, which adapts to body contours for pressure relief and temperature regulation. Selecting the right foam depends on prioritizing either EVA's resilience and moisture resistance or latex's comfort and eco-friendly benefits to suit specific cushion applications and user preferences.
Infographic: Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam vs Latex foam for Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com