Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture resistance and higher durability for packaging inserts, making it ideal for protecting sensitive electronics. Open-cell foam provides better cushioning and breathability, suitable for lightweight, shock-absorbing packaging applications.
Table of Comparison
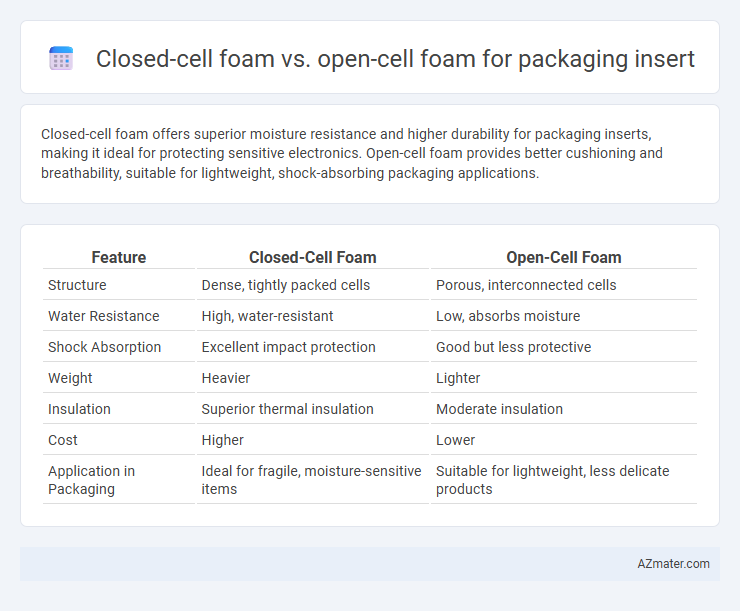
| Feature | Closed-Cell Foam | Open-Cell Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Dense, tightly packed cells | Porous, interconnected cells |
| Water Resistance | High, water-resistant | Low, absorbs moisture |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent impact protection | Good but less protective |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Insulation | Superior thermal insulation | Moderate insulation |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Application in Packaging | Ideal for fragile, moisture-sensitive items | Suitable for lightweight, less delicate products |
Introduction to Foam Packaging Inserts
Closed-cell foam packaging inserts feature a dense structure with sealed air pockets providing superior water resistance, higher durability, and enhanced protection against impact and compression. Open-cell foam packaging inserts are lighter, more flexible, and offer excellent cushioning by absorbing shocks through interconnected air pockets, making them ideal for delicate items requiring gentle handling. Choosing between closed-cell and open-cell foam depends on the specific packaging needs, balancing factors like moisture resistance, strength, and cost-effectiveness.
What is Closed-Cell Foam?
Closed-cell foam is a dense, rigid material with tightly packed cells that do not allow air or water to pass through, making it highly moisture-resistant and durable for packaging inserts. It provides superior impact absorption and structural support, protecting fragile items from damage during shipping. Its resistance to compression and ability to maintain shape under heavy loads make it ideal for preserving the integrity of sensitive products.
What is Open-Cell Foam?
Open-cell foam is a lightweight, porous material with interconnected air pockets, offering excellent cushioning and shock absorption for packaging inserts. Its breathable structure allows it to compress easily, protecting delicate items from impact while reducing overall weight and material cost. Unlike closed-cell foam, open-cell foam provides superior flexibility but lower moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging fragile, lightweight products in dry environments.
Key Differences Between Closed-Cell and Open-Cell Foam
Closed-cell foam has a dense structure with sealed cells that provide superior moisture resistance, higher compression strength, and excellent cushioning, making it ideal for protective packaging inserts. Open-cell foam features interconnected, porous cells that absorb shock and offer flexibility but are less resistant to moisture and compression compared to closed-cell foam. The choice depends on specific packaging needs, with closed-cell preferred for moisture-sensitive and heavy-duty protection, while open-cell suits lightweight, impact-absorbing applications.
Protective Performance Comparison
Closed-cell foam offers superior protective performance for packaging inserts due to its higher density and impermeability, effectively absorbing shocks and preventing moisture penetration. Open-cell foam, while lighter and more flexible, provides less rigid cushioning and can compress more easily under pressure, reducing impact resistance. For applications requiring maximum protection against impact, compression, and environmental factors, closed-cell foam is the preferred choice.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture resistance due to its dense, impermeable structure, making it ideal for packaging inserts exposed to humidity or liquids. Open-cell foam, with its porous nature, absorbs moisture easily, reducing durability and increasing the risk of damage in wet conditions. For long-term protection and enhanced durability in packaging inserts, closed-cell foam is the preferred choice.
Weight and Flexibility Considerations
Closed-cell foam offers higher density and weight compared to open-cell foam, providing superior impact resistance and rigid support for packaging inserts. Open-cell foam, being lighter and more flexible, allows better cushioning and conforms easily to delicate or irregularly shaped items. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing lightweight cushioning or sturdier protection based on the product's fragility and shipping conditions.
Cost Analysis: Closed-Cell vs Open-Cell Foam
Closed-cell foam generally incurs higher initial costs due to its denser structure and superior water resistance, making it ideal for protecting sensitive or heavy products in packaging inserts. Open-cell foam is more cost-effective with lower material and manufacturing expenses but offers less durability and cushioning capability. Selecting between closed-cell and open-cell foam depends on balancing upfront budget constraints with long-term product protection requirements, where closed-cell foam often reduces damage-related costs despite its higher price.
Best Use Cases for Each Foam Type
Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture resistance and high structural rigidity, making it ideal for packaging delicate electronics, pharmaceuticals, and medical devices that require protection from impact and environmental factors. Open-cell foam provides excellent cushioning and breathability, suited for packaging lightweight, fragile items such as glassware, artwork, and textiles where shock absorption and airflow are essential. For heavy-duty packaging with exposure to moisture, closed-cell foam is preferred, while open-cell foam excels in applications needing soft padding and ventilation.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture resistance, higher durability, and excellent impact protection, making it ideal for heavy, delicate, or moisture-sensitive items in packaging inserts. Open-cell foam provides better cushioning and flexibility at a lower cost, suitable for lightweight, non-fragile products requiring breathability. Selecting the right foam depends on factors such as product fragility, environmental conditions, and budget constraints to ensure optimal protection and cost-efficiency.
Infographic: Closed-cell foam vs Open-cell foam for Packaging insert
 azmater.com
azmater.com