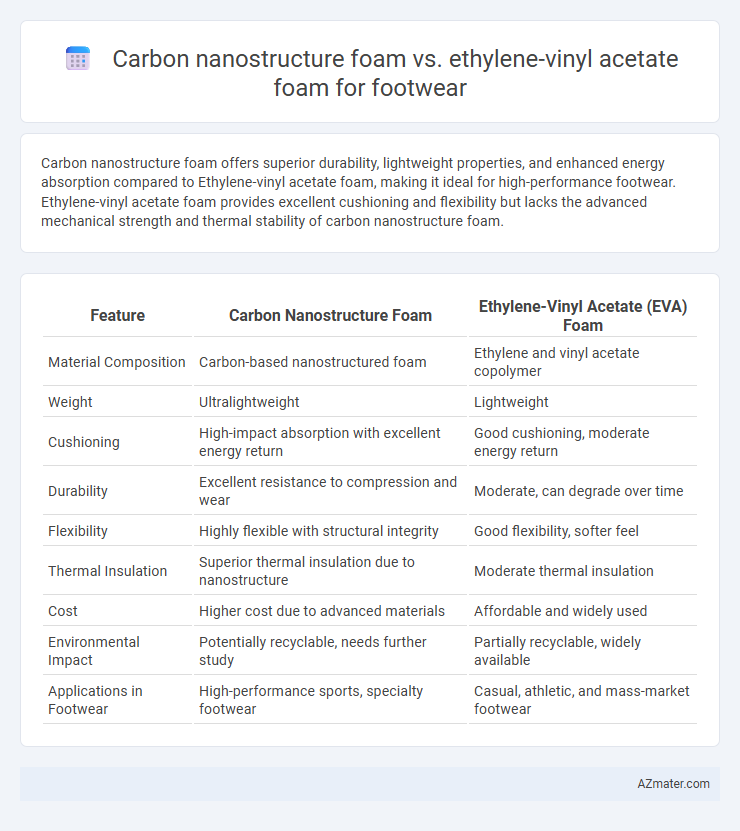
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior durability, lightweight properties, and enhanced energy absorption compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam, making it ideal for high-performance footwear. Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam provides excellent cushioning and flexibility but lacks the advanced mechanical strength and thermal stability of carbon nanostructure foam.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Carbon Nanostructure Foam | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Carbon-based nanostructured foam | Ethylene and vinyl acetate copolymer |
| Weight | Ultralightweight | Lightweight |
| Cushioning | High-impact absorption with excellent energy return | Good cushioning, moderate energy return |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to compression and wear | Moderate, can degrade over time |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible with structural integrity | Good flexibility, softer feel |
| Thermal Insulation | Superior thermal insulation due to nanostructure | Moderate thermal insulation |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced materials | Affordable and widely used |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially recyclable, needs further study | Partially recyclable, widely available |
| Applications in Footwear | High-performance sports, specialty footwear | Casual, athletic, and mass-market footwear |
Introduction to Advanced Footwear Foams
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior mechanical strength, thermal insulation, and lightweight properties compared to traditional Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, revolutionizing advanced footwear technology. The enhanced durability and energy return of carbon nanostructure foam improve performance and comfort in high-impact activities. EVA foam remains widely used for its cost-effectiveness and cushioning but lacks the advanced structural benefits provided by carbon nanostructure foams in modern footwear design.
What is Carbon Nanostructure Foam?
Carbon nanostructure foam is an advanced material composed of carbon-based nanoscale frameworks that provide exceptional strength, lightweight properties, and superior energy absorption. Its unique porous architecture enhances cushioning, durability, and thermal insulation, making it ideal for high-performance footwear applications. Compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, carbon nanostructure foam offers improved mechanical resilience and better impact resistance, contributing to enhanced comfort and longevity in footwear products.
Understanding Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is a lightweight, flexible material widely used in footwear for its excellent cushioning, shock absorption, and durability. Its closed-cell structure provides superior water resistance and energy return, enhancing comfort and performance in athletic and casual shoes. Compared to carbon nanostructure foam, EVA offers cost-effectiveness and proven wear resistance, making it a preferred choice for midsoles and insoles in various types of footwear.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability Comparison
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, offering higher tensile strength and enhanced resistance to wear and tear. Its nano-reinforced matrix provides exceptional durability under repetitive stress, making it ideal for high-performance footwear applications. EVA foam, while lightweight and flexible, tends to degrade faster with prolonged use and exhibits lower compressive strength relative to carbon nanostructure foam.
Cushioning and Comfort: User Experience Insights
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior cushioning properties in footwear, offering enhanced shock absorption and energy return compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam. Users report improved comfort with carbon nanostructure foam due to its lightweight design and adaptive support, reducing foot fatigue during prolonged wear. EVA foam remains popular for its affordability and adequate comfort but may lack the advanced responsiveness and durability of carbon-based foams in high-performance applications.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior breathability and moisture management in footwear by enabling enhanced air circulation through its porous, nano-engineered framework, effectively reducing foot sweat and odor. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, while lightweight and cushioning, exhibits lower moisture-wicking properties due to its closed-cell structure, which can trap heat and moisture. Consequently, carbon nanostructure foam provides a more comfortable, dry environment for prolonged wear, making it optimal for high-performance athletic footwear applications.
Weight and Flexibility Analysis
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits significantly lower density compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, resulting in lighter footwear applications that enhance wearer comfort and reduce fatigue. Its unique nanostructured morphology provides superior flexibility and resilience, allowing for better energy absorption and improved foot mobility during dynamic activities. EVA foam, while flexible, tends to be denser and less responsive, making carbon nanostructure foam a preferred choice for advanced, lightweight footwear designs emphasizing performance and durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon nanostructure foam in footwear offers superior durability and lightweight properties while exhibiting increased recyclability compared to traditional ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam. EVA foam, though widely used, is derived from non-renewable petroleum resources and presents challenges in biodegradability and environmental pollution during production and disposal. The integration of carbon nanostructures can reduce material usage and extend product lifespan, enhancing sustainability by minimizing waste and carbon footprint in the footwear industry.
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
Carbon nanostructure foam, known for its superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced durability, typically incurs higher manufacturing costs due to complex production processes and scarce raw materials. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam remains widely available and cost-effective, making it the preferred choice in mass-market footwear due to its balance of cushioning, flexibility, and affordability. Market availability heavily favors EVA foam, supported by established supply chains and extensive commercialization, whereas carbon nanostructure foam is largely restricted to niche or high-performance footwear segments due to limited scalability and higher price points.
Future Trends in Footwear Foam Materials
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior strength-to-weight ratio, enhanced thermal conductivity, and improved durability compared to traditional ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, driving its adoption in advanced footwear applications. Innovations in nanomaterial integration and bio-based composites are expected to accelerate, promoting more sustainable, high-performance foams that enhance comfort and energy return. The footwear industry is increasingly investing in research on carbon-based foams to meet rising demands for lightweight, resilient, and eco-friendly materials in athletic and casual shoes.
Infographic: Carbon nanostructure foam vs Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam for Footwear
 azmater.com
azmater.com