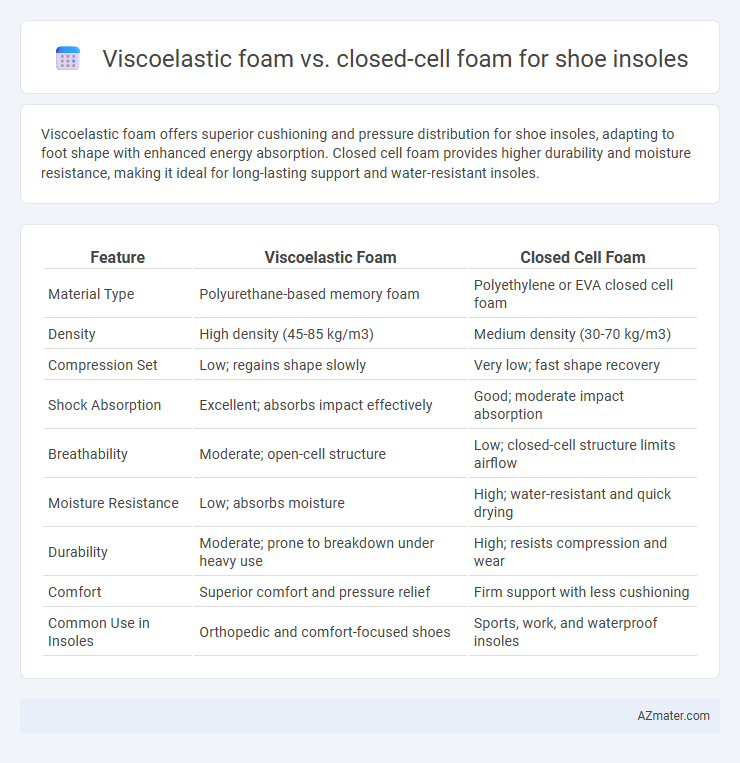
Viscoelastic foam offers superior cushioning and pressure distribution for shoe insoles, adapting to foot shape with enhanced energy absorption. Closed cell foam provides higher durability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for long-lasting support and water-resistant insoles.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Viscoelastic Foam | Closed Cell Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyurethane-based memory foam | Polyethylene or EVA closed cell foam |
| Density | High density (45-85 kg/m3) | Medium density (30-70 kg/m3) |
| Compression Set | Low; regains shape slowly | Very low; fast shape recovery |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent; absorbs impact effectively | Good; moderate impact absorption |
| Breathability | Moderate; open-cell structure | Low; closed-cell structure limits airflow |
| Moisture Resistance | Low; absorbs moisture | High; water-resistant and quick drying |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to breakdown under heavy use | High; resists compression and wear |
| Comfort | Superior comfort and pressure relief | Firm support with less cushioning |
| Common Use in Insoles | Orthopedic and comfort-focused shoes | Sports, work, and waterproof insoles |
Introduction to Foam Types for Shoe Insoles
Viscoelastic foam, commonly known as memory foam, offers superior cushioning by closely conforming to the foot's shape, providing pressure relief and enhanced comfort in shoe insoles. Closed cell foam features a dense, sealed structure that resists water absorption and provides firm support and durability, making it ideal for high-impact activities. Selecting between these foam types depends on the desired balance of softness, support, moisture resistance, and durability for optimal footwear performance.
What is Viscoelastic Foam?
Viscoelastic foam, commonly known as memory foam, is a high-density polyurethane material designed to contour to the shape of the foot, providing personalized cushioning and pressure relief. Unlike closed cell foam, which consists of tightly packed cells that trap air to offer firm support and durability, viscoelastic foam absorbs impact and reduces stress on joints through slow recovery and enhanced energy dispersion. Its viscoelastic properties make it ideal for shoe insoles aimed at improving comfort, shock absorption, and reducing fatigue during prolonged wear.
What is Closed Cell Foam?
Closed cell foam is a dense, impermeable material characterized by its tightly packed cells that trap gas, providing excellent cushioning and water resistance for shoe insoles. Its structure delivers firm support and durability, making it ideal for shock absorption and moisture protection in footwear applications. Unlike viscoelastic foam, closed cell foam offers less contouring but superior resilience and longevity under repeated pressure.
Comfort and Cushioning Comparison
Viscoelastic foam offers superior comfort and cushioning for shoe insoles due to its ability to contour to the foot's shape and absorb impact evenly, reducing pressure points and enhancing shock absorption. Closed cell foam provides firmer support with higher durability and moisture resistance but lacks the adaptive cushioning properties of viscoelastic foam. For users prioritizing all-day comfort and pressure relief, viscoelastic foam is the preferred choice, while closed cell foam suits those needing more structural support and longevity.
Support and Stability Differences
Viscoelastic foam in shoe insoles provides superior cushioning with excellent energy absorption, adapting to the foot's shape for personalized support but may offer less firm stability compared to closed cell foam. Closed cell foam insoles deliver enhanced structural support and durability due to their dense, rigid composition, ensuring better stability during high-impact activities. The choice between these foams depends on whether priority is comfort and shock absorption or firm support and long-lasting stability.
Durability and Longevity
Viscoelastic foam insoles offer excellent durability due to their high resilience and ability to regain shape after compression, providing long-lasting comfort and support. Closed cell foam insoles resist moisture and maintain structural integrity over time, enhancing longevity by preventing degradation from sweat and environmental factors. Viscoelastic foam excels in shock absorption and pressure distribution, while closed cell foam outperforms in durability against water damage and wear.
Moisture and Odor Resistance
Closed cell foam excels in moisture resistance due to its dense, non-porous structure that prevents water absorption, making it highly effective at keeping feet dry. Viscoelastic foam, while offering superior cushioning and pressure relief, tends to retain moisture because of its open-cell design, which can promote odor development over time. Selecting closed cell foam for shoe insoles enhances odor control by minimizing bacterial growth linked to trapped moisture.
Breathability and Temperature Regulation
Viscoelastic foam excels in breathability and temperature regulation due to its open-cell structure, allowing better air circulation and moisture wicking inside shoe insoles. Closed cell foam, characterized by its dense and compact structure, offers minimal airflow, often trapping heat and reducing comfort during prolonged wear. Choosing viscoelastic foam enhances shoe insole performance by maintaining cooler, dryer conditions critical for foot health.
Cost and Value Considerations
Viscoelastic foam offers superior cushioning and pressure relief, often preferred for high-end shoe insoles despite a higher initial cost compared to closed cell foam. Closed cell foam provides better durability and moisture resistance at a lower price point, making it a cost-effective choice for budget-conscious consumers. The value of viscoelastic foam lies in enhanced comfort and support, while closed cell foam excels in longevity and affordability.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Needs
Viscoelastic foam offers superior pressure relief and contouring by conforming to the foot's shape, ideal for those seeking enhanced comfort and shock absorption. Closed cell foam provides greater durability and moisture resistance, making it suitable for high-impact activities and long-lasting support. Selecting the right foam depends on prioritizing cushioning and adaptability versus firmness and longevity in your shoe insole.
Infographic: Viscoelastic foam vs Closed cell foam for Shoe insole
 azmater.com
azmater.com