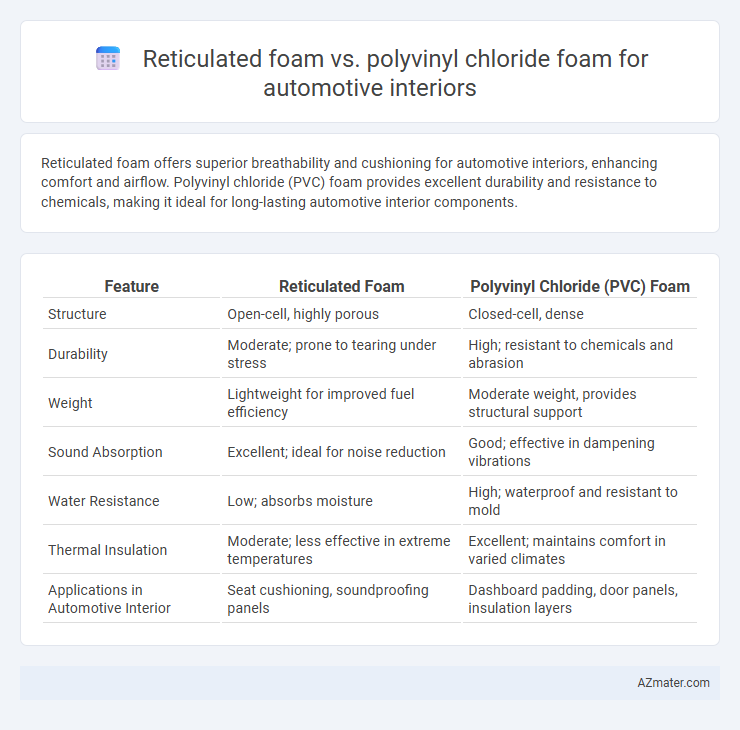
Reticulated foam offers superior breathability and cushioning for automotive interiors, enhancing comfort and airflow. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides excellent durability and resistance to chemicals, making it ideal for long-lasting automotive interior components.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Reticulated Foam | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Open-cell, highly porous | Closed-cell, dense |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to tearing under stress | High; resistant to chemicals and abrasion |
| Weight | Lightweight for improved fuel efficiency | Moderate weight, provides structural support |
| Sound Absorption | Excellent; ideal for noise reduction | Good; effective in dampening vibrations |
| Water Resistance | Low; absorbs moisture | High; waterproof and resistant to mold |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate; less effective in extreme temperatures | Excellent; maintains comfort in varied climates |
| Applications in Automotive Interior | Seat cushioning, soundproofing panels | Dashboard padding, door panels, insulation layers |
Introduction to Automotive Interior Foams
Reticulated foam and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam serve distinct roles in automotive interiors, offering tailored solutions based on performance requirements. Reticulated foam is prized for its open-cell structure, promoting superior airflow and moisture drainage, making it ideal for filtration and cushioning applications. PVC foam, with its closed-cell composition, provides excellent durability, chemical resistance, and noise dampening, frequently used in trim panels, headliners, and door insulations.
Overview of Reticulated Foam
Reticulated foam offers high open-cell structure with excellent air and fluid flow, making it ideal for automotive interior applications requiring superior ventilation and sound absorption. Its durable polyurethane composition provides resistance to oils, chemicals, and temperature variations commonly encountered in vehicle cabins. Compared to polyvinyl chloride foam, reticulated foam ensures enhanced breathability and quicker moisture evaporation, improving passenger comfort and cabin air quality.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) foam is a widely used material in automotive interiors due to its excellent durability, chemical resistance, and versatility in molding complex shapes. This closed-cell foam offers superior weather resistance and fire retardancy compared to reticulated foam, making it ideal for dashboard panels, door trims, and headliners. PVC foam's lightweight nature and sound absorption properties enhance vehicle comfort while contributing to overall safety standards compliance.
Material Composition and Structure Comparison
Reticulated foam consists of an open-cell structure formed by removing cell membranes, enhancing breathability and fluid drainage, while polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam features a closed-cell matrix providing superior rigidity and water resistance. The material composition of reticulated foam primarily involves polyurethane, allowing for cushioning and sound absorption, whereas PVC foam is synthetically produced with vinyl polymer chains offering durability and chemical resistance. In automotive interiors, reticulated foam is favored for applications requiring ventilation and softness, whereas PVC foam suits structural components demanding stiffness and moisture barrier properties.
Key Performance Characteristics
Reticulated foam offers superior breathability and cushioning due to its open-cell structure, making it ideal for automotive seat padding and ventilation applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides excellent durability, chemical resistance, and structural rigidity, often used for interior panels and insulation components. Key performance distinctions include reticulated foam's enhanced air and moisture permeability, while PVC foam excels in impact resistance and long-term dimensional stability.
Comfort and Aesthetics in Automotive Applications
Reticulated foam offers superior breathability and cushioning in automotive interiors, enhancing passenger comfort through effective air circulation and moisture management. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides a durable, smooth surface with excellent shape retention, contributing to sleek and visually appealing interior panels. Both materials balance comfort and aesthetics, with reticulated foam excelling in ventilation and PVC foam offering enhanced design versatility and longevity.
Durability and Lifespan
Reticulated foam offers superior durability in automotive interiors due to its open-cell structure, which provides excellent resistance to wear, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, extending its lifespan significantly. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and high temperatures, leading to cracking and reduced durability over time. For long-term automotive interior applications, reticulated foam outperforms PVC foam by maintaining structural integrity and cushioning properties over a prolonged period.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reticulated foam offers enhanced breathability and is often made from materials with better recyclability profiles, reducing environmental impact in automotive interiors compared to traditional polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam. PVC foam production and disposal contribute to higher emissions of hazardous chemicals and pose challenges in recycling, negatively affecting sustainability efforts in the automotive sector. Choosing reticulated foam supports improved lifecycle emissions and aligns with increasing regulatory demands for eco-friendly automotive materials.
Cost Analysis: Reticulated vs PVC Foam
Reticulated foam typically offers a higher upfront cost compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam due to its open-cell structure and manufacturing complexity, but provides superior breathability and sound absorption for automotive interiors. PVC foam, being denser and closed-cell, tends to be more cost-effective for large-scale production, offering durability and moisture resistance with lower material and processing expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership, reticulated foam may incur additional expenses in maintenance and replacement, while PVC foam delivers longer lifespan and consistent performance, influencing automotive manufacturers' material selection based on budget and functional requirements.
Best Choice for Automotive Interiors
Reticulated foam offers superior breathability and durability, making it an excellent choice for automotive interiors requiring efficient air circulation and long-lasting comfort. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV exposure, ensuring optimal performance in harsh automotive environments. Selecting the best material depends on specific interior needs, with reticulated foam preferred for ventilation and cushioning, while PVC foam is favored for enhanced durability and environmental resistance.
Infographic: Reticulated foam vs Polyvinyl chloride foam for Automotive interior
 azmater.com
azmater.com