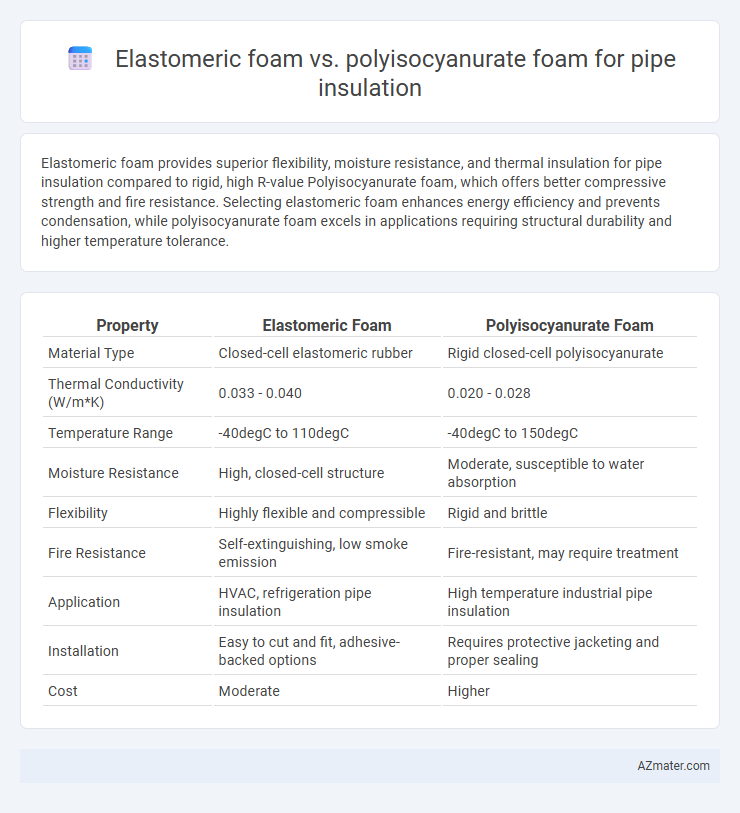
Elastomeric foam provides superior flexibility, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation for pipe insulation compared to rigid, high R-value Polyisocyanurate foam, which offers better compressive strength and fire resistance. Selecting elastomeric foam enhances energy efficiency and prevents condensation, while polyisocyanurate foam excels in applications requiring structural durability and higher temperature tolerance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Elastomeric Foam | Polyisocyanurate Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Closed-cell elastomeric rubber | Rigid closed-cell polyisocyanurate |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | 0.033 - 0.040 | 0.020 - 0.028 |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 110degC | -40degC to 150degC |
| Moisture Resistance | High, closed-cell structure | Moderate, susceptible to water absorption |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and compressible | Rigid and brittle |
| Fire Resistance | Self-extinguishing, low smoke emission | Fire-resistant, may require treatment |
| Application | HVAC, refrigeration pipe insulation | High temperature industrial pipe insulation |
| Installation | Easy to cut and fit, adhesive-backed options | Requires protective jacketing and proper sealing |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Pipe Insulation Materials
Elastomeric foam offers flexible, closed-cell insulation with excellent moisture resistance and thermal performance, making it ideal for piping systems subject to temperature fluctuations and condensation. Polyisocyanurate foam provides rigid, high R-value insulation with superior fire resistance and structural integrity, commonly used in industrial and commercial pipe insulation applications. Selecting between elastomeric and polyisocyanurate foam depends on specific requirements such as flexibility, thermal conductivity, moisture control, and fire safety standards for the piping system.
Overview of Elastomeric Foam
Elastomeric foam is a flexible, closed-cell insulation material primarily made from synthetic rubber, widely used for pipe insulation due to its superior resistance to moisture, vapor permeability, and temperature extremes ranging from -297degF to 220degF (-183degC to 104degC). Its low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.24 to 0.26 Btu*in/hr*ft2*degF (0.034 to 0.037 W/m*K), ensures efficient energy conservation and condensation control in HVAC systems and chilled water piping. Elastomeric foam also offers excellent durability, ease of installation, and resistance to UV radiation and microbial growth compared to rigid Polyisocyanurate foam insulation.
