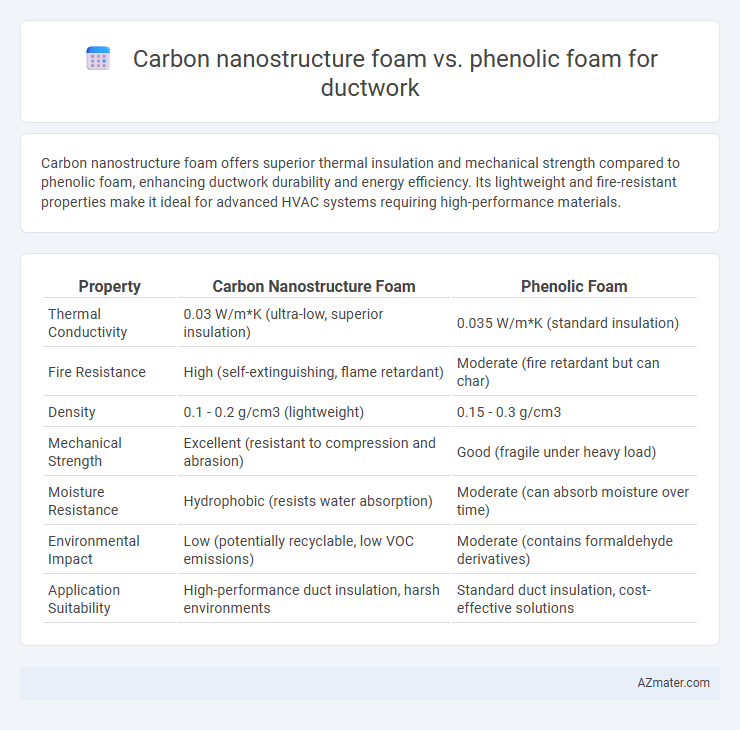
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior thermal insulation and mechanical strength compared to phenolic foam, enhancing ductwork durability and energy efficiency. Its lightweight and fire-resistant properties make it ideal for advanced HVAC systems requiring high-performance materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Nanostructure Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.03 W/m*K (ultra-low, superior insulation) | 0.035 W/m*K (standard insulation) |
| Fire Resistance | High (self-extinguishing, flame retardant) | Moderate (fire retardant but can char) |
| Density | 0.1 - 0.2 g/cm3 (lightweight) | 0.15 - 0.3 g/cm3 |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent (resistant to compression and abrasion) | Good (fragile under heavy load) |
| Moisture Resistance | Hydrophobic (resists water absorption) | Moderate (can absorb moisture over time) |
| Environmental Impact | Low (potentially recyclable, low VOC emissions) | Moderate (contains formaldehyde derivatives) |
| Application Suitability | High-performance duct insulation, harsh environments | Standard duct insulation, cost-effective solutions |
Introduction to Ductwork Insulation Materials
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior thermal conductivity and lightweight properties compared to traditional phenolic foam, making it highly effective for ductwork insulation. Phenolic foam remains popular due to its excellent fire resistance and cost efficiency in HVAC applications. Choosing between these materials depends on factors such as insulation performance requirements, fire safety standards, and budget constraints for ductwork systems.
Overview of Carbon Nanostructure Foam
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits exceptional thermal insulation and mechanical strength due to its porous architecture composed of interconnected carbon nanotubes and graphene networks. Its low density and high thermal stability make it highly suitable for advanced ductwork applications requiring flame resistance and energy efficiency. Compared to traditional phenolic foam, carbon nanostructure foam offers superior durability, lower thermal conductivity, and enhanced chemical resistance, promoting longer service life in HVAC systems.
Phenolic Foam: Properties and Uses
Phenolic foam is a lightweight, rigid insulation material characterized by excellent fire resistance, low smoke emission, and superior thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for ductwork applications. Its closed-cell structure provides high dimensional stability and moisture resistance, enhancing durability in HVAC systems. Phenolic foam's flame-retardant nature and low thermal conductivity significantly improve energy efficiency and safety standards in commercial and industrial duct installations.
Insulation Performance: Thermal Conductivity Comparison
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits significantly lower thermal conductivity, typically around 0.02 W/m*K, compared to phenolic foam which ranges from 0.025 to 0.035 W/m*K, resulting in superior insulation performance for ductwork applications. The nanostructure's ultra-lightweight matrix and high porosity reduce heat transfer more effectively than the conventional phenolic resin matrix. This enhanced thermal resistance improves energy efficiency and temperature control within HVAC systems.
Fire Resistance and Safety Aspects
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior fire resistance compared to phenolic foam due to its enhanced thermal stability and reduced flammability, which lowers the risk of toxic smoke emission during combustion. Phenolic foam, while inherently flame retardant, can release hazardous gases under high temperatures, posing greater safety concerns in ductwork applications. Selecting carbon nanostructure foam for ductwork improves overall fire safety by minimizing flame spread, smoke production, and toxic exposure in building environments.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior moisture resistance compared to phenolic foam, preventing water absorption that can compromise ductwork performance. Its enhanced structural integrity ensures long-term durability under varying environmental conditions while phenolic foam tends to degrade faster when exposed to humidity. Selecting carbon nanostructure foam improves lifespan and reduces maintenance costs for duct systems in moisture-prone settings.
Weight and Structural Impact on Ductwork
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits significantly lower density compared to phenolic foam, resulting in reduced overall ductwork weight and enhanced ease of installation. The superior mechanical strength of carbon nanostructure foam minimizes structural deformation under load, improving duct integrity and longevity. Phenolic foam, while offering fire resistance, tends to add more weight and may require additional support structures to maintain duct stability.
Installation and Handling Considerations
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior lightweight properties and enhanced structural integrity, facilitating easier handling and quicker installation in ductwork applications compared to traditional phenolic foam. Phenolic foam, while effective for thermal insulation, is more brittle and requires careful handling to avoid breakage, potentially increasing installation time and labor costs. The increased durability and flexibility of carbon nanostructure foam reduce the risk of damage during transportation and installation, improving overall project efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior environmental sustainability compared to phenolic foam due to its lightweight nature, which reduces overall material usage and energy consumption during transportation and installation. Phenolic foam, while providing effective insulation, involves the use of formaldehyde-based resins and produces more volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during manufacturing and disposal. The enhanced durability and recyclability of carbon nanostructure foam further minimize landfill waste and lower the carbon footprint associated with ductwork materials.
Cost Analysis and Long-term Value
Carbon nanostructure foam offers higher initial costs compared to phenolic foam but delivers superior thermal insulation and enhanced fire resistance, reducing long-term energy and maintenance expenses in ductwork applications. Phenolic foam remains more affordable upfront, with decent insulation and fire-retardant properties, yet may incur higher replacement or repair costs over time due to lower durability. Evaluating life-cycle costs reveals carbon nanostructure foam provides better value through extended service life and improved performance metrics despite the premium initial investment.
Infographic: Carbon nanostructure foam vs Phenolic foam for Ductwork
 azmater.com
azmater.com