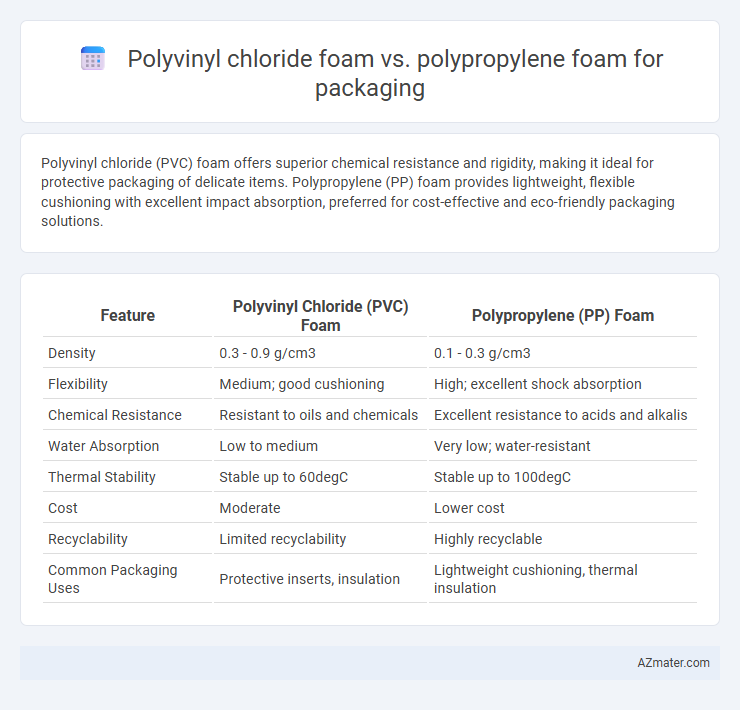
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior chemical resistance and rigidity, making it ideal for protective packaging of delicate items. Polypropylene (PP) foam provides lightweight, flexible cushioning with excellent impact absorption, preferred for cost-effective and eco-friendly packaging solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam | Polypropylene (PP) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.3 - 0.9 g/cm3 | 0.1 - 0.3 g/cm3 |
| Flexibility | Medium; good cushioning | High; excellent shock absorption |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to oils and chemicals | Excellent resistance to acids and alkalis |
| Water Absorption | Low to medium | Very low; water-resistant |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 60degC | Stable up to 100degC |
| Cost | Moderate | Lower cost |
| Recyclability | Limited recyclability | Highly recyclable |
| Common Packaging Uses | Protective inserts, insulation | Lightweight cushioning, thermal insulation |
Introduction to Polymer Foams in Packaging
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam and polypropylene (PP) foam are widely utilized polymer foams in packaging due to their lightweight structure and excellent cushioning properties. PVC foam offers superior chemical resistance and rigidity, making it ideal for protective packaging requiring durability, while PP foam is valued for its higher impact absorption and recyclability, supporting sustainable packaging solutions. Both materials provide thermal insulation and moisture resistance, with applications tailored to product sensitivity and environmental considerations in packaging design.
Material Composition: Polyvinyl Chloride vs. Polypropylene
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam consists primarily of polymerized vinyl chloride, featuring a dense molecular structure that offers excellent rigidity and chemical resistance, making it ideal for protective packaging applications requiring durability. Polypropylene (PP) foam is composed of polymerized propylene units, characterized by a lower density and higher flexibility, providing superior cushioning and impact absorption for delicate items. The differing molecular compositions result in PVC foam being more resistant to chemicals and moisture, while PP foam excels in lightweight and shock-absorbing properties.
Manufacturing Processes of PVC and PP Foams
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam manufacturing involves polymerization followed by chemical or physical foaming techniques, where gas is introduced under specific temperature and pressure conditions to create a lightweight, closed-cell structure ideal for protective packaging. Polypropylene (PP) foam is produced through melt blending and gas injection, often utilizing supercritical CO2 or nitrogen to expand the polymer melt, resulting in a flexible, durable foam with excellent impact resistance. Both processes require precise control over temperature, pressure, and foaming agents to optimize the cellular structure, density, and mechanical properties tailored for packaging applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits higher mechanical strength and superior impact resistance compared to polypropylene (PP) foam, making it ideal for protective packaging of heavy or fragile items. PVC foam's rigidity and tensile strength offer enhanced durability under compressive stress, whereas PP foam tends to be more flexible but less load-bearing. For applications requiring robust cushioning and long-term structural integrity, PVC foam outperforms PP foam in mechanical performance metrics.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits superior chemical resistance to acids, bases, and hydrocarbons compared to polypropylene (PP) foam, making it suitable for packaging sensitive and corrosive materials. PP foam offers better thermal resistance, maintaining structural integrity at higher temperatures up to 100degC, whereas PVC foam softens around 80degC. The choice between PVC and PP foam for packaging depends on the specific storage conditions, balancing chemical exposure risks against temperature tolerances.
Weight and Density Differences
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam typically has a higher density, ranging from 33 to 300 kg/m3, making it heavier compared to polypropylene (PP) foam, which usually falls between 15 to 100 kg/m3. This density difference impacts packaging weight significantly, with PP foam offering lighter weight solutions that enhance shipping efficiency and reduce transportation costs. The denser PVC foam provides superior rigidity and cushioning, while the lighter PP foam excels in applications where weight reduction is crucial without compromising basic protection.
Cost Effectiveness in Packaging Applications
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers moderate cost-effectiveness with good durability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for protective packaging that requires cushioning and long-term stability. Polypropylene (PP) foam generally provides superior cost efficiency due to its lightweight nature, recyclability, and excellent impact absorption, especially for high-volume packaging applications. For budget-conscious packaging solutions emphasizing environmental benefits, PP foam often outperforms PVC foam in overall value and lifecycle costs.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam has a higher environmental impact compared to polypropylene (PP) foam due to the release of toxic chemicals like dioxins during its production and disposal, contributing to pollution and health risks. Polypropylene foam is more eco-friendly, being chemically inert and producing fewer emissions throughout its lifecycle, making it a preferred choice for sustainable packaging. In terms of recyclability, PP foam is easier to recycle because it is widely accepted in recycling facilities and can be reprocessed into new products, whereas PVC foam recycling is limited and often costly due to the material's complex chemical structure.
Suitability for Specific Packaging Needs
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers excellent chemical resistance and durability, making it suitable for packaging fragile items requiring strong impact absorption and protection against moisture. Polypropylene (PP) foam excels in lightweight cushioning and superior elasticity, ideal for packaging electronics and lightweight consumer goods needing shock resistance and flexibility. PVC foam is preferred for heavy-duty industrial packaging, while PP foam is favored in consumer-focused applications demanding eco-friendliness and recyclability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam for Packaging
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers excellent rigidity, chemical resistance, and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging and protective applications. Polypropylene (PP) foam provides superior flexibility, lightweight cushioning, and environmental resistance, often preferred for fragile goods and eco-friendly solutions. Selecting the right foam depends on the specific packaging requirements, balancing factors such as weight, impact absorption, and environmental considerations.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride foam vs Polypropylene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com