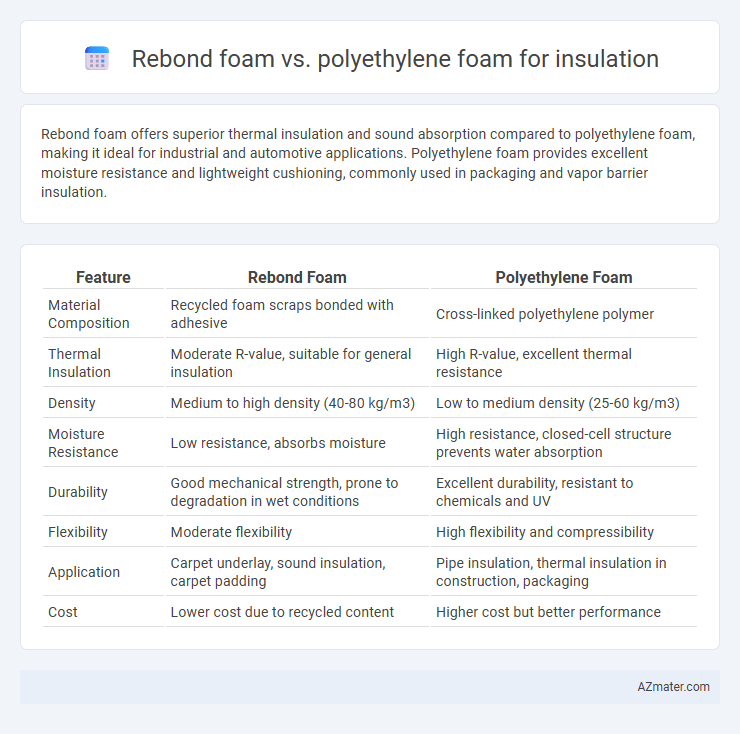
Rebond foam offers superior thermal insulation and sound absorption compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for industrial and automotive applications. Polyethylene foam provides excellent moisture resistance and lightweight cushioning, commonly used in packaging and vapor barrier insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rebond Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Recycled foam scraps bonded with adhesive | Cross-linked polyethylene polymer |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate R-value, suitable for general insulation | High R-value, excellent thermal resistance |
| Density | Medium to high density (40-80 kg/m3) | Low to medium density (25-60 kg/m3) |
| Moisture Resistance | Low resistance, absorbs moisture | High resistance, closed-cell structure prevents water absorption |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength, prone to degradation in wet conditions | Excellent durability, resistant to chemicals and UV |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility and compressibility |
| Application | Carpet underlay, sound insulation, carpet padding | Pipe insulation, thermal insulation in construction, packaging |
| Cost | Lower cost due to recycled content | Higher cost but better performance |
Introduction to Rebond Foam and Polyethylene Foam
Rebond foam, made from recycled foam scraps bonded together, offers high density and excellent thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for soundproofing and cushioning applications. Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell, lightweight material with superior moisture resistance, thermal insulation, and durability, commonly used in packaging and insulation panels. Both materials provide effective insulation, but rebond foam excels in compression resistance, while polyethylene foam is favored for moisture and chemical resistance.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Process
Rebond foam is primarily made from shredded scrap polyurethane foam bonded together using adhesives and high compression, resulting in a dense, resilient material ideal for soundproofing and cushioning. Polyethylene foam is produced through the extrusion of polyethylene resin, creating a closed-cell, lightweight, and moisture-resistant structure well-suited for thermal insulation and impact absorption. The manufacturing process of rebond foam emphasizes recycling and bonding of existing foam scraps, whereas polyethylene foam involves polymer melting and foaming agents to achieve its cellular structure.
Thermal Insulation Properties Compared
Rebond foam, composed of recycled polyurethane scraps, offers effective thermal insulation with an R-value typically ranging from 3.0 to 3.5 per inch, making it suitable for sound absorption and moderate thermal resistance. Polyethylene foam, a closed-cell material, provides superior thermal insulation with an R-value between 4.0 and 5.0 per inch, delivering enhanced moisture resistance and durability in various temperature conditions. The higher R-value and water resistance of polyethylene foam generally make it a better choice for insulation applications requiring long-term thermal performance and environmental protection.
Acoustic Insulation Capabilities
Rebond foam demonstrates superior acoustic insulation capabilities due to its dense structure and ability to absorb sound waves effectively, reducing noise transmission in various environments. Polyethylene foam offers moderate sound dampening but excels more in impact absorption and thermal insulation rather than soundproofing. Choosing rebond foam for acoustic insulation ensures enhanced noise reduction, particularly in commercial and industrial applications requiring robust sound control.
Durability and Longevity
Rebond foam offers superior durability due to its dense structure made from recycled foam scraps, making it resistant to compression and wear over time. Polyethylene foam provides excellent resistance to moisture and chemical damage, contributing to its longevity in insulation applications exposed to harsh environments. Both materials excel in longevity, but rebond foam is preferred for high-impact durability while polyethylene foam is ideal for moisture-prone settings.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Rebond foam offers moderate moisture resistance but tends to absorb water over time, making it less suitable for environments with high humidity or direct exposure to water. Polyethylene foam exhibits superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, preventing water absorption and maintaining insulation performance even in wet conditions. Chemically, polyethylene foam is more resistant to oils, solvents, and acids, whereas rebond foam can degrade or lose integrity when exposed to harsh chemicals.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Rebond foam, made from recycled scrap foam, offers enhanced sustainability by reducing landfill waste and promoting circular economy principles, whereas polyethylene foam relies on petrochemical sources with higher carbon footprints. Both materials provide effective thermal insulation, but rebond foam's use of reclaimed materials significantly lowers environmental impact compared to virgin polyethylene foam production. Lifecycle assessments reveal rebond foam as a greener option, aligning with eco-friendly building standards and reducing resource depletion in insulation applications.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Rebond foam offers superior cost-effectiveness for insulation due to its higher density and durability, which reduces long-term replacement costs compared to polyethylene foam. Although polyethylene foam has a lower upfront price, its inferior thermal resistance and susceptibility to compression can lead to increased energy expenses and maintenance over time. Investing in rebond foam often results in better overall value through enhanced insulation performance and longevity.
Common Applications in Insulation
Rebond foam, composed of recycled foam scraps bonded together, offers excellent sound absorption and compression resistance, making it ideal for acoustic insulation in walls, ceilings, and flooring underlays. Polyethylene foam, known for its closed-cell structure and moisture resistance, is commonly used in pipe insulation, radiant floor heating, and vapor barriers, providing thermal insulation and preventing condensation. Both materials are valued for their durability and energy efficiency in residential, commercial, and industrial insulation applications.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Insulation Needs
Rebond foam offers superior durability and excellent sound absorption, making it ideal for insulation in high-impact environments such as gyms and industrial areas. Polyethylene foam provides outstanding thermal insulation and moisture resistance while being lightweight and easy to install, suitable for residential and light commercial applications. Selecting the right foam depends on factors like required thermal performance, impact resistance, and environmental exposure to optimize insulation efficiency and longevity.
Infographic: Rebond foam vs Polyethylene foam for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com