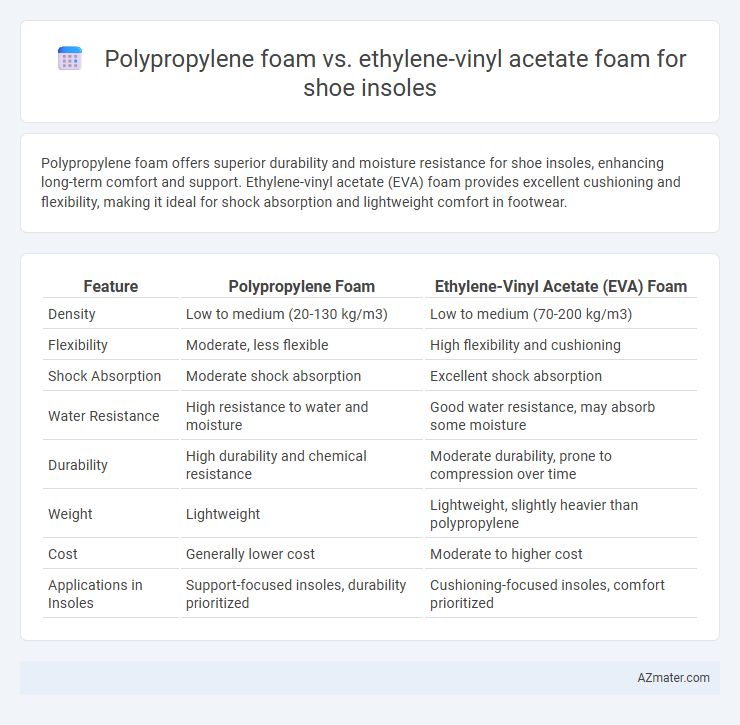
Polypropylene foam offers superior durability and moisture resistance for shoe insoles, enhancing long-term comfort and support. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides excellent cushioning and flexibility, making it ideal for shock absorption and lightweight comfort in footwear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polypropylene Foam | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low to medium (20-130 kg/m3) | Low to medium (70-200 kg/m3) |
| Flexibility | Moderate, less flexible | High flexibility and cushioning |
| Shock Absorption | Moderate shock absorption | Excellent shock absorption |
| Water Resistance | High resistance to water and moisture | Good water resistance, may absorb some moisture |
| Durability | High durability and chemical resistance | Moderate durability, prone to compression over time |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight, slightly heavier than polypropylene |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Moderate to higher cost |
| Applications in Insoles | Support-focused insoles, durability prioritized | Cushioning-focused insoles, comfort prioritized |
Introduction to Shoe Insole Materials
Polypropylene foam offers lightweight durability and excellent moisture resistance, making it suitable for shoe insoles aimed at long-term wear and structural support. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam excels in cushioning and flexibility, providing superior shock absorption and comfort underfoot. Both materials are popular in footwear manufacturing due to their unique balance of resilience, comfort, and cost-effectiveness.
What is Polypropylene (PP) Foam?
Polypropylene (PP) foam is a lightweight, closed-cell foam known for its excellent cushioning, durability, and moisture resistance, making it a popular choice for shoe insoles. Its chemical structure provides high heat resistance and resilience, enhancing comfort and stability during prolonged wear. Compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, PP foam offers superior stiffness and impact absorption, which supports better foot arch support and longevity in footwear applications.
What is Ethylene-vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam?
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is a lightweight, flexible polymer widely used in shoe insoles due to its excellent shock absorption and cushioning properties. Compared to polypropylene foam, EVA offers superior elasticity and resilience, enhancing comfort and reducing foot fatigue during prolonged wear. Its closed-cell structure also provides water resistance and durability, making it a preferred choice for athletic and casual footwear.
Comfort Comparison: PP Foam vs. EVA Foam
Polypropylene (PP) foam offers firm support with excellent durability and resistance to compression, providing a stable base for shoe insoles but less cushioning compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam. EVA foam excels in shock absorption and flexibility, delivering superior comfort and energy return, making it ideal for prolonged wear and high-impact activities. The choice between PP and EVA foams in shoe insoles hinges on the balance between required support and cushioning, with EVA favored for enhanced comfort and PP preferred for structural resilience.
Durability and Longevity of PP vs. EVA Insoles
Polypropylene (PP) foam insoles demonstrate superior durability compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, maintaining structural integrity and cushioning effectiveness over extended periods of use. PP foam resists compression set and deformation better, resulting in longer-lasting support and comfort for shoe insoles. EVA foam, while lightweight and flexible, tends to lose resilience and compress more quickly under repeated stress, reducing overall longevity compared to PP-based insoles.
Cushioning and Shock Absorption Analysis
Polypropylene foam offers higher rigidity and durability, providing moderate cushioning and good shock absorption suitable for stability-focused shoe insoles. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam exhibits superior softness and flexibility, delivering enhanced cushioning and excellent shock absorption, which improves comfort during prolonged wear. The choice between the two materials depends on balancing the need for long-lasting support (polypropylene) versus lightweight, responsive cushioning (EVA).
Breathability and Odor Control
Polypropylene foam offers high breathability due to its open-cell structure, which facilitates air circulation and moisture wicking, making it effective in reducing foot odor. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, while providing excellent cushioning, has a closed-cell structure that limits breathability and can trap moisture, potentially leading to odor build-up. For shoe insoles prioritizing breathability and odor control, polypropylene foam is preferred over EVA foam for maintaining a fresher and drier foot environment.
Weight and Flexibility in Shoe Insoles
Polypropylene foam offers lightweight properties with moderate flexibility, making it suitable for durable shoe insoles that require structural support. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is lighter and more flexible than polypropylene, providing superior cushioning and adaptability for enhanced comfort in footwear. The choice between the two materials depends on the balance needed between stability (polypropylene) and softness with flexibility (EVA) in shoe insole design.
Cost and Sustainability Considerations
Polypropylene foam offers lower production costs and higher durability, making it a budget-friendly choice for shoe insoles, while Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam generally entails higher expenses but provides superior cushioning and flexibility. From a sustainability perspective, polypropylene foam is less biodegradable and relies heavily on fossil fuels, whereas EVA foam can be produced with bio-based content and exhibits better recyclability options. Selecting between the two depends on balancing initial cost constraints against long-term environmental impact goals in footwear manufacturing.
Which Foam is Best for Shoe Insoles?
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior cushioning and flexibility compared to polypropylene foam, making it the preferred choice for shoe insoles aimed at comfort and shock absorption. EVA foam's lightweight structure and excellent energy return reduce foot fatigue during prolonged use, while polypropylene foam provides more rigidity and durability but less impact protection. For optimal support and comfort in shoe insoles, EVA foam consistently outperforms polypropylene foam in both athletic and casual footwear applications.
Infographic: Polypropylene foam vs Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam for Shoe insole
 azmater.com
azmater.com