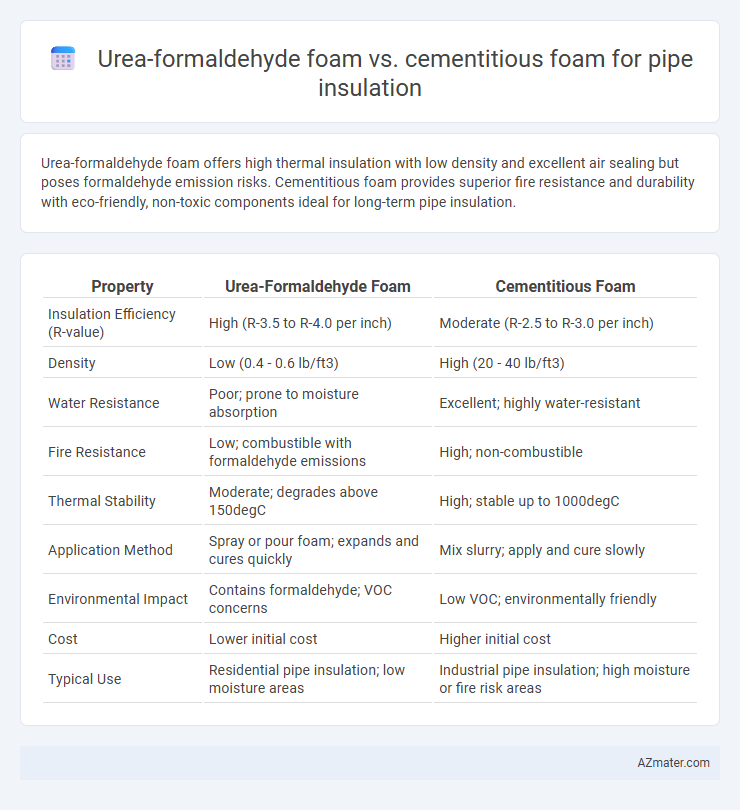
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers high thermal insulation with low density and excellent air sealing but poses formaldehyde emission risks. Cementitious foam provides superior fire resistance and durability with eco-friendly, non-toxic components ideal for long-term pipe insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Urea-Formaldehyde Foam | Cementitious Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation Efficiency (R-value) | High (R-3.5 to R-4.0 per inch) | Moderate (R-2.5 to R-3.0 per inch) |
| Density | Low (0.4 - 0.6 lb/ft3) | High (20 - 40 lb/ft3) |
| Water Resistance | Poor; prone to moisture absorption | Excellent; highly water-resistant |
| Fire Resistance | Low; combustible with formaldehyde emissions | High; non-combustible |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate; degrades above 150degC | High; stable up to 1000degC |
| Application Method | Spray or pour foam; expands and cures quickly | Mix slurry; apply and cure slowly |
| Environmental Impact | Contains formaldehyde; VOC concerns | Low VOC; environmentally friendly |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Typical Use | Residential pipe insulation; low moisture areas | Industrial pipe insulation; high moisture or fire risk areas |
Introduction to Pipe Insulation Materials
Pipe insulation materials such as urea-formaldehyde foam and cementitious foam serve to enhance energy efficiency and prevent heat loss in plumbing and HVAC systems. Urea-formaldehyde foam offers superior thermal resistance and lightweight properties, making it ideal for indoor applications where moisture control is critical. Cementitious foam provides excellent fire resistance and durability, suitable for industrial environments with higher temperature demands.
Overview of Urea-Formaldehyde Foam
Urea-formaldehyde foam is a lightweight, rigid insulation material commonly used in pipe insulation due to its excellent thermal resistance and moisture resistance properties. It offers superior heat retention compared to cementitious foam, with a typical R-value ranging from 4 to 5 per inch, making it energy efficient for maintaining pipe temperatures. The foam's closed-cell structure also provides good sound insulation and resistance to mold growth, making it suitable for both residential and commercial applications.
Overview of Cementitious Foam
Cementitious foam is a lightweight, non-combustible insulation material that provides excellent thermal and acoustic properties for pipe insulation in industrial and commercial applications. Its composition primarily includes cement, water, and aerating agents, resulting in a rigid, durable foam that resists moisture, fire, and chemical degradation, making it suitable for harsh environments. Unlike urea-formaldehyde foam, cementitious foam does not emit harmful gases and offers superior fire resistance, enhancing safety and longevity in pipe insulation systems.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers superior thermal insulation with lower thermal conductivity values, typically around 0.02 to 0.03 W/m*K, providing efficient heat retention for pipe insulation applications. Cementitious foam, while more fire-resistant and durable, exhibits higher thermal conductivity in the range of 0.05 to 0.08 W/m*K, resulting in comparatively reduced insulating performance. The choice between these materials hinges on balancing insulation efficiency against structural and fire safety requirements in industrial piping systems.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers moderate moisture resistance but is more prone to degradation and mold growth when exposed to prolonged damp conditions, reducing its durability in wet environments. Cementitious foam provides superior moisture resistance due to its non-organic composition, maintaining structural integrity and insulating properties even under high humidity or water exposure. The enhanced durability of cementitious foam makes it the preferred choice for long-term pipe insulation in environments susceptible to moisture infiltration.
Fire Resistance and Safety Properties
Urea-formaldehyde foam provides effective thermal insulation but has limited fire resistance, often releasing toxic gases such as formaldehyde when exposed to high temperatures. Cementitious foam offers superior fire resistance due to its non-combustible, inorganic composition, significantly reducing the risk of fire propagation along pipes. Safety properties favor cementitious foam for pipe insulation in environments requiring enhanced fire protection and minimal toxic emissions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Urea-formaldehyde foam insulation releases low levels of formaldehyde, a volatile organic compound (VOC) contributing to indoor air pollution and potential health risks, whereas cementitious foam is free from such harmful emissions, enhancing its environmental safety. Cementitious foam uses non-toxic, mineral-based materials with higher fire resistance and better recyclability, promoting sustainability through reduced environmental footprint and longer lifespan. The carbon footprint of cementitious foam is generally lower due to fewer chemical additives and the use of abundant natural resources, making it a more eco-friendly choice for pipe insulation.
Installation Process and Practicality
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers a lighter, faster installation process due to its spray-foam application that expands to fill voids, making it ideal for irregular pipe shapes and tight spaces. Cementitious foam requires mixing and manual application, resulting in longer curing times but provides superior fire resistance and durability. In terms of practicality, urea-formaldehyde foam is preferred for quick retrofits and minimal downtime, whereas cementitious foam is better suited for long-term industrial use in high-temperature environments.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Urea-formaldehyde foam generally offers lower initial material and installation costs compared to cementitious foam, making it a budget-friendly choice for pipe insulation in residential and light commercial applications. Cementitious foam, while more expensive upfront due to higher material density and specialized application processes, provides superior durability and fire resistance, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Evaluating lifecycle cost analysis reveals that urea-formaldehyde is cost-effective for short-term projects, whereas cementitious foam yields better economic value in industrial settings with stringent safety and longevity requirements.
Application Suitability and Recommendations
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers excellent thermal insulation and moisture resistance, making it ideal for indoor pipe insulation in dry environments. Cementitious foam provides superior fire resistance and durability, suitable for outdoor or industrial pipe insulation exposed to harsh conditions. For optimal results, choose urea-formaldehyde foam in controlled indoor settings and cementitious foam where fire safety and mechanical protection are critical.
Infographic: Urea-formaldehyde foam vs Cementitious foam for Pipe insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com