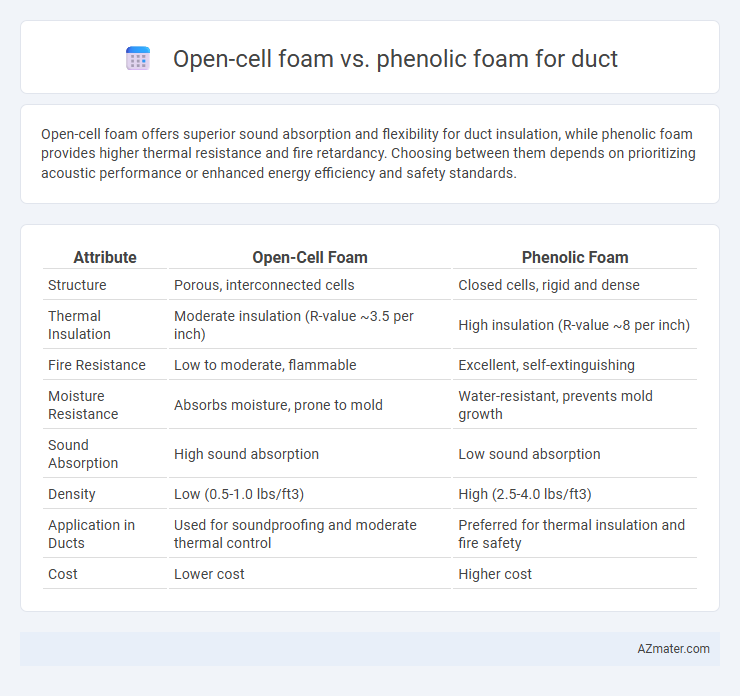
Open-cell foam offers superior sound absorption and flexibility for duct insulation, while phenolic foam provides higher thermal resistance and fire retardancy. Choosing between them depends on prioritizing acoustic performance or enhanced energy efficiency and safety standards.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Open-Cell Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Porous, interconnected cells | Closed cells, rigid and dense |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation (R-value ~3.5 per inch) | High insulation (R-value ~8 per inch) |
| Fire Resistance | Low to moderate, flammable | Excellent, self-extinguishing |
| Moisture Resistance | Absorbs moisture, prone to mold | Water-resistant, prevents mold growth |
| Sound Absorption | High sound absorption | Low sound absorption |
| Density | Low (0.5-1.0 lbs/ft3) | High (2.5-4.0 lbs/ft3) |
| Application in Ducts | Used for soundproofing and moderate thermal control | Preferred for thermal insulation and fire safety |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Duct Insulation Materials
Duct insulation materials significantly impact HVAC system efficiency, with open-cell foam and phenolic foam being prominent choices. Open-cell foam offers excellent sound absorption and flexibility, making it ideal for irregular duct shapes, while phenolic foam provides superior thermal insulation and fire resistance due to its closed-cell structure and inherent fire-retardant properties. Selecting the appropriate foam depends on factors like thermal conductivity, fire rating, moisture resistance, and application environment in duct insulation projects.
Overview of Open-Cell Foam for Ductwork
Open-cell foam for ductwork offers superior sound absorption and thermal insulation due to its porous structure, making it ideal for reducing noise transmission and improving energy efficiency in HVAC systems. Its lightweight, flexible composition allows for easy installation and excellent adhesion to duct surfaces, enhancing overall system performance. Compared to phenolic foam, open-cell foam provides better moisture vapor permeability, which helps prevent condensation and mold growth inside ducts.
Overview of Phenolic Foam for Ductwork
Phenolic foam is a high-performance insulation material widely used in ductwork due to its superior thermal resistance and excellent fire-retardant properties. It offers low smoke emission and enhanced structural rigidity compared to open-cell foam, making it ideal for commercial HVAC systems requiring stringent fire safety standards. Its closed-cell structure also provides effective moisture resistance, reducing condensation risks within ducts.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Open-cell foam provides moderate thermal insulation with an R-value typically ranging from 3.5 to 4.0 per inch, offering good sound absorption but higher air permeability compared to phenolic foam. Phenolic foam exhibits superior thermal insulation properties, with R-values around 4.5 to 5.0 per inch, along with exceptional fire resistance and low smoke emission ideal for duct insulation in commercial and industrial applications. The closed-cell structure of phenolic foam enhances thermal barrier performance and durability, making it more effective for energy-efficient HVAC systems compared to the more permeable open-cell foam.
Fire Resistance and Safety Differences
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance compared to open-cell foam, characterized by its low smoke emission and self-extinguishing properties, making it ideal for duct insulation in fire-critical environments. Open-cell foam, while providing good thermal and acoustic insulation, is more combustible and produces denser smoke, presenting higher safety risks in fire scenarios. Fire safety standards such as ASTM E84 and UL 723 often favor phenolic foam for duct applications due to its enhanced fire retardant performance and reduced toxic fume release.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Phenolic foam offers superior moisture resistance compared to open-cell foam, making it highly effective for duct insulation in humid environments. Its closed-cell structure prevents water absorption, enhancing long-term durability and reducing mold growth risks. Open-cell foam, while providing good thermal insulation, tends to absorb moisture, which can compromise its structural integrity and insulation performance over time.
Acoustic Insulation Capabilities
Open-cell foam offers superior sound absorption due to its porous structure, effectively reducing airborne noise within duct systems by trapping sound waves. Phenolic foam provides excellent thermal insulation with moderate acoustic performance but is less effective than open-cell foam at attenuating high-frequency sounds. Combining open-cell foam's acoustic insulation with phenolic foam's fire resistance can optimize duct liner solutions for noise control and safety compliance.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Open-cell foam offers easier installation due to its lightweight and flexible structure, allowing it to conform seamlessly to complex duct shapes and tight spaces. Phenolic foam, while rigid and less adaptable, provides a more challenging installation process that requires precise cutting and fitting to maintain its insulation integrity. The flexibility of open-cell foam reduces labor time and improves air sealing compared to phenolic foam's brittle nature, making it ideal for ducts with irregular geometries.
Cost and Lifespan Analysis
Open-cell foam for ducts typically offers a lower initial cost but has a shorter lifespan due to its susceptibility to moisture absorption and compression over time. Phenolic foam, while more expensive upfront, provides superior durability and fire resistance, resulting in a longer lifespan and reduced replacement frequency. Cost analysis favors open-cell foam for budget constraints, whereas phenolic foam proves more cost-effective long-term due to its enhanced performance and longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Open-cell foam and phenolic foam differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability for duct insulation. Open-cell foam, made from water-blown technology, offers lower global warming potential (GWP) with fewer harmful blowing agents and is often more recyclable, enhancing green building certifications like LEED. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance and thermal performance but typically involves higher embodied carbon and uses phenol-formaldehyde resins, raising concerns about toxicity and end-of-life disposal.
Infographic: Open-cell foam vs Phenolic foam for Duct
 azmater.com
azmater.com