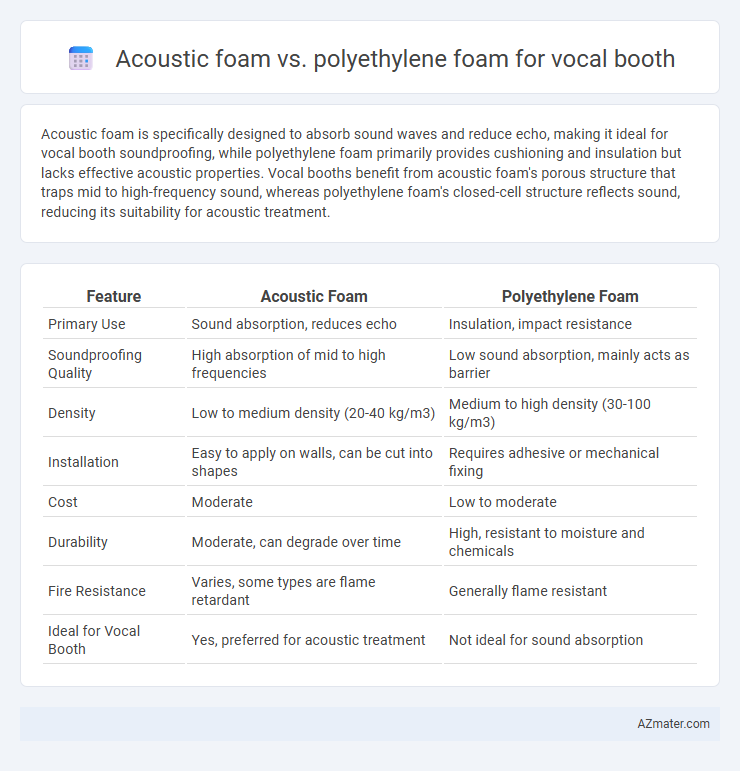
Acoustic foam is specifically designed to absorb sound waves and reduce echo, making it ideal for vocal booth soundproofing, while polyethylene foam primarily provides cushioning and insulation but lacks effective acoustic properties. Vocal booths benefit from acoustic foam's porous structure that traps mid to high-frequency sound, whereas polyethylene foam's closed-cell structure reflects sound, reducing its suitability for acoustic treatment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Acoustic Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Sound absorption, reduces echo | Insulation, impact resistance |
| Soundproofing Quality | High absorption of mid to high frequencies | Low sound absorption, mainly acts as barrier |
| Density | Low to medium density (20-40 kg/m3) | Medium to high density (30-100 kg/m3) |
| Installation | Easy to apply on walls, can be cut into shapes | Requires adhesive or mechanical fixing |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Durability | Moderate, can degrade over time | High, resistant to moisture and chemicals |
| Fire Resistance | Varies, some types are flame retardant | Generally flame resistant |
| Ideal for Vocal Booth | Yes, preferred for acoustic treatment | Not ideal for sound absorption |
Introduction: Acoustic Foam vs Polyethylene Foam for Vocal Booths
Acoustic foam offers superior sound absorption with its open-cell structure, effectively reducing reflections and echo in vocal booths. Polyethylene foam, being denser and closed-cell, provides excellent insulation but limited acoustic treatment properties. Choosing the right foam depends on prioritizing sound control accuracy versus thermal and impact insulation in vocal booth design.
Overview of Acoustic Foam Properties
Acoustic foam, typically made from open-cell polyurethane or melamine, offers superior sound absorption by trapping air within its porous structure, effectively reducing mid to high-frequency noise and minimizing echo in vocal booths. Its lightweight and flexible nature allows for easy installation and customization, enhancing speech clarity and recording quality. Polyethylene foam, with a closed-cell structure, provides limited sound absorption but excels in durability and moisture resistance, making it less effective for acoustic treatment compared to specialized acoustic foam.
