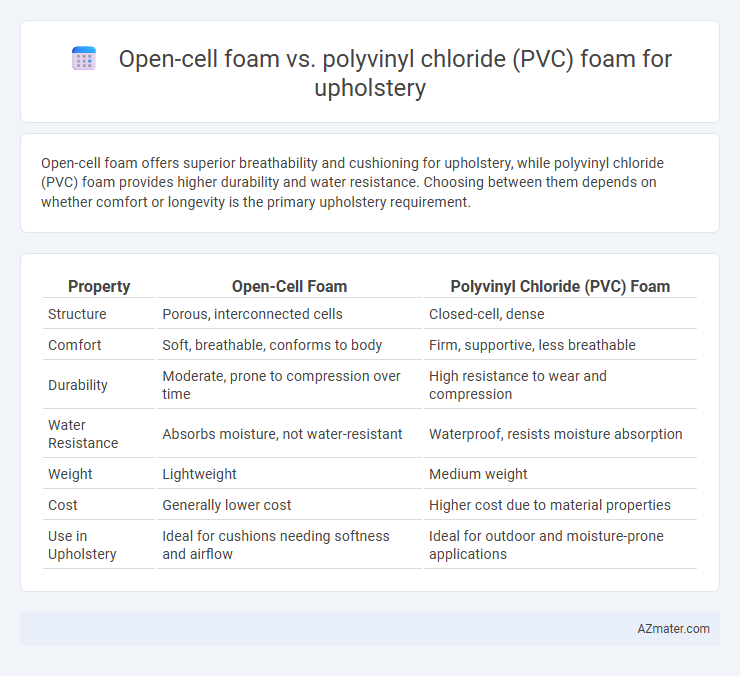
Open-cell foam offers superior breathability and cushioning for upholstery, while polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides higher durability and water resistance. Choosing between them depends on whether comfort or longevity is the primary upholstery requirement.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Open-Cell Foam | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Porous, interconnected cells | Closed-cell, dense |
| Comfort | Soft, breathable, conforms to body | Firm, supportive, less breathable |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to compression over time | High resistance to wear and compression |
| Water Resistance | Absorbs moisture, not water-resistant | Waterproof, resists moisture absorption |
| Weight | Lightweight | Medium weight |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to material properties |
| Use in Upholstery | Ideal for cushions needing softness and airflow | Ideal for outdoor and moisture-prone applications |
Introduction to Upholstery Foam Materials
Open-cell foam offers superior breathability and cushioning, making it ideal for upholstery projects requiring comfort and airflow. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides enhanced durability, water resistance, and easy maintenance, suited for heavy-use or outdoor furniture applications. Choosing between open-cell foam and PVC foam depends on factors like comfort, durability, and environmental exposure in upholstery design.
What is Open-Cell Foam?
Open-cell foam is a type of polyurethane foam characterized by interconnected pores that allow air and moisture to pass through, making it highly breathable and soft. In upholstery, this foam offers superior comfort and cushioning due to its flexible, lightweight structure, but it is less dense and provides lower support compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam. Unlike PVC foam, which is closed-cell, water-resistant, and more rigid, open-cell foam is preferred for applications requiring enhanced airflow and softer cushioning.
Understanding Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) foam is a closed-cell material known for its durability, water resistance, and chemical stability, making it ideal for upholstery in environments exposed to moisture or heavy use. Unlike open-cell foam, PVC foam provides excellent structural support and resistance to compression, contributing to longer-lasting furniture cushioning. Its lightweight nature combined with easy maintenance and resistance to mold and mildew enhances the overall performance and lifespan of upholstered products.
Key Differences Between Open-Cell and PVC Foam
Open-cell foam offers superior breathability and softness due to its porous structure, making it ideal for comfort-focused upholstery applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, on the other hand, provides higher durability, water resistance, and structural rigidity, suitable for heavy-use or outdoor furniture. The key differences lie in their density, moisture absorption, and lifespan, with open-cell foam being lighter and more flexible, while PVC foam excels in strength and longevity.
Comfort and Support Comparison
Open-cell foam offers superior breathability and cushioning, providing a soft, plush feel ideal for upholstery that prioritizes comfort. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, being denser and more rigid, delivers enhanced support and durability, making it suitable for furniture requiring firmer seating and longer-lasting resilience. The choice between open-cell and PVC foam hinges on balancing the need for softness and airflow versus structural support and longevity in upholstered furniture.
Durability and Lifespan
Open-cell foam offers superior breathability and comfort but tends to have lower durability and a shorter lifespan compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, which is denser and more resistant to wear, moisture, and UV damage. PVC foam is highly favored in upholstery for its ability to maintain shape and structural integrity over extended periods, making it ideal for high-traffic furniture. Longevity of PVC foam typically surpasses open-cell foam by several years, contributing to reduced maintenance and replacement costs in commercial and residential applications.
Moisture Resistance and Breathability
Open-cell foam offers superior breathability and allows moisture to evaporate quickly, reducing the risk of mold and mildew in upholstery applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides excellent moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, preventing water absorption but limiting airflow. Choosing between open-cell foam and PVC foam depends on the balance needed between ventilation and moisture barrier properties for the specific upholstery use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Open-cell foam, made primarily from polyurethane, offers better biodegradability compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) foam, which contains chlorine compounds that complicate recycling and release toxic chemicals during disposal. PVC foam production involves high energy consumption and emits harmful dioxins, negatively impacting air quality and ecosystem health. Choosing open-cell foam for upholstery supports lower environmental footprints and aligns with growing sustainability standards in the furniture industry.
Cost Considerations for Upholstery Projects
Open-cell foam typically offers a lower initial cost compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, making it a budget-friendly option for upholstery projects with moderate use requirements. PVC foam, while more expensive upfront, provides better durability and resistance to moisture, which can reduce long-term replacement and maintenance costs in high-traffic or humid environments. Selecting between these materials depends on balancing immediate budget constraints and expected lifespan and performance needs of the upholstery.
Which Foam is Best for Your Upholstery Needs?
Open-cell foam offers superior breathability and cushioning, making it ideal for upholstery requiring softness and airflow, while polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides greater durability, water resistance, and structural support. For furniture subjected to heavy use or exposed to moisture, PVC foam is the best choice due to its resilience and easy maintenance. Conversely, open-cell foam is preferred for applications prioritizing comfort and ventilation, such as seat cushions and backrests.
Infographic: Open-cell foam vs Polyvinyl chloride foam for Upholstery
 azmater.com
azmater.com