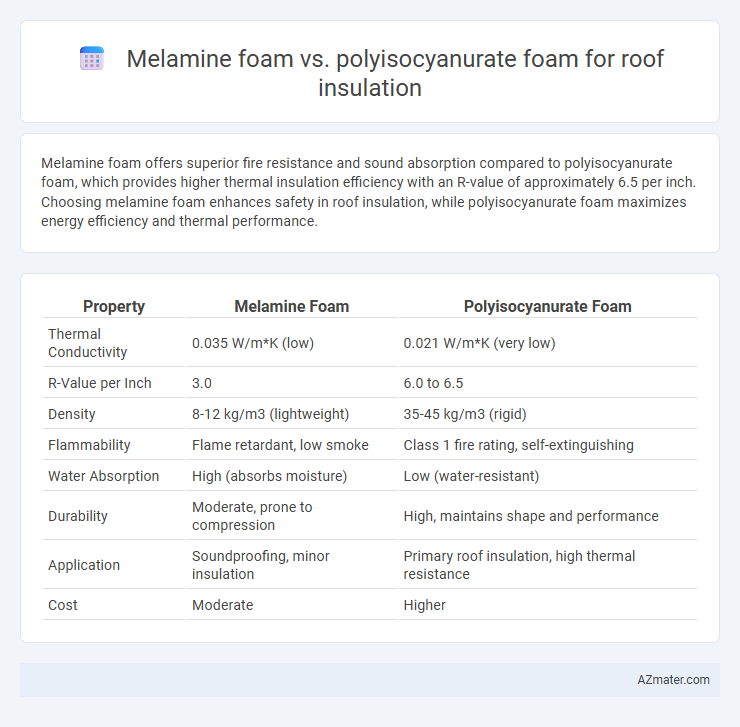
Melamine foam offers superior fire resistance and sound absorption compared to polyisocyanurate foam, which provides higher thermal insulation efficiency with an R-value of approximately 6.5 per inch. Choosing melamine foam enhances safety in roof insulation, while polyisocyanurate foam maximizes energy efficiency and thermal performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Melamine Foam | Polyisocyanurate Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.035 W/m*K (low) | 0.021 W/m*K (very low) |
| R-Value per Inch | 3.0 | 6.0 to 6.5 |
| Density | 8-12 kg/m3 (lightweight) | 35-45 kg/m3 (rigid) |
| Flammability | Flame retardant, low smoke | Class 1 fire rating, self-extinguishing |
| Water Absorption | High (absorbs moisture) | Low (water-resistant) |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to compression | High, maintains shape and performance |
| Application | Soundproofing, minor insulation | Primary roof insulation, high thermal resistance |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Roof Insulation Materials
Melamine foam offers excellent thermal insulation with added sound absorption, making it suitable for energy-efficient roofing systems. Polyisocyanurate foam, known for its high R-value per inch, provides superior thermal resistance and enhanced fire retardancy, often used in commercial roof applications. Both materials contribute to reducing heat transfer and improving overall building performance, but their distinct properties determine optimal usage based on project specifications.
Overview of Melamine Foam
Melamine foam is an open-cell, lightweight material known for its superior sound absorption and thermal insulation properties, making it effective in reducing heat transfer through roofs. Compared to polyisocyanurate foam, melamine foam offers higher fire resistance and enhanced breathability due to its porous structure, which helps prevent moisture buildup within roofing systems. Its low density and ability to maintain performance over a wide temperature range position melamine foam as a versatile option for energy-efficient roof insulation.
Overview of Polyisocyanurate Foam
Polyisocyanurate foam is a high-performance rigid insulation material commonly used in roof insulation due to its superior thermal resistance, with R-values typically ranging from 6 to 7 per inch. Its closed-cell structure provides excellent moisture resistance and dimensional stability, making it suitable for flat or low-slope roofing systems exposed to harsh weather conditions. Compared to melamine foam, polyisocyanurate foam offers greater structural strength and fire resistance, contributing to improved energy efficiency and durability in commercial and residential roofing applications.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Melamine foam offers excellent thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity typically around 0.03 W/m*K, providing effective heat resistance and sound absorption for roof applications. Polyisocyanurate foam outperforms melamine foam in thermal efficiency, featuring thermal conductivity values as low as 0.02 W/m*K, which results in superior R-values and enhanced energy savings for building envelopes. The higher closed-cell structure of polyisocyanurate foam contributes to greater thermal resistance, making it a preferred choice for high-performance roof insulation systems.
Fire Resistance and Safety Features
Melamine foam offers excellent fire resistance with a high ignition point, producing minimal smoke and toxic gases, making it safer for roof insulation in fire-prone areas. Polyisocyanurate foam provides superior thermal insulation but is more flammable and can release hazardous fumes when exposed to fire. Choosing melamine foam enhances roof safety by reducing fire hazards, while polyisocyanurate requires additional fire retardant treatments to meet safety standards.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Melamine foam offers excellent moisture resistance due to its open-cell structure, which allows for quick drying and prevents mold growth, making it suitable for humid environments. Polyisocyanurate foam, with its closed-cell composition, provides superior durability and moisture resistance by creating a rigid, water-impermeable barrier that enhances thermal performance and structural integrity. Both materials perform well, but polyisocyanurate foam excels in long-term durability under roof loads while melamine foam is advantageous for moisture management in insulation applications.
Installation Process and Ease
Melamine foam offers simple, flexible installation due to its lightweight and easily cut material, making it ideal for tight or irregular roof spaces without special tools. Polyisocyanurate (PIR) foam boards require precise handling and cutting, often needing mechanical fasteners and professional installation to ensure proper fit and thermal performance. Melamine foam's ease reduces labor time and complexity, while polyisocyanurate's rigid structure demands more skill but provides superior structural support.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Melamine foam offers low environmental impact due to its non-toxic composition and high thermal insulation, reducing energy consumption in buildings. Polyisocyanurate foam provides superior insulation with a higher R-value per inch, but its production involves petrochemicals and blowing agents with higher global warming potential. Choosing melamine foam supports sustainability goals by minimizing harmful emissions and promoting recyclable materials, while polyisocyanurate foam delivers enhanced energy efficiency despite a larger carbon footprint during manufacture.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Melamine foam generally offers lower initial costs compared to polyisocyanurate foam, making it a budget-friendly option for roof insulation in residential and commercial projects. Polyisocyanurate foam delivers higher thermal resistance (R-value) per inch, which can lead to greater energy savings and long-term cost benefits despite its higher upfront price. Evaluating the lifecycle cost including installation, energy efficiency, and maintenance expenses is crucial for determining the most cost-effective insulation material for specific roofing applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam for Roof Insulation
Melamine foam offers superior sound absorption and fire resistance, making it ideal for noise-sensitive or high-temperature environments, while polyisocyanurate foam provides higher R-value per inch, excellent thermal insulation, and moisture resistance, suitable for energy-efficient roofing systems. Selecting the right foam depends on specific project requirements such as desired insulation performance, fire safety standards, and budget constraints. Polyisocyanurate foam generally excels in thermal performance, whereas melamine foam is favored for acoustic and fire-related applications in roof insulation.
Infographic: Melamine foam vs Polyisocyanurate foam for Roof insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com