Overview of Polyethylene Foam Properties
Polyethylene foam offers exceptional durability, high impact resistance, and excellent moisture resistance, making it a practical choice for vocal booth construction where longevity and environmental factors are concerns. Its closed-cell structure provides moderate sound absorption but is less effective in controlling mid to high-frequency reflections compared to acoustic foam designed explicitly for sound treatment. The foam's lightweight and easy-to-cut nature facilitate custom booth designs, though its acoustic performance is generally inferior to specialized acoustic foam products aimed at optimizing vocal clarity.
Sound Absorption Capabilities Compared
Acoustic foam offers superior sound absorption due to its open-cell structure that traps and dissipates sound waves effectively, making it ideal for vocal booths. Polyethylene foam, with its closed-cell configuration, provides limited sound absorption and is better suited for impact cushioning rather than noise control. For vocal booth applications requiring optimal reduction of mid to high-frequency sound reflections, acoustic foam delivers significantly better performance.
Noise Isolation and Reduction Efficiency
Acoustic foam excels in high-frequency noise absorption, making it ideal for controlling reflections and reducing echo within vocal booths, while polyethylene foam offers superior low-frequency noise isolation due to its dense, closed-cell structure. The open-cell design of acoustic foam enhances diffusion and sound absorption but lacks the mass needed for effective soundproofing, whereas polyethylene foam's thickness and density contribute to better blocking of external noise. For optimal vocal booth performance, combining acoustic foam's reflective treatment with polyethylene foam's solid noise isolation can achieve balanced reduction across a broad frequency spectrum.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Acoustic foam, typically made from polyurethane or melamine, offers straightforward installation with adhesive sprays or Velcro strips and conforms well to irregular surfaces, enhancing sound absorption in vocal booths. Polyethylene foam, being denser and more rigid, requires mechanical fasteners or custom cutting for precise fitting, which can complicate installation but provides superior durability and shape retention. Flexibility in acoustic foam allows easier customization for varied booth sizes and shapes, while polyethylene foam's rigidity may limit adjustments but contributes to long-term structural integrity.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Acoustic foam offers superior sound absorption and fire resistance but tends to degrade faster with prolonged exposure to humidity and UV light, requiring occasional replacement. Polyethylene foam shows excellent durability against moisture, chemicals, and physical wear, making it easier to maintain in high-humidity environments. Maintenance for acoustic foam involves careful cleaning with low moisture, while polyethylene foam can withstand more aggressive cleaning methods without compromising structural integrity.
Cost Analysis: Acoustic vs Polyethylene Foam
Acoustic foam typically costs more per square foot than polyethylene foam due to its specialized sound-absorbing properties tailored for vocal booths. Polyethylene foam offers a more budget-friendly option with moderate acoustic benefits but may require higher thickness or quantity to achieve similar soundproofing levels, increasing overall expenses. Evaluating long-term investment in sound quality versus initial cost helps determine the most cost-effective choice for vocal booth acoustic treatment.
Suitability for Different Vocal Booth Applications
Acoustic foam, specifically open-cell polyurethane or melamine variants, excels in vocal booths by absorbing mid to high-frequency sound waves, enhancing speech clarity and reducing echo, making it ideal for recording studios and podcasting setups. Polyethylene foam, often closed-cell, provides superior sound isolation and bass trapping due to its density but offers less absorption of higher frequencies, making it more suitable for vocal booths in environments with heavy external noise or requiring bass control. Choosing between the two depends on the vocal booth's acoustic goals: acoustic foam optimizes voice clarity and reflection control, while polyethylene foam prioritizes sound isolation and low-frequency management.
Conclusion: Which Foam is Best for Vocal Booths?
Acoustic foam is best for vocal booths due to its superior sound absorption properties, effectively reducing echo and minimizing sound reflections across mid to high frequencies. Polyethylene foam, while more durable and moisture-resistant, lacks the porous structure needed for significant acoustic treatment, making it less suitable for vocal clarity enhancement. For optimal vocal booth performance, acoustic foam provides better acoustic insulation and sound quality improvement compared to polyethylene foam.
Infographic: Acoustic foam vs Polyethylene foam for Vocal booth
 azmater.com
azmater.com