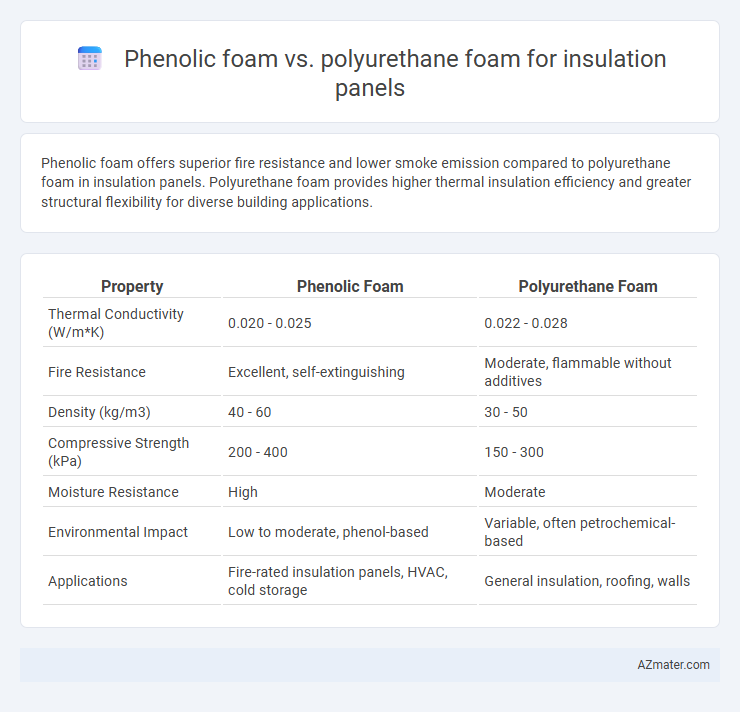
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and lower smoke emission compared to polyurethane foam in insulation panels. Polyurethane foam provides higher thermal insulation efficiency and greater structural flexibility for diverse building applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Phenolic Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | 0.020 - 0.025 | 0.022 - 0.028 |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent, self-extinguishing | Moderate, flammable without additives |
| Density (kg/m3) | 40 - 60 | 30 - 50 |
| Compressive Strength (kPa) | 200 - 400 | 150 - 300 |
| Moisture Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Low to moderate, phenol-based | Variable, often petrochemical-based |
| Applications | Fire-rated insulation panels, HVAC, cold storage | General insulation, roofing, walls |
Introduction to Phenolic and Polyurethane Foams
Phenolic foam is a rigid, closed-cell insulation material known for its excellent fire resistance, low smoke emission, and high thermal performance, typically composed of phenol-formaldehyde resin. Polyurethane foam offers superior thermal insulation and flexibility, created from the reaction between polyols and diisocyanates, often utilized for sealing and insulating applications due to its low thermal conductivity. Both foams serve distinct purposes in insulation panels, with phenolic foam favored for fire safety and polyurethane foam valued for its versatility and moisture resistance.
Overview of Insulation Panel Applications
Phenolic foam insulation panels offer superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and excellent thermal performance, making them ideal for commercial buildings, cold storage, and industrial facilities requiring stringent fire safety standards. Polyurethane foam panels provide high insulation values, moisture resistance, and structural strength, commonly used in residential construction, refrigeration, and HVAC systems. Both foams are versatile in wall, roof, and floor applications, but phenolic foam is preferred where fire safety and smoke control are paramount, while polyurethane excels in applications demanding higher R-values and moisture resistance.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with a lower thermal conductivity typically around 0.020 W/m*K, compared to polyurethane foam which ranges from 0.022 to 0.028 W/m*K, making phenolic panels more effective in minimizing heat transfer. The closed-cell structure of phenolic foam provides better fire resistance and dimensional stability, enhancing long-term insulation performance in building applications. Polyurethane foam, while slightly less efficient thermally, offers greater flexibility and faster curing times, influencing insulation panel selection based on specific project requirements.
Fire Resistance and Safety Ratings
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance compared to polyurethane foam, achieving higher fire safety ratings such as Euroclass B-s1,d0 versus the more flammable Euroclass E typical of polyurethane panels. Its char-forming properties reduce smoke emission and flame spread, making phenolic foam an ideal choice for insulation applications requiring stringent fire safety standards. Polyurethane foam, while providing excellent thermal insulation, generally poses greater fire hazards due to its lower ignition point and higher smoke toxicity.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Phenolic foam offers superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, which significantly reduces water absorption and prevents mold growth compared to polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam, while providing good thermal insulation, tends to absorb more moisture over time, potentially compromising its R-value and structural integrity. Chemically, phenolic foam exhibits enhanced resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents, making it a more durable choice for harsh environments than polyurethane foam, which can degrade when exposed to certain chemicals.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and emits fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to polyurethane foam, contributing to lower environmental toxicity during production and use. Polyurethane foam relies heavily on petrochemical resources and typically has higher global warming potential (GWP) due to blowing agents, whereas phenolic foam's manufacturing process incorporates more sustainable raw materials with reduced carbon footprint. Both insulation panels provide effective thermal performance, but phenolic foam's greater recyclability and lower smoke emissions make it a more sustainable choice for environmentally conscious building applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Phenolic foam exhibits superior mechanical strength due to its rigid, thermoset structure, making it highly resistant to compression and deformation over time compared to polyurethane foam, which is more flexible but less structurally robust. In terms of durability, phenolic foam offers enhanced fire resistance, dimensional stability, and moisture resistance, resulting in longer-lasting insulation panels under harsh environmental conditions. Polyurethane foam, while providing excellent thermal insulation, tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and mechanical stress, reducing its effectiveness in demanding applications.
Cost Analysis and Installation Considerations
Phenolic foam insulation panels generally have a higher initial cost compared to polyurethane foam due to their superior fire resistance and thermal performance. Installation of phenolic foam requires specialized handling to avoid damage given its brittleness, which can increase labor costs, whereas polyurethane foam panels are more flexible and easier to cut and fit onsite, reducing installation time and expenses. Long-term energy savings from phenolic foam's lower thermal conductivity may offset upfront costs, but polyurethane foam remains the more cost-effective option for projects with tight budgets and simpler installation needs.
Typical Uses and Industry Preferences
Phenolic foam insulation panels are preferred in industries requiring superior fire resistance and low smoke emission, such as commercial buildings and public transport. Polyurethane foam insulation panels dominate residential and industrial sectors due to their high thermal conductivity and cost-effective production. Typical uses for phenolic foam include wall cladding and roofing where fire codes are strict, while polyurethane foam is commonly utilized in HVAC ducting and refrigerated transport for enhanced thermal performance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam for Insulation Panels
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and low smoke emissions, making it ideal for applications requiring stringent fire safety standards, while polyurethane foam excels in thermal insulation efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The choice between phenolic and polyurethane foam depends on balancing fire performance, thermal conductivity values typically ranging from 0.020 to 0.025 W/m*K, and budget constraints specific to the project. Prioritizing project-specific criteria such as fire codes compliance, R-value requirements, and lifecycle costs ensures the optimal selection of insulation panel foam.
Infographic: Phenolic foam vs Polyurethane foam for Insulation panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com