Latex foam offers superior elasticity and breathability for shoe insoles, enhancing comfort and moisture management. Ethylene vinyl acetate foam provides excellent shock absorption and durability, making it ideal for long-lasting cushioning in footwear.
Table of Comparison
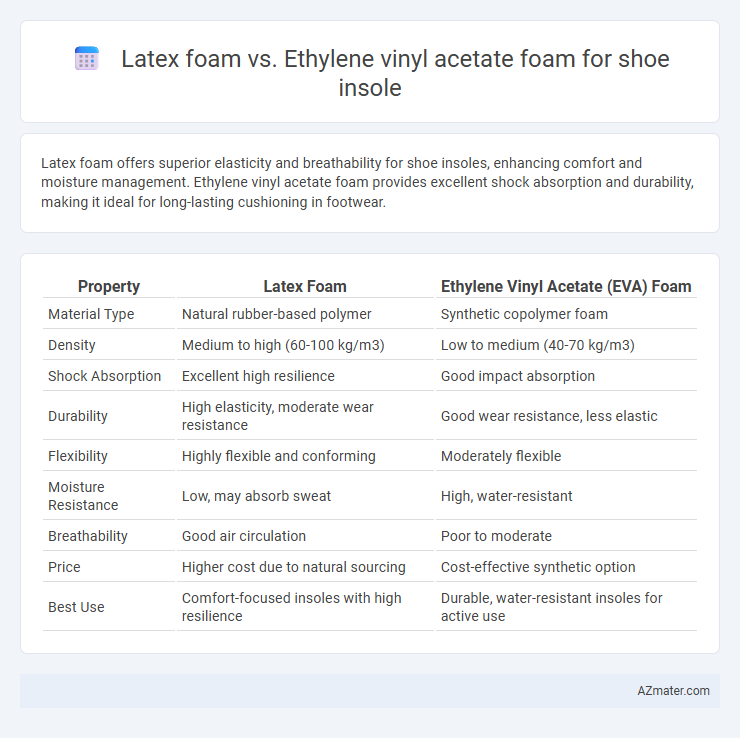
| Property | Latex Foam | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural rubber-based polymer | Synthetic copolymer foam |
| Density | Medium to high (60-100 kg/m3) | Low to medium (40-70 kg/m3) |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent high resilience | Good impact absorption |
| Durability | High elasticity, moderate wear resistance | Good wear resistance, less elastic |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and conforming | Moderately flexible |
| Moisture Resistance | Low, may absorb sweat | High, water-resistant |
| Breathability | Good air circulation | Poor to moderate |
| Price | Higher cost due to natural sourcing | Cost-effective synthetic option |
| Best Use | Comfort-focused insoles with high resilience | Durable, water-resistant insoles for active use |
Introduction to Shoe Insole Materials
Latex foam and ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam are popular materials for shoe insoles due to their cushioning and durability. Latex foam offers excellent elasticity, breathability, and natural moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for comfort and odor control. EVA foam provides lightweight support, shock absorption, and resistance to compression, which enhances foot stability and reduces impact during walking or running.
What is Latex Foam?
Latex foam is a natural material derived from rubber tree sap, characterized by its high elasticity, durability, and breathability, making it ideal for shoe insoles. It offers excellent cushioning and support by conforming to foot contours, reducing pressure points and enhancing comfort. Compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) foam, latex foam provides superior resilience and moisture-wicking properties, which contribute to long-lasting freshness and reduced odor in footwear.
What is Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam?
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) foam is a lightweight, flexible, and durable material widely used in shoe insoles for its excellent shock absorption and cushioning properties. EVA foam provides superior compression resistance and moisture resistance compared to latex foam, making it ideal for prolonged wear and high-impact activities. Its closed-cell structure enhances durability and prevents water absorption, contributing to better foot support and comfort.
Comfort and Cushioning Comparison
Latex foam offers superior elasticity and breathability, providing enhanced cushioning and lasting comfort for shoe insoles, especially suitable for prolonged wear. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam delivers excellent shock absorption with a lightweight and durable structure, promoting effective impact dispersion during high-impact activities. Both materials provide good cushioning, but latex foam excels in flexibility and moisture management, while EVA is preferred for its resilience and cost-effectiveness.
Durability and Lifespan
Latex foam insoles offer superior elasticity and resilience, which contributes to a longer lifespan due to their natural ability to regain shape after compression. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides excellent shock absorption but tends to compress and degrade faster under repeated stress, reducing overall durability. When selecting insoles based on durability and lifespan, latex foam is preferred for prolonged use, while EVA is suitable for short-term comfort and flexibility.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Latex foam offers excellent breathability due to its open-cell structure, allowing air circulation that helps keep feet cool and dry during prolonged wear. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, while providing good cushioning and durability, has a denser composition, which can limit airflow and reduce moisture evaporation. For insoles prioritizing moisture management, latex foam is often preferred because it facilitates better ventilation and quicker drying compared to EVA foam.
Shock Absorption and Support
Latex foam offers superior shock absorption due to its natural elasticity and resilience, effectively reducing impact forces on the foot during high-impact activities. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides excellent support and cushioning with a lightweight and durable structure, maintaining shape and stability under prolonged pressure. While latex foam excels in responsiveness and energy return, EVA foam is favored for its consistent support and resistance to compression set in shoe insoles.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Latex foam, derived from natural rubber, offers biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) foam, which is petroleum-based and less environmentally friendly due to its longer decomposition time and reliance on fossil fuels. Sustainable sourcing of natural latex reduces deforestation risks and supports renewable agriculture, while EVA's production involves toxic chemicals and contributes to plastic pollution. Choosing latex foam insoles promotes eco-conscious footwear by minimizing landfill waste and encouraging circular economy practices in the shoe industry.
Cost and Availability
Latex foam insoles typically cost more due to natural material sourcing and specialized manufacturing, but they offer superior elasticity and moisture resistance. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is more widely available and cost-effective because it is synthetically produced and easier to mass-produce at scale. The balance between cost-efficiency and availability often makes EVA foam the preferred choice for mainstream shoe insoles.
Which Foam is Best for Your Shoes?
Latex foam offers superior cushioning, elasticity, and breathability, making it ideal for high-impact activities and long-term comfort in shoe insoles. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides excellent shock absorption, lightweight durability, and moisture resistance, suited for everyday wear and sports footwear. Choosing between latex and EVA foam depends on your specific needs: opt for latex foam if you prioritize flexibility and natural cushioning, or select EVA foam for a balance of support, resilience, and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Latex foam vs Ethylene vinyl acetate foam for Shoe Insole
 azmater.com
azmater.com