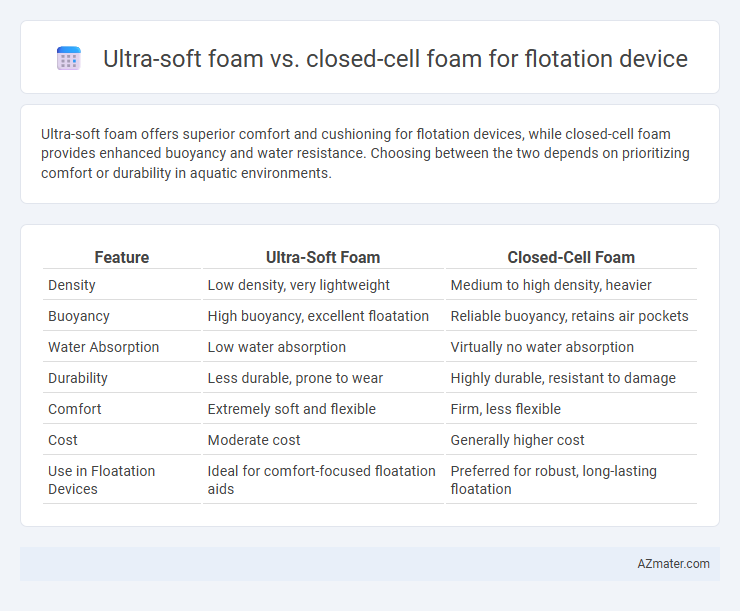
Ultra-soft foam offers superior comfort and cushioning for flotation devices, while closed-cell foam provides enhanced buoyancy and water resistance. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing comfort or durability in aquatic environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-Soft Foam | Closed-Cell Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low density, very lightweight | Medium to high density, heavier |
| Buoyancy | High buoyancy, excellent floatation | Reliable buoyancy, retains air pockets |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption | Virtually no water absorption |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to wear | Highly durable, resistant to damage |
| Comfort | Extremely soft and flexible | Firm, less flexible |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Generally higher cost |
| Use in Floatation Devices | Ideal for comfort-focused floatation aids | Preferred for robust, long-lasting floatation |
Introduction: Understanding Floatation Device Materials
Ultra-soft foam offers exceptional comfort and buoyancy due to its low density and high flexibility, making it ideal for prolonged wear in flotation devices. Closed-cell foam provides superior water resistance and durability by preventing water absorption, enhancing safety and longevity in aquatic environments. Selecting the right foam material depends on balancing comfort, buoyancy, and water resistance requirements for specific flotation applications.
What is Ultra-Soft Foam?
Ultra-soft foam is a highly compressible, lightweight material commonly used in flotation devices for its exceptional comfort and buoyancy. This foam type features an open-cell structure that allows air permeability, enhancing softness while maintaining sufficient flotation support in water. In contrast to closed-cell foam, ultra-soft foam provides better cushioning but may absorb water over time, impacting long-term buoyancy.
What is Closed-Cell Foam?
Closed-cell foam is a type of foam characterized by tightly packed cells that are completely enclosed and not interconnected, making it highly water-resistant and buoyant, ideal for flotation devices. Its dense structure prevents water absorption, ensuring durability and consistent performance in marine environments. Compared to ultra-soft foam, closed-cell foam offers superior rigidity and support, enhancing safety and reliability in flotation applications.
Buoyancy Comparison: Ultra-Soft vs Closed-Cell Foam
Closed-cell foam exhibits higher buoyancy than ultra-soft foam due to its dense, air-trapped structure that resists water absorption and maintains flotation over time. Ultra-soft foam, while comfortable and flexible, tends to absorb water more easily, reducing its buoyant effectiveness in prolonged use. For floatation devices prioritizing consistent lift and durability, closed-cell foam remains the superior choice.
Comfort and Flexibility: User Experience Differences
Ultra-soft foam offers superior cushioning and conforms closely to the body, enhancing overall comfort for prolonged use in floatation devices. Closed-cell foam provides greater structural support and rigidity, resulting in less flexibility but improved buoyancy and durability. Users often prefer ultra-soft foam for activities requiring extended wear, while closed-cell foam suits scenarios demanding stability and resistance to water absorption.
Durability and Longevity of Foam Types
Closed-cell foam offers superior durability and longevity compared to ultra-soft foam due to its dense, water-resistant structure that resists compression and damage over time. Ultra-soft foam, while comfortable and lightweight, tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to water and repeated mechanical stress, leading to reduced buoyancy and effectiveness. For flotation devices requiring long-term reliability, closed-cell foam remains the preferred choice for maintaining consistent performance and durability.
Water Absorption and Maintenance Needs
Ultra-soft foam typically exhibits higher water absorption due to its open-cell structure, necessitating more frequent drying and maintenance to prevent mold and degradation. Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance by preventing water ingress, resulting in lower maintenance requirements and enhanced durability for flotation devices. Choosing closed-cell foam reduces long-term upkeep and maintains buoyancy more effectively in aquatic environments.
Safety Standards and Certifications
Ultra-soft foam used in flotation devices is engineered to meet stringent safety standards such as ISO 12402, ensuring high buoyancy and impact absorption for enhanced user protection. Closed-cell foam, widely certified under US Coast Guard and CE regulations, offers superior water resistance and durability, preventing water absorption that could compromise flotation performance. Both foam types undergo rigorous testing for buoyancy, compressive strength, and toxicity, aligning with international certification requirements to guarantee safety and reliability in aquatic environments.
Ideal Applications: Choosing the Right Foam
Ultra-soft foam excels in comfort-focused flotation devices due to its exceptional cushioning and flexibility, making it ideal for personal flotation devices worn for extended periods such as life jackets and pool floats. Closed-cell foam offers superior buoyancy and water resistance, making it the preferred choice for rescue devices, kayaks, and rigid floatation aids where durability and minimal water absorption are critical. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing comfort needs with performance requirements in marine safety and recreational equipment.
Conclusion: Which Foam is Best for Your Floatation Device?
Ultra-soft foam excels in comfort and flexibility, making it ideal for floatation devices prioritizing user experience and prolonged wear. Closed-cell foam offers superior buoyancy, water resistance, and durability, ensuring reliable floatation and longevity in various water conditions. Choosing between these foams depends on whether comfort or maximum buoyancy and durability are the primary needs for your floatation device.
Infographic: Ultra-soft foam vs Closed-cell foam for Floatation device
 azmater.com
azmater.com