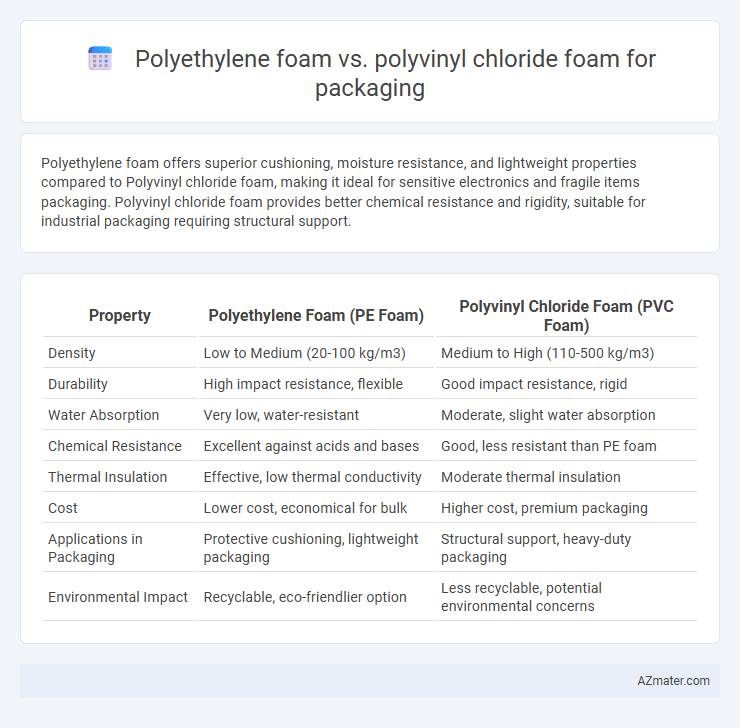
Polyethylene foam offers superior cushioning, moisture resistance, and lightweight properties compared to Polyvinyl chloride foam, making it ideal for sensitive electronics and fragile items packaging. Polyvinyl chloride foam provides better chemical resistance and rigidity, suitable for industrial packaging requiring structural support.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Foam (PE Foam) | Polyvinyl Chloride Foam (PVC Foam) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low to Medium (20-100 kg/m3) | Medium to High (110-500 kg/m3) |
| Durability | High impact resistance, flexible | Good impact resistance, rigid |
| Water Absorption | Very low, water-resistant | Moderate, slight water absorption |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids and bases | Good, less resistant than PE foam |
| Thermal Insulation | Effective, low thermal conductivity | Moderate thermal insulation |
| Cost | Lower cost, economical for bulk | Higher cost, premium packaging |
| Applications in Packaging | Protective cushioning, lightweight packaging | Structural support, heavy-duty packaging |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, eco-friendlier option | Less recyclable, potential environmental concerns |
Introduction to Polyethylene Foam and Polyvinyl Chloride Foam
Polyethylene foam is a lightweight, closed-cell material known for its excellent cushioning, shock absorption, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for protecting delicate items during shipping. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers a rigid, durable structure with enhanced chemical resistance and fire retardant properties, often used for packaging that requires structural support and longevity. Both foams serve distinct purposes in packaging due to their unique physical and chemical characteristics, with polyethylene foam favored for flexible cushioning and PVC foam chosen for its strength and stability.
Chemical Composition and Structure Differences
Polyethylene foam consists of long chains of ethylene monomers, resulting in a non-polar, hydrophobic, and flexible cellular structure that provides excellent cushioning and impact resistance in packaging applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is made from vinyl chloride monomers, incorporating chlorine atoms that create a polar, rigid, and dense matrix with higher chemical resistance and flame retardant properties. The chemical composition differences lead to polyethylene foam's superior elasticity and lightweight nature, whereas PVC foam offers enhanced durability and structural integrity for heavy-duty packaging needs.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyethylene foam exhibits excellent compressive strength and superior impact resistance, making it ideal for cushioning fragile items during shipping. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers higher tensile strength and better dimensional stability, which is advantageous for structural packaging requiring rigidity. Comparing density ranges, polyethylene foam typically varies from 20 to 60 kg/m3, providing flexibility, whereas PVC foam ranges from 80 to 200 kg/m3, delivering firmer mechanical support.
Cushioning and Impact Resistance
Polyethylene foam offers superior cushioning and impact resistance due to its closed-cell structure, effectively absorbing shocks and protecting fragile items during transit. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, while denser and more rigid, provides less flexibility in cushioning but excels in durability and chemical resistance for heavy-duty packaging needs. For packaging applications requiring maximum protection against impact and vibration, polyethylene foam remains the more effective choice.
Weight and Density Analysis
Polyethylene foam typically exhibits a lower density range of 16 to 48 kg/m3 compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, which ranges from 50 to 300 kg/m3, making polyethylene foam significantly lighter for packaging applications. The reduced weight of polyethylene foam contributes to easier handling and lower transportation costs, while its lower density provides cushioning properties ideal for protecting delicate items. In contrast, PVC foam's higher density offers greater rigidity and impact resistance, suitable for packaging heavier or more fragile products requiring enhanced structural support.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene foam offers superior recyclability due to its thermoplastic nature, allowing repeated melting and reforming without significant degradation, which reduces landfill waste. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam poses environmental challenges as it releases harmful dioxins and chlorine compounds during production and incineration, complicating recycling efforts and contributing to pollution. Selecting polyethylene foam for packaging minimizes ecological footprint through easier recycling and less toxic emissions compared to PVC foam's environmental impact.
Cost Considerations in Packaging
Polyethylene foam offers a cost-effective solution for packaging due to its low material and production expenses, making it ideal for bulk shipments and protective cushioning. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam typically incurs higher costs because of its chemical composition and manufacturing complexity, but provides enhanced durability and chemical resistance that may justify the investment for specialized packaging needs. Evaluating the balance between initial material costs and long-term performance helps businesses optimize packaging budgets while maintaining product safety.
Common Packaging Applications
Polyethylene foam is widely used in packaging for cushioning fragile items like electronics and glassware due to its excellent shock absorption and lightweight properties. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides superior chemical resistance and rigidity, making it ideal for protective packaging in industrial and automotive applications. Both materials serve different packaging needs, with polyethylene foam excelling in protective padding and PVC foam preferred for structural support and durability.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Polyethylene foam offers excellent chemical resistance and non-toxicity, making it compliant with FDA regulations for food packaging and safe for various consumer goods. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, while durable, often contains additives like plasticizers and stabilizers that may raise concerns regarding toxicity and environmental impact, complicating regulatory approval for sensitive applications. Choosing polyethylene foam ensures higher safety standards and easier adherence to global regulatory requirements, reducing risks associated with harmful emissions and material leaching.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Polyethylene foam offers superior cushioning, moisture resistance, and lightweight durability, making it ideal for delicate electronics and fragile items during shipping. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides greater rigidity, chemical resistance, and flame retardancy, suitable for heavy-duty packaging that requires structural support and protection against harsh environments. Selecting the right foam depends on product fragility, exposure conditions, and specific packaging requirements to ensure optimal protection and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Polyethylene foam vs Polyvinyl chloride foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com