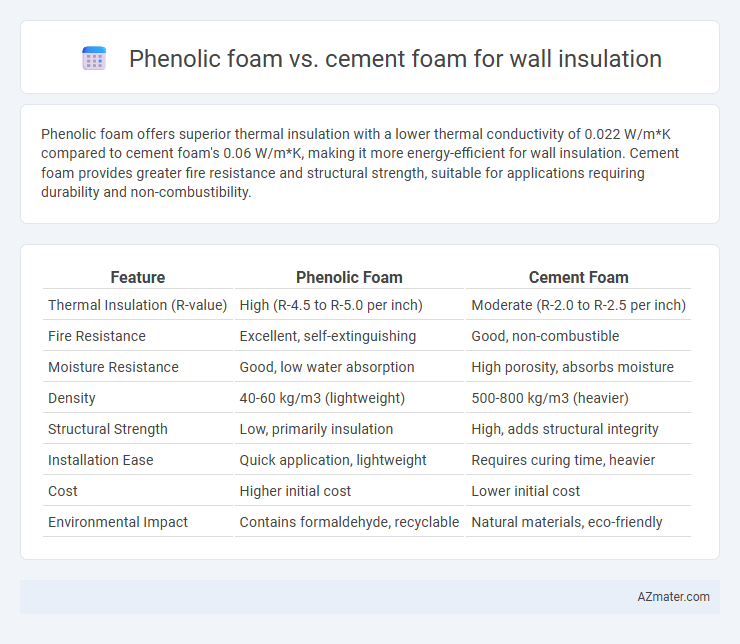
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with a lower thermal conductivity of 0.022 W/m*K compared to cement foam's 0.06 W/m*K, making it more energy-efficient for wall insulation. Cement foam provides greater fire resistance and structural strength, suitable for applications requiring durability and non-combustibility.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Phenolic Foam | Cement Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation (R-value) | High (R-4.5 to R-5.0 per inch) | Moderate (R-2.0 to R-2.5 per inch) |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent, self-extinguishing | Good, non-combustible |
| Moisture Resistance | Good, low water absorption | High porosity, absorbs moisture |
| Density | 40-60 kg/m3 (lightweight) | 500-800 kg/m3 (heavier) |
| Structural Strength | Low, primarily insulation | High, adds structural integrity |
| Installation Ease | Quick application, lightweight | Requires curing time, heavier |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Environmental Impact | Contains formaldehyde, recyclable | Natural materials, eco-friendly |
Introduction to Wall Insulation Materials
Phenolic foam and cement foam are advanced insulation materials used in modern construction for enhanced thermal performance and structural integrity. Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and low thermal conductivity, making it ideal for energy-efficient wall insulation, while cement foam provides excellent strength, durability, and moisture resistance suitable for exterior wall applications. Selecting between phenolic foam and cement foam depends on specific project requirements such as thermal efficiency, fire safety standards, and environmental exposure conditions.
What Is Phenolic Foam?
Phenolic foam is a high-performance insulating material known for its superior thermal resistance with an R-value typically around 4.0 to 8.0 per inch, making it highly effective for wall insulation compared to cement foam, which generally offers lower thermal efficiency. This closed-cell foam is fire-resistant, moisture-resistant, and provides excellent structural stability, contributing to enhanced energy savings and durability in building applications. Phenolic foam's lightweight nature and low thermal conductivity make it a preferred choice over cement foam in environments requiring stringent insulation standards.
What Is Cement Foam?
Cement foam is a lightweight, aerated concrete material used for wall insulation and thermal protection, consisting of cement, water, and foam agents that create numerous tiny air pockets. Its high compressive strength, fire resistance, and moisture durability make it ideal for structural walls where insulation and load-bearing capabilities are essential. Unlike phenolic foam, cement foam offers better mechanical performance but lower thermal insulation efficiency, often used in industrial and commercial building applications.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Phenolic foam provides superior thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity typically around 0.020 W/m*K, making it highly efficient in reducing heat transfer through walls. Cement foam, while offering good fire resistance and structural benefits, generally has a higher thermal conductivity ranging from 0.07 to 0.12 W/m*K, resulting in lower insulation performance compared to phenolic foam. The enhanced insulating capability of phenolic foam contributes to better energy savings and indoor temperature regulation in building applications.
Fire Resistance: Phenolic Foam vs Cement Foam
Phenolic foam exhibits superior fire resistance due to its inherent char-forming properties and low smoke emission, making it highly effective against flame spread and heat release. Cement foam, while non-combustible and providing excellent fireproofing capabilities, tends to be heavier and may lack the thermal insulation efficiency of phenolic foam. Fire resistance in wall insulation demands balancing flame retardancy with insulation performance, where phenolic foam often outperforms cement foam in preventing fire propagation and ensuring occupant safety.
Moisture and Water Resistance
Phenolic foam offers superior moisture resistance compared to cement foam due to its closed-cell structure, which significantly reduces water absorption and vapor permeability. Cement foam, while providing good thermal insulation, tends to be more porous and susceptible to water infiltration, leading to potential degradation and reduced insulating performance over time. For applications requiring robust moisture and water resistance in wall insulation, phenolic foam is often the preferred material.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Phenolic foam offers superior mechanical strength with high compressive and flexural properties, making it ideal for load-bearing insulation applications. Cement foam provides excellent durability against moisture, fire, and pests, ensuring long-term structural integrity in harsh environments. Comparing both, phenolic foam excels in lightweight rigidity, while cement foam outperforms in robust endurance and environmental resistance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with a lower global warming potential due to its reduced blowing agent emissions and long service life, making it a more sustainable choice compared to cement foam. Cement foam, while utilizing abundant raw materials like cement and water, has a higher embodied carbon footprint because of energy-intensive cement production, though it provides excellent fire resistance and durability. Choosing phenolic foam supports energy efficiency in buildings, but cement foam benefits sustainability through its potential for recycling and inclusion of industrial by-products such as fly ash.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with an R-value ranging from 7.0 to 8.0 per inch, often resulting in lower heating and cooling costs despite a higher upfront price compared to cement foam, which typically provides an R-value of around 2.0 to 3.0 per inch. Cement foam is generally more affordable initially and provides good fire resistance and durability but may increase long-term energy expenses due to its lower insulating efficiency. Evaluating lifecycle costs, phenolic foam tends to be more cost-effective for applications demanding high energy efficiency and reduced maintenance over time.
Best Applications and Recommendations
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation and fire resistance, making it ideal for internal wall insulation in residential and commercial buildings where energy efficiency and safety are priorities. Cement foam, with its excellent compression strength and moisture resistance, suits exterior wall insulation and applications in humid or load-bearing environments. For optimal performance, choose phenolic foam for lightweight, low-conductivity insulation, while cement foam is recommended for durable, weather-resistant exterior insulation solutions.
Infographic: Phenolic foam vs Cement foam for Wall insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com