Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior thermal conductivity and mechanical strength compared to Polyisocyanurate foam, enhancing roof insulation efficiency and durability. Its lightweight, high porosity structure provides improved energy savings and fire resistance over traditional Polyisocyanurate insulation.
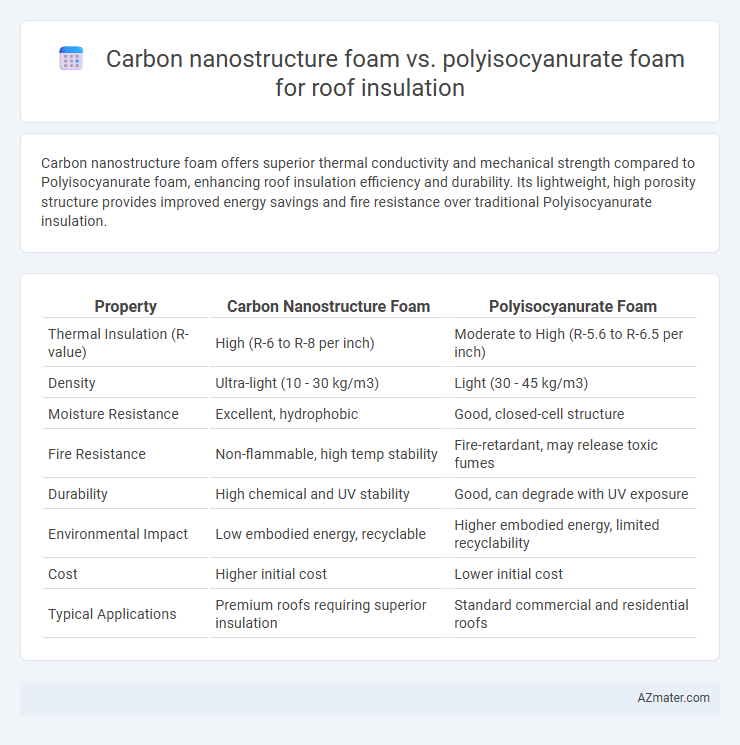
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Nanostructure Foam | Polyisocyanurate Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation (R-value) | High (R-6 to R-8 per inch) | Moderate to High (R-5.6 to R-6.5 per inch) |
| Density | Ultra-light (10 - 30 kg/m3) | Light (30 - 45 kg/m3) |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent, hydrophobic | Good, closed-cell structure |
| Fire Resistance | Non-flammable, high temp stability | Fire-retardant, may release toxic fumes |
| Durability | High chemical and UV stability | Good, can degrade with UV exposure |
| Environmental Impact | Low embodied energy, recyclable | Higher embodied energy, limited recyclability |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Typical Applications | Premium roofs requiring superior insulation | Standard commercial and residential roofs |
Introduction to Roof Insulation Materials
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior thermal conductivity and enhanced durability compared to traditional Polyisocyanurate foam, making it an innovative choice for roof insulation. Polyisocyanurate foam remains widely used due to its high R-value per inch and cost-effectiveness in reducing heat transfer. The integration of carbon nanostructures improves insulation performance by increasing thermal resistance and structural stability, directly impacting energy efficiency in building envelopes.
Overview of Carbon Nanostructure Foam
Carbon nanostructure foam offers exceptional thermal insulation properties due to its high surface area and low density, making it a cutting-edge material for roof insulation. Its unique interconnected pore structure enhances thermal resistance while providing superior mechanical strength and durability compared to traditional foams like polyisocyanurate. This innovative foam also exhibits excellent fire resistance and moisture stability, contributing to long-term energy efficiency and reduced maintenance costs in roofing applications.
Properties of Polyisocyanurate Foam
Polyisocyanurate foam offers superior thermal insulation with a high R-value, typically ranging from 6 to 7 per inch, making it highly effective for roof insulation. It exhibits excellent fire resistance due to its closed-cell structure and inherent fire-retardant properties. Additionally, Polyisocyanurate foam has low moisture absorption and strong dimensional stability, ensuring long-term durability in roofing applications.
Thermal Efficiency Comparison
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior thermal conductivity properties compared to polyisocyanurate foam, offering enhanced insulation performance with lower thermal bridging. The nanostructured foam's thermal resistance (R-value) per inch significantly surpasses that of conventional polyisocyanurate, enabling thinner insulation layers while maintaining optimal energy efficiency. This advanced material reduces heat transfer more effectively, contributing to improved roof thermal management and longer-term energy savings.
Fire Resistance and Safety Aspects
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior fire resistance compared to polyisocyanurate foam due to its inherent thermal stability and low combustibility, significantly reducing the risk of flame spread in roof insulation applications. Polyisocyanurate foam, while offering good insulation properties, tends to produce toxic smoke and gases when exposed to high temperatures, raising safety concerns during fire incidents. The advanced nanostructured composition of carbon foam enhances its ability to act as a thermal barrier, improving overall building safety and compliance with stringent fire codes.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior mechanical strength due to its high tensile strength and elasticity, making it highly resistant to compression and deformation under heavy loads. In contrast, polyisocyanurate foam provides good compressive strength but tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and moisture, affecting its long-term durability. The nanostructured foam's enhanced durability and resistance to environmental stressors offer extended service life for roof insulation applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior environmental sustainability due to its enhanced thermal insulation properties, which reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions over the building lifecycle. Its production involves advanced nanomaterials with lower carbon footprints compared to conventional polyisocyanurate foam, which relies on petrochemical-based components and blowing agents contributing to ozone depletion and global warming potential. Life cycle assessments indicate that carbon nanostructure foam improves energy efficiency sustainably, promoting longer roof lifespan and minimizing environmental impact in comparison to traditional polyisocyanurate insulation.
Installation Processes and Practical Considerations
Carbon nanostructure foam offers a lightweight, highly durable insulation option with a straightforward spray or panel installation that conforms well to complex roof geometries, enhancing thermal performance and reducing labor time. Polyisocyanurate foam typically requires rigid panels or spray foam application, demanding precise cutting and fitting to avoid thermal bridging and ensure optimal R-value, which can increase installation complexity and costs. Practical considerations include carbon nanostructure foam's superior fire resistance and moisture barrier properties, while polyisocyanurate foam is widely available and cost-effective but may require additional vapor retarders in humid climates.
Cost Analysis and Economic Viability
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior thermal insulation with a higher initial cost compared to conventional polyisocyanurate foam, which remains more cost-effective for large-scale roof insulation projects. The enhanced energy efficiency of carbon nanostructure foam can lead to reduced heating and cooling expenses, potentially offsetting its upfront investment over time. Economic viability favors polyisocyanurate foam for budget-conscious applications, while carbon nanostructure foam suits scenarios prioritizing long-term energy savings and performance.
Future Trends in Roof Insulation Technologies
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior thermal conductivity and enhanced structural strength compared to traditional polyisocyanurate foam, positioning it as a promising material in future roof insulation technologies. Innovations in nanomaterials enable carbon-based foams to deliver better energy efficiency, fire resistance, and longevity while reducing environmental impact. Emerging trends focus on integrating these advanced foams with smart insulation systems and sustainable building practices to meet increasingly stringent energy codes and reduce carbon footprints in construction.
Infographic: Carbon nanostructure foam vs Polyisocyanurate foam for Roof insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com