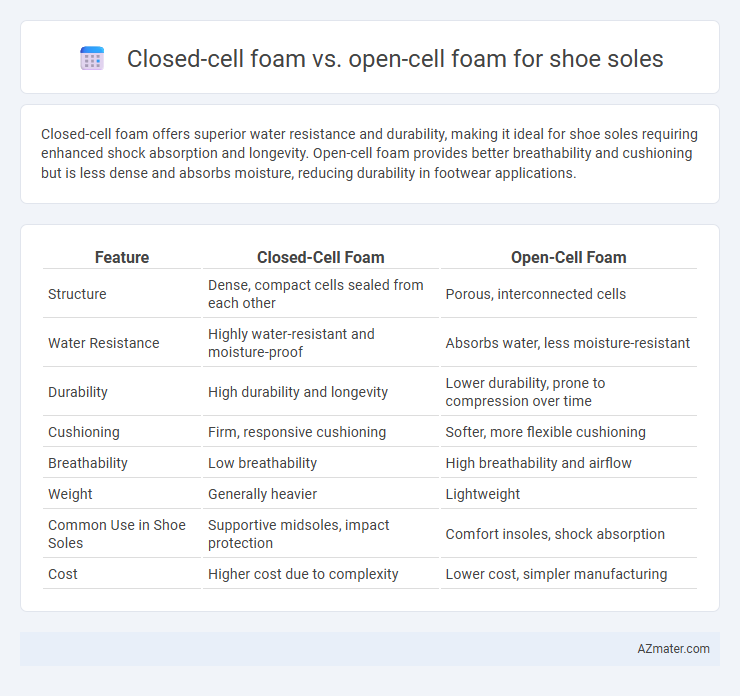
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance and durability, making it ideal for shoe soles requiring enhanced shock absorption and longevity. Open-cell foam provides better breathability and cushioning but is less dense and absorbs moisture, reducing durability in footwear applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Closed-Cell Foam | Open-Cell Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Dense, compact cells sealed from each other | Porous, interconnected cells |
| Water Resistance | Highly water-resistant and moisture-proof | Absorbs water, less moisture-resistant |
| Durability | High durability and longevity | Lower durability, prone to compression over time |
| Cushioning | Firm, responsive cushioning | Softer, more flexible cushioning |
| Breathability | Low breathability | High breathability and airflow |
| Weight | Generally heavier | Lightweight |
| Common Use in Shoe Soles | Supportive midsoles, impact protection | Comfort insoles, shock absorption |
| Cost | Higher cost due to complexity | Lower cost, simpler manufacturing |
Introduction to Foam Types in Shoe Soles
Closed-cell foam in shoe soles offers superior durability, water resistance, and higher density, making it ideal for impact absorption and long-term wear. Open-cell foam provides greater breathability, flexibility, and cushioning due to its porous structure, enhancing comfort and moisture management. Selecting between closed-cell and open-cell foam depends on performance priorities such as support, weight, and environmental exposure in footwear design.
What is Closed-Cell Foam?
Closed-cell foam consists of tiny, sealed cells that are tightly packed, providing superior water resistance, durability, and firm cushioning ideal for shoe soles. This structure prevents moisture absorption, enhances shock absorption, and offers long-lasting support compared to open-cell foam, which is softer and more breathable but less durable. The dense molecular design of closed-cell foam ensures stability and resilience, making it a preferred choice for high-performance footwear applications.
What is Open-Cell Foam?
Open-cell foam in shoe soles features interconnected air pockets, making it highly breathable and flexible, which enhances comfort and cushioning. Its porous structure absorbs moisture more easily, providing excellent shock absorption but less water resistance compared to closed-cell foam. Open-cell foam is ideal for lightweight, breathable footwear that prioritizes softness and flexibility over durability in wet conditions.
Material Composition and Structure
Closed-cell foam for shoe soles features a dense structure composed of tightly packed, air-impermeable cells made primarily from polyurethane or EVA, providing superior water resistance and durability. Open-cell foam consists of interconnected, porous cells typically formed from softer polyurethane, offering enhanced flexibility and breathability but less moisture resistance. The material composition and cellular structure directly impact cushioning, shock absorption, and long-term performance characteristics of shoe soles.
Cushioning and Comfort Comparison
Closed-cell foam offers higher density and superior shock absorption, making it ideal for shoe soles requiring enhanced cushioning and impact protection. Open-cell foam provides greater breathability and a softer, more flexible feel, promoting comfort during prolonged wear but with less durability under heavy pressure. The choice between closed-cell and open-cell foam depends on balancing cushioning requirements with ventilation and overall comfort preferences in footwear design.
Durability and Longevity
Closed-cell foam offers superior durability and longevity for shoe soles due to its dense, rigid structure that resists compression and moisture infiltration, maintaining cushioning and shape over time. In contrast, open-cell foam, characterized by its softer, more flexible texture, tends to absorb water and compress more easily, which can lead to faster wear and reduced lifespan. Brands often prefer closed-cell foam in athletic and work shoes where prolonged durability and support are critical.
Water Resistance and Breathability
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance due to its dense structure that prevents water absorption, making it ideal for shoe soles exposed to wet conditions. Open-cell foam provides increased breathability through its interconnected porous network, enhancing moisture and heat dissipation for improved foot comfort. Choosing between closed-cell and open-cell foam depends on the balance required between water resistance and ventilation in the shoe design.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Closed-cell foam offers higher density and rigidity, resulting in heavier shoe soles with enhanced shock absorption and durability. Open-cell foam features a lighter, more porous structure, providing greater flexibility and improved breathability but less durability under heavy impact. Weight-sensitive footwear applications favor open-cell foam, while closed-cell foam suits designs requiring firm support and long-lasting cushioning.
Cost Implications for Manufacturers and Consumers
Closed-cell foam, characterized by its dense structure and superior durability, generally incurs higher manufacturing costs due to more complex production processes and raw material expenses, which translates to increased retail prices for consumers. Open-cell foam, being less dense and easier to produce, offers a more cost-effective option for manufacturers, allowing more affordable pricing that appeals to budget-conscious buyers. Both materials impact the overall cost-effectiveness of shoe soles, with closed-cell foam favored for premium, long-lasting footwear, while open-cell foam suits cost-sensitive markets valuing cushioning over longevity.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Foam for Your Needs
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance and durability, making it ideal for outdoor and water-related shoe soles where moisture exposure is high. Open-cell foam provides excellent breathability and cushioning, best suited for athletic and casual shoes requiring enhanced comfort and airflow. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing factors like moisture resistance, flexibility, and shock absorption based on specific shoe performance needs.
Infographic: Closed-cell foam vs Open-cell foam for Shoe sole
 azmater.com
azmater.com