Overview of Polyisocyanurate Foam
Polyisocyanurate foam, commonly abbreviated as PIR, is a rigid closed-cell insulation material known for its high thermal resistance and excellent fire-retardant properties, making it ideal for pipe insulation applications where energy efficiency and safety are priorities. This foam exhibits superior compressive strength and dimensional stability compared to elastomeric foam, enabling it to maintain its insulating performance under mechanical stress and thermal cycling. Its low thermal conductivity and resistance to moisture absorption contribute to reducing heat loss and preventing condensation on pipes, enhancing system longevity and operational efficiency.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Elastomeric foam offers thermal conductivity values typically around 0.035 to 0.040 W/m*K, providing effective insulation for temperatures ranging from -50degC to 105degC. Polyisocyanurate foam demonstrates superior thermal resistance with conductivity as low as 0.020 to 0.025 W/m*K and higher R-values, making it more efficient for high-temperature applications up to 150degC. The lower thermal conductivity of polyisocyanurate foam results in improved energy savings and reduced heat loss compared to elastomeric foam in pipe insulation systems.
Moisture Resistance and Vapor Permeability
Elastomeric foam offers superior moisture resistance and low vapor permeability, making it highly effective in preventing condensation on pipes and maintaining insulation integrity in humid environments. Polyisocyanurate foam, while providing high thermal insulation values, tends to have higher vapor permeability, which can allow moisture infiltration and potential degradation over time. Selecting elastomeric foam ensures enhanced protection against moisture-related damage and extends the lifespan of pipe insulation systems in moisture-prone applications.
Fire Resistance and Safety Considerations
Elastomeric foam and polyisocyanurate foam differ significantly in fire resistance for pipe insulation, with polyisocyanurate offering superior flame retardancy due to its high char formation and low smoke production. Elastomeric foam provides moderate fire resistance but releases more toxic gases when burned, raising safety concerns in confined spaces. Safety considerations favor polyisocyanurate foam in environments requiring strict fire codes and minimal smoke toxicity, while elastomeric foam suits applications needing flexibility and moisture resistance.
Flexibility and Ease of Installation
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility and compressibility, making it easier to install on curved or irregular pipe surfaces compared to polyisocyanurate foam, which is more rigid and brittle. This flexibility reduces the risk of cracks and gaps, enhancing thermal insulation performance and minimizing installation time. Elastomeric foam's lightweight and self-sealing properties further simplify handling and fitting around complex pipe geometries.
Durability and Longevity
Elastomeric foam offers excellent durability with high resistance to moisture, UV exposure, and physical damage, making it ideal for long-term pipe insulation in both indoor and outdoor environments. Polyisocyanurate foam provides superior thermal insulation but can be more susceptible to moisture absorption and degradation over time, potentially shortening its lifespan when exposed to harsh conditions. For applications demanding extended longevity and resilience, elastomeric foam generally outperforms polyisocyanurate foam due to its flexible, closed-cell structure that maintains integrity under fluctuating temperatures and environmental stress.
Cost Analysis and Economic Factors
Elastomeric foam typically incurs higher upfront costs compared to polyisocyanurate foam but offers superior flexibility and long-term durability, reducing replacement and maintenance expenses over time. Polyisocyanurate foam is generally more cost-effective initially due to lower material prices and enhanced thermal resistance, which can lead to energy savings and operational cost reductions. Economic factors such as lifecycle cost analysis, installation complexity, and insulation performance under varying temperature conditions greatly influence the overall cost-efficiency of these materials for pipe insulation.
Application Suitability and Industry Recommendations
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility and excellent thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for chilled water and HVAC piping systems with frequent temperature fluctuations and condensation control requirements. Polyisocyanurate foam, known for its higher R-value per inch and robust compressive strength, suits applications demanding rigid insulation and fire resistance, commonly recommended in industrial and commercial pipe insulation standards. Industry guidelines prioritize elastomeric foam for environments requiring moisture resistance and ease of installation, while polyisocyanurate is preferred in scenarios with stringent energy codes and mechanical protection needs.
Infographic: Elastomeric foam vs Polyisocyanurate foam for Pipe insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com