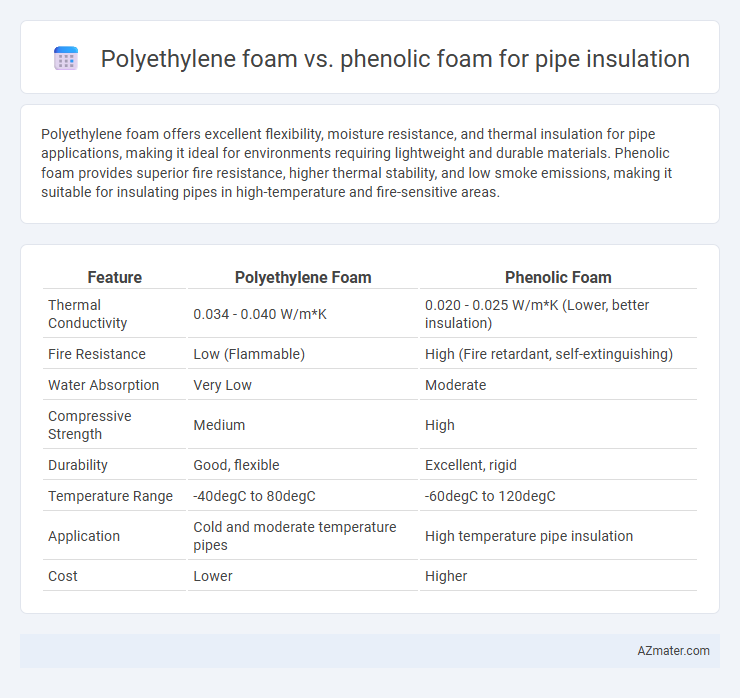
Polyethylene foam offers excellent flexibility, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation for pipe applications, making it ideal for environments requiring lightweight and durable materials. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance, higher thermal stability, and low smoke emissions, making it suitable for insulating pipes in high-temperature and fire-sensitive areas.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyethylene Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.034 - 0.040 W/m*K | 0.020 - 0.025 W/m*K (Lower, better insulation) |
| Fire Resistance | Low (Flammable) | High (Fire retardant, self-extinguishing) |
| Water Absorption | Very Low | Moderate |
| Compressive Strength | Medium | High |
| Durability | Good, flexible | Excellent, rigid |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 80degC | -60degC to 120degC |
| Application | Cold and moderate temperature pipes | High temperature pipe insulation |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Pipe Insulation Materials
Polyethylene foam and phenolic foam are prominent materials used for pipe insulation due to their distinct thermal and physical properties. Polyethylene foam offers excellent flexibility, moisture resistance, and effective thermal insulation with an R-value typically ranging from 3.6 to 4.2 per inch, making it suitable for general plumbing and HVAC applications. Phenolic foam stands out for its superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and higher compressive strength, with R-values around 4.2 to 4.5 per inch, ideal for industrial and high-temperature insulation needs.
Overview of Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam is a lightweight, closed-cell insulation material known for its excellent moisture resistance and thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for pipe insulation in both residential and commercial applications. Its flexibility allows for easy installation around pipes of various diameters, while its resistance to chemicals and UV degradation extends its durability in diverse environments. Compared to phenolic foam, polyethylene foam offers superior impact resistance and is less brittle, though it may have a lower maximum temperature tolerance.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a rigid, closed-cell insulation material known for its superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and excellent thermal performance, making it ideal for pipe insulation in high-temperature and fire-sensitive environments. Its low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.020-0.025 W/m*K, ensures efficient heat retention and energy savings compared to polyethylene foam, which has higher flammability and thermal conductivity. Phenolic foam's dimensional stability and resistance to moisture absorption further enhance its suitability for industrial and commercial pipe insulation applications.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Polyethylene foam offers excellent thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity typically around 0.035 W/m*K, making it effective against heat loss in pipe insulation. Phenolic foam exhibits superior thermal resistance, with thermal conductivity values as low as 0.020 W/m*K, providing enhanced insulation performance in high-temperature applications. The lower thermal conductivity of phenolic foam results in better energy efficiency and reduced heat transfer compared to polyethylene foam in pipe insulation systems.
Moisture Resistance: Polyethylene vs. Phenolic
Polyethylene foam offers superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, effectively preventing water absorption and maintaining insulation performance in damp environments. Phenolic foam, while providing excellent thermal insulation, is more susceptible to moisture penetration because of its open-cell composition, which can lead to reduced insulating efficiency and potential material degradation over time. Selecting polyethylene foam for pipe insulation is advantageous in applications requiring long-term moisture resistance and durability against water exposure.
Fire Safety and Smoke Toxicity
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance compared to polyethylene foam, exhibiting low flame spread and self-extinguishing properties critical for pipe insulation in fire-sensitive environments. Phenolic foam produces significantly lower smoke density and reduced toxic gas emissions, such as carbon monoxide and hydrogen cyanide, enhancing occupant safety during a fire event. In contrast, polyethylene foam tends to burn readily, generating high levels of dense smoke and toxic fumes, making it less suitable for applications where fire safety and smoke toxicity are prioritized.
Installation and Flexibility Considerations
Polyethylene foam offers superior flexibility, making it easier to install around curved pipes and irregular shapes without requiring special tools or adhesives. Phenolic foam is more rigid and brittle, demanding precise cutting and careful handling during installation to avoid cracking or damage. The lightweight nature and compressibility of polyethylene foam contribute to faster installation times and adaptability in confined spaces compared to the more rigid and less forgiving phenolic foam.
Longevity and Durability
Polyethylene foam offers excellent longevity and durability for pipe insulation due to its high resistance to moisture, chemicals, and physical impact, making it ideal for environments prone to abrasion or mechanical stress. Phenolic foam excels in fire resistance and thermal stability, maintaining its insulating properties over prolonged exposure to high temperatures, which enhances its service life in applications requiring stringent fire codes. While polyethylene foam provides greater flexibility and resilience against physical wear, phenolic foam is superior in maintaining structural integrity and insulation efficiency in harsh thermal conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene foam, derived from petrochemicals, has lower thermal insulation properties but is recyclable and less harmful to the environment compared to phenolic foam, which contains formaldehyde and produces toxic gases during combustion. Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and insulation performance but poses higher environmental risks due to its chemical composition and challenges in recycling. Sustainable pipe insulation solutions prioritize materials like polyethylene foam for their lower carbon footprint and ease of end-of-life management.
Cost Analysis and Economic Factors
Polyethylene foam generally offers a lower initial cost compared to phenolic foam, making it a more budget-friendly choice for pipe insulation in large-scale projects. Phenolic foam, despite its higher upfront price, provides better thermal insulation and fire resistance, which can lead to long-term savings in energy costs and enhanced safety compliance. Evaluating lifecycle costs, including installation, maintenance, and energy efficiency, is crucial for determining the most cost-effective insulation material in specific industrial applications.
Infographic: Polyethylene foam vs Phenolic foam for Pipe insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com