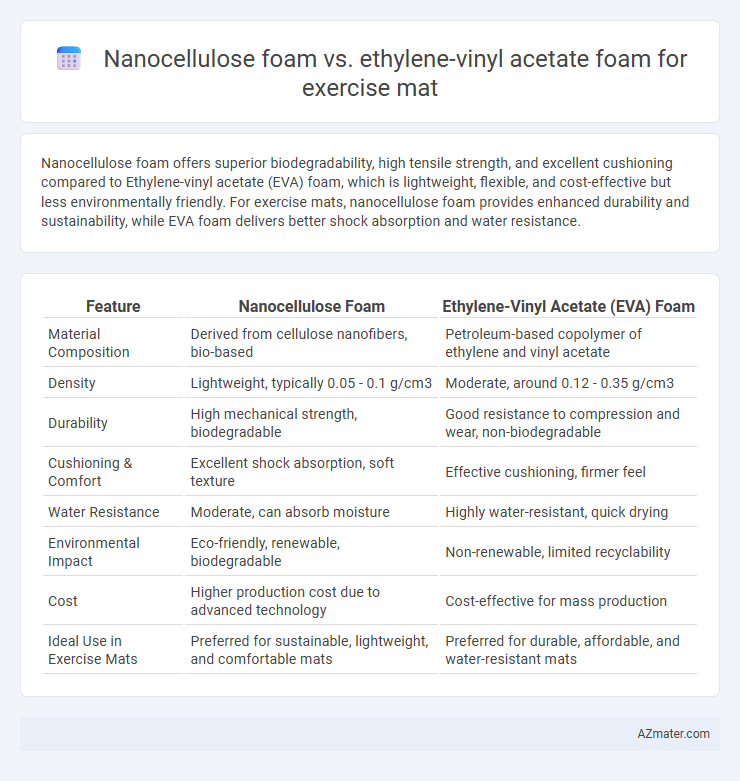
Nanocellulose foam offers superior biodegradability, high tensile strength, and excellent cushioning compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, which is lightweight, flexible, and cost-effective but less environmentally friendly. For exercise mats, nanocellulose foam provides enhanced durability and sustainability, while EVA foam delivers better shock absorption and water resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nanocellulose Foam | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Derived from cellulose nanofibers, bio-based | Petroleum-based copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate |
| Density | Lightweight, typically 0.05 - 0.1 g/cm3 | Moderate, around 0.12 - 0.35 g/cm3 |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, biodegradable | Good resistance to compression and wear, non-biodegradable |
| Cushioning & Comfort | Excellent shock absorption, soft texture | Effective cushioning, firmer feel |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, can absorb moisture | Highly water-resistant, quick drying |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, renewable, biodegradable | Non-renewable, limited recyclability |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to advanced technology | Cost-effective for mass production |
| Ideal Use in Exercise Mats | Preferred for sustainable, lightweight, and comfortable mats | Preferred for durable, affordable, and water-resistant mats |
Introduction to Nanocellulose and Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Foams
Nanocellulose foam, derived from plant fibers, offers exceptional lightweight strength, biodegradability, and high porosity, making it an eco-friendly alternative for exercise mats. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, a synthetic polymer blend, is widely used in exercise mats due to its excellent cushioning, flexibility, and moisture resistance. Both materials provide unique properties for comfort and durability, but nanocellulose stands out for sustainability and breathability in sports equipment applications.
Material Composition: Nanocellulose vs EVA
Nanocellulose foam is derived from renewable cellulose nanofibers, offering high tensile strength, biodegradability, and excellent moisture-wicking properties ideal for eco-friendly exercise mats. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam consists of a synthetic polymer blend known for its flexibility, cushioning, and durability, but it lacks biodegradability and relies on petrochemical sources. The material composition directly impacts environmental sustainability and performance characteristics, with nanocellulose providing a natural alternative to EVA's traditional synthetic makeup.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Comparison
Nanocellulose foam offers superior environmental benefits for exercise mats due to its biodegradability, renewable sourcing from plant fibers, and lower carbon footprint compared to traditional Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. The production of nanocellulose foam consumes less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions, enhancing its sustainability profile. EVA foam, although durable and widely used, contributes to plastic waste accumulation and relies heavily on fossil fuel resources, making nanocellulose foam a more eco-friendly alternative for sustainable fitness products.
Durability and Lifespan in Exercise Mat Applications
Nanocellulose foam exhibits superior durability and a longer lifespan in exercise mat applications due to its high tensile strength, resistance to wear, and excellent mechanical properties. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, while offering good cushioning and flexibility, tends to degrade faster under repeated stress and environmental exposure, reducing its effective lifespan. The nanocellulose-based mats maintain structural integrity and performance over extended periods, making them more suitable for rigorous and long-term exercise use.
Comfort and Cushioning: User Experience
Nanocellulose foam offers superior comfort and cushioning for exercise mats due to its lightweight structure and excellent shock absorption properties, enhancing user experience by reducing joint stress during workouts. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides firm support and durability but may feel denser and less responsive compared to nanocellulose, potentially impacting prolonged comfort. Users seeking a softer, more adaptive surface often prefer nanocellulose foam, while EVA remains favored for its resilience and cost-effectiveness in exercise mat applications.
Slip Resistance and Safety Features
Nanocellulose foam offers superior slip resistance compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam due to its higher surface friction and natural hydrophilic properties, reducing the risk of slipping during intense workouts. Its biodegradable nature enhances safety by minimizing toxic chemical exposure often associated with EVA foam production. Moreover, nanocellulose foam provides better impact absorption and breathability, contributing to overall user safety during exercise routines.
Odor and Allergen Considerations
Nanocellulose foam offers superior odor resistance and hypoallergenic properties compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, making it an ideal choice for exercise mats used in sensitive environments. Unlike EVA foam, which can emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and cause allergic reactions due to chemical additives, nanocellulose foam is naturally derived and biodegradable, minimizing off-gassing and skin irritations. The enhanced breathability and moisture-wicking capabilities of nanocellulose foam further reduce odor buildup and allergen accumulation, ensuring a cleaner and safer workout surface.
Weight, Portability, and Storage
Nanocellulose foam offers significantly lower weight and higher compressibility compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, enhancing portability for exercise mats. Its superior structural properties allow the mat to be rolled or folded into a compact size, facilitating easy storage and transport. EVA foam, while durable, tends to be bulkier and heavier, making it less convenient for users prioritizing lightweight and space-saving solutions.
Cost Analysis: Affordability of Both Foams
Nanocellulose foam typically incurs higher production costs due to advanced processing techniques and raw material expenses compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, which benefits from established, cost-effective manufacturing processes. EVA foam offers greater affordability and widespread availability, making it a budget-friendly option for exercise mats without compromising basic cushioning and durability. The price difference often influences consumer choice, with EVA foam dominating the market for cost-sensitive buyers seeking reliable performance.
Future Trends in Exercise Mat Materials
Nanocellulose foam offers superior biodegradability and enhanced mechanical strength compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, making it a promising sustainable alternative for exercise mats. Future trends emphasize eco-friendly materials like nanocellulose due to increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for zero-waste fitness products. Innovations in nanocellulose processing aim to improve cushioning and durability, potentially surpassing EVA's current market dominance in exercise mat manufacturing.
Infographic: Nanocellulose foam vs Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam for Exercise mat
 azmater.com
azmater.com