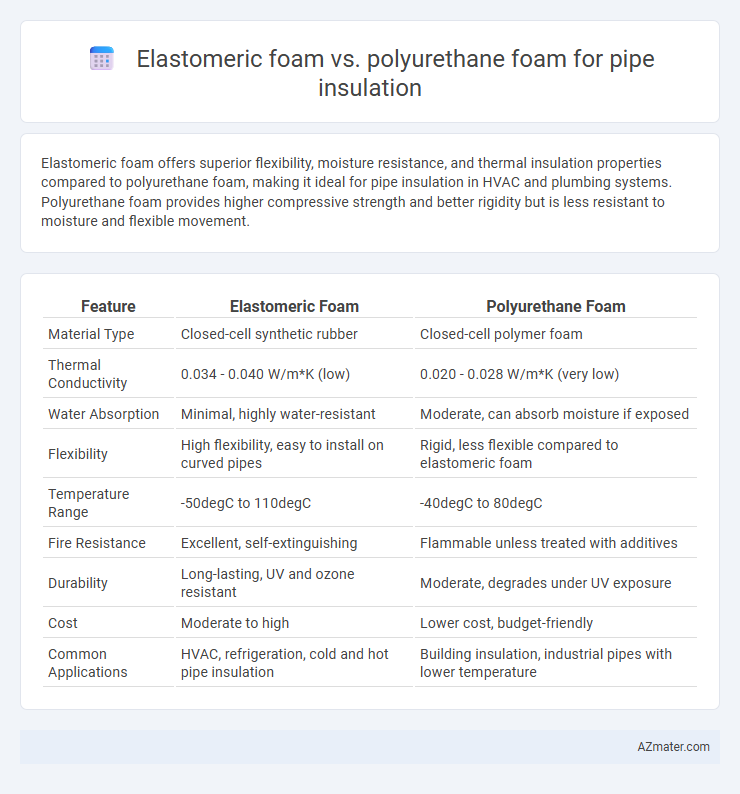
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation properties compared to polyurethane foam, making it ideal for pipe insulation in HVAC and plumbing systems. Polyurethane foam provides higher compressive strength and better rigidity but is less resistant to moisture and flexible movement.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Elastomeric Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Closed-cell synthetic rubber | Closed-cell polymer foam |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.034 - 0.040 W/m*K (low) | 0.020 - 0.028 W/m*K (very low) |
| Water Absorption | Minimal, highly water-resistant | Moderate, can absorb moisture if exposed |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, easy to install on curved pipes | Rigid, less flexible compared to elastomeric foam |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 110degC | -40degC to 80degC |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent, self-extinguishing | Flammable unless treated with additives |
| Durability | Long-lasting, UV and ozone resistant | Moderate, degrades under UV exposure |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Lower cost, budget-friendly |
| Common Applications | HVAC, refrigeration, cold and hot pipe insulation | Building insulation, industrial pipes with lower temperature |
Introduction: Choosing the Right Pipe Insulation
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation, making it ideal for preventing condensation and energy loss in piping systems. Polyurethane foam provides excellent rigidity and high thermal resistance but may lack the flexibility and vapor barrier effectiveness of elastomeric materials. Selecting the right pipe insulation depends on factors such as temperature range, environmental conditions, and application requirements to optimize energy efficiency and system longevity.
Understanding Elastomeric Foam Insulation
Elastomeric foam insulation offers superior flexibility and a closed-cell structure that provides excellent moisture resistance and thermal performance, making it ideal for insulating pipes in HVAC and refrigeration systems. Unlike polyurethane foam, elastomeric foam maintains durability and flexibility across a wide temperature range, reducing the risk of cracking and ensuring long-term insulation efficiency. This material's low thermal conductivity and resistance to mold growth enhance energy savings and protect piping infrastructure from corrosion and condensation.
Overview of Polyurethane Foam Insulation
Polyurethane foam insulation offers high thermal resistance with an R-value typically ranging from 6 to 7 per inch, making it highly effective for pipe insulation in both commercial and industrial applications. Its closed-cell structure provides excellent moisture resistance, reducing the risk of condensation and corrosion on pipe surfaces. Compared to elastomeric foam, polyurethane foam is more rigid and durable, offering superior mechanical strength and long-term performance in harsh environments.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Elastomeric foam offers superior thermal insulation with lower thermal conductivity values, typically around 0.033 to 0.040 W/m*K, compared to polyurethane foam, which ranges from 0.022 to 0.028 W/m*K, making polyurethane foam more effective in reducing heat transfer. Elastomeric insulation excels in moisture resistance and flexibility, enhancing long-term performance in pipe insulation applications, while polyurethane provides higher R-values per inch but may degrade faster in humid environments. Selecting between elastomeric and polyurethane foam should consider thermal conductivities, moisture resistance, and operational temperature ranges to optimize energy efficiency and durability.
Moisture Resistance and Water Vapor Permeability
Elastomeric foam offers superior moisture resistance and low water vapor permeability, preventing condensation and reducing the risk of corrosion under insulation (CUI) in pipe systems. Polyurethane foam, while providing good thermal insulation, generally exhibits higher water vapor permeability, making it less effective in environments with high humidity or potential water exposure. Selecting elastomeric foam for pipe insulation enhances durability and energy efficiency by maintaining a dry insulation layer and minimizing moisture ingress.
Fire Safety and Flame Retardancy
Elastomeric foam offers superior fire safety and flame retardancy compared to polyurethane foam, featuring inherent self-extinguishing properties and low smoke emissions during combustion. Polyurethane foam is more flammable and can release toxic gases when exposed to flames, making it less suitable for applications requiring stringent fire standards. Selecting elastomeric foam for pipe insulation enhances compliance with fire codes such as ASTM E84 and NFPA 286, reducing fire hazards in commercial and industrial settings.
Mechanical Durability and Flexibility
Elastomeric foam offers superior mechanical durability with high resistance to abrasion, tearing, and compression, making it ideal for long-term pipe insulation in demanding environments. It maintains excellent flexibility even at low temperatures, allowing easy installation around complex pipe geometries without cracking. Polyurethane foam, while providing good thermal insulation, is less flexible and more prone to mechanical damage, limiting its effectiveness in applications requiring frequent movement or vibration resistance.
Installation Process and Ease
Elastomeric foam features a flexible, pre-slit design that simplifies wrapping around pipes and requires minimal adhesive, enabling faster and cleaner installation. Polyurethane foam often demands cutting and fitting on-site, sometimes needing additional sealing measures to ensure airtight insulation, which can prolong installation time. The inherent flexibility and lightweight nature of elastomeric foam generally make it easier and more efficient to install compared to rigid polyurethane foam.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Elastomeric foam pipe insulation typically has a higher upfront cost compared to polyurethane foam but offers superior durability, flexibility, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, which reduces maintenance expenses and extends service life. Polyurethane foam insulation is generally less expensive initially but may require more frequent replacement or additional protective measures, increasing long-term costs. Considering ROI, elastomeric foam's lower lifecycle costs and enhanced energy efficiency often lead to greater savings and faster payback despite its higher initial investment.
Applications: Which Foam Suits Your Needs?
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation, making it ideal for plumbing, HVAC, and refrigeration systems exposed to varying temperatures and humidity levels. Polyurethane foam excels in providing higher R-values and rigidity, suitable for insulated pipe systems requiring structural support and lower thermal conductivity. Choosing between elastomeric and polyurethane foam depends on factors like environmental conditions, thermal performance needs, and mechanical durability in your specific pipe insulation application.
Infographic: Elastomeric foam vs Polyurethane foam for Pipe insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com