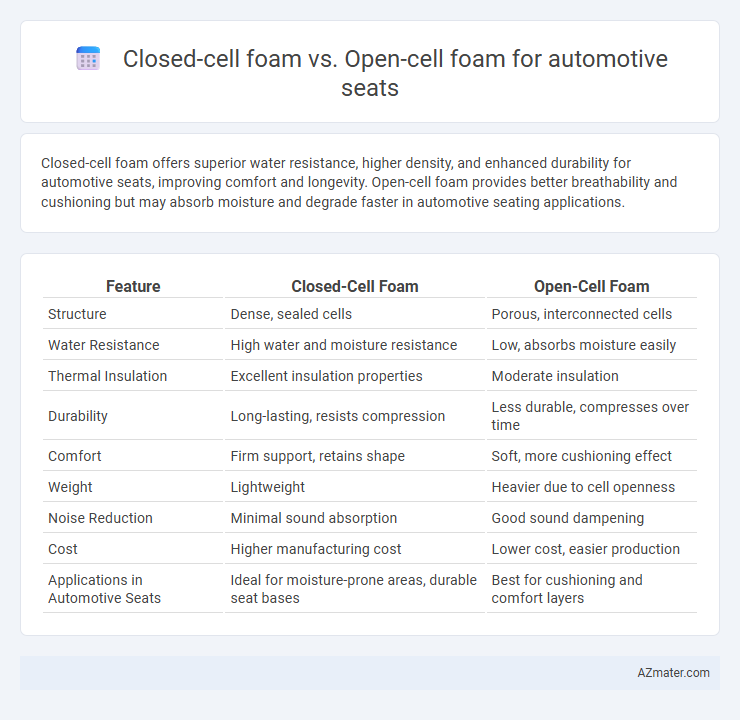
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance, higher density, and enhanced durability for automotive seats, improving comfort and longevity. Open-cell foam provides better breathability and cushioning but may absorb moisture and degrade faster in automotive seating applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Closed-Cell Foam | Open-Cell Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Dense, sealed cells | Porous, interconnected cells |
| Water Resistance | High water and moisture resistance | Low, absorbs moisture easily |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent insulation properties | Moderate insulation |
| Durability | Long-lasting, resists compression | Less durable, compresses over time |
| Comfort | Firm support, retains shape | Soft, more cushioning effect |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to cell openness |
| Noise Reduction | Minimal sound absorption | Good sound dampening |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower cost, easier production |
| Applications in Automotive Seats | Ideal for moisture-prone areas, durable seat bases | Best for cushioning and comfort layers |
Overview of Closed-Cell vs Open-Cell Foam
Closed-cell foam features a dense structure with sealed air pockets, providing superior water resistance and durability for automotive seats, while open-cell foam has interconnected pores that offer better breathability and cushioning comfort. Closed-cell foam typically offers higher thermal insulation and support, making it ideal for heavy-duty use and improved vehicle longevity. Open-cell foam excels in providing lightweight cushioning and enhanced pressure distribution, contributing to overall driver and passenger comfort during extended travel.
Structural Differences Between Foam Types
Closed-cell foam features a dense, airtight structure with cells encapsulated by rigid walls, providing superior water resistance and higher durability for automotive seat applications. Open-cell foam consists of interconnected, porous cells allowing air and moisture to pass through, resulting in softer cushioning but reduced structural integrity. These fundamental structural differences impact seat comfort, weight, and longevity in vehicle interiors.
Cushioning and Comfort Comparison
Closed-cell foam offers superior cushioning and higher density, providing better support and durability for automotive seats, especially under prolonged use. Open-cell foam delivers enhanced breathability and softer comfort, allowing air circulation to reduce heat buildup, ideal for passengers seeking plushness. The choice depends on balancing firm support from closed-cell foam with the lightweight, breathable properties of open-cell foam to optimize overall seating comfort.
Weight and Density Considerations
Closed-cell foam used in automotive seats typically has a higher density and greater weight compared to open-cell foam, providing enhanced durability and resistance to moisture. Open-cell foam offers a lighter weight alternative with lower density, improving overall vehicle fuel efficiency but potentially sacrificing some structural support and longevity. Weight and density considerations play a crucial role in balancing comfort, safety, and performance in automotive seat design.
Durability and Longevity in Automotive Seats
Closed-cell foam exhibits superior durability and longevity in automotive seats due to its dense structure that resists moisture absorption, compression, and deformation over time. Open-cell foam, while providing better breathability and comfort, tends to degrade faster under constant pressure and exposure to humidity, leading to reduced seat support and lifespan. Automotive manufacturers often prefer closed-cell foam for long-lasting seat cushions that maintain shape and performance in demanding environments.
Moisture and Water Resistance Properties
Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture and water resistance properties for automotive seats, as its tightly packed cells prevent water absorption and inhibit mold growth. Open-cell foam, with its interconnected porous structure, tends to absorb moisture, leading to faster degradation and reduced durability in humid or wet conditions. Choosing closed-cell foam enhances seat longevity by maintaining structural integrity and resisting mold and mildew formation in automotive environments.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Closed-cell foam offers superior thermal insulation for automotive seats due to its dense structure that minimizes heat transfer and prevents moisture absorption. Open-cell foam, with its porous architecture, allows more air circulation, leading to lower insulation efficiency and increased heat retention by the body rather than blocking external temperature changes. The higher R-value of closed-cell foam makes it the preferred choice for maintaining consistent seat temperature under varying climate conditions.
Noise and Vibration Dampening Abilities
Closed-cell foam offers superior noise and vibration dampening in automotive seats due to its dense, impermeable structure that effectively blocks sound transmission and absorbs vibrations. Open-cell foam, while more breathable and softer, allows for greater sound passage and less effective vibration absorption, making it less ideal for reducing cabin noise. Selecting closed-cell foam enhances acoustic comfort and minimizes road noise and mechanical vibrations for a quieter ride.
Cost Implications and Budget Analysis
Closed-cell foam offers higher durability and moisture resistance for automotive seats but comes at a higher material and manufacturing cost compared to open-cell foam. Open-cell foam delivers better breathability and comfort at a lower price point, making it a budget-friendly option for mass production. Analyzing total cost of ownership, including lifespan and replacement frequency, favors closed-cell foam for premium vehicles while open-cell foam suits economy and mid-range models.
Best Applications for Each Foam Type in Automotive Seating
Closed-cell foam offers superior support and moisture resistance, making it ideal for automotive seat cushions where durability and firmness are critical, especially in high-use or outdoor vehicles. Open-cell foam provides excellent breathability and comfort, suitable for luxury car seats and areas requiring enhanced ventilation and softness. Choosing between closed-cell and open-cell foam depends on the desired balance of support, comfort, and environmental exposure in automotive seating applications.
Infographic: Closed-cell foam vs Open-cell foam for Automotive seat
 azmater.com
azmater.com