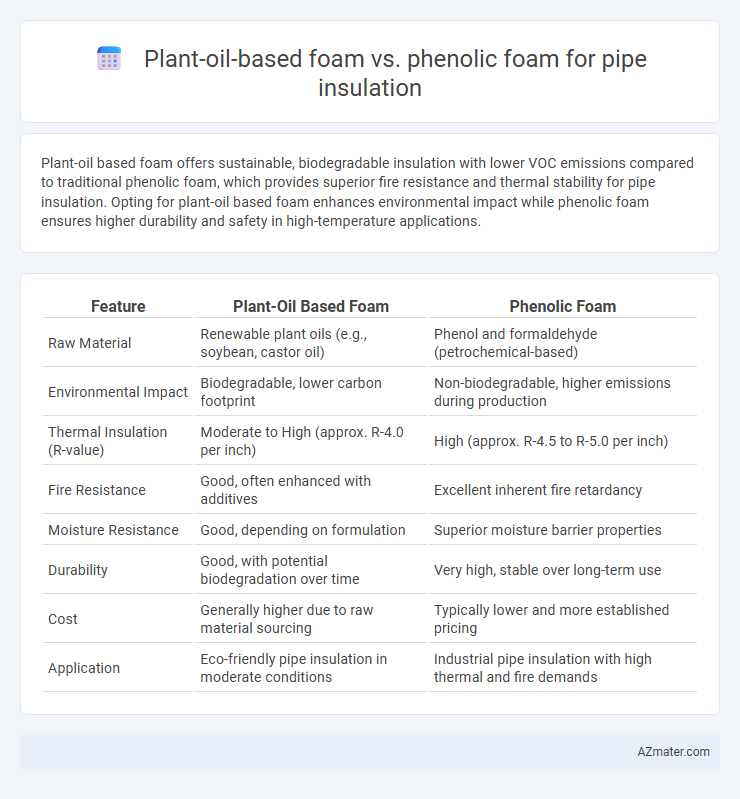
Plant-oil based foam offers sustainable, biodegradable insulation with lower VOC emissions compared to traditional phenolic foam, which provides superior fire resistance and thermal stability for pipe insulation. Opting for plant-oil based foam enhances environmental impact while phenolic foam ensures higher durability and safety in high-temperature applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plant-Oil Based Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Renewable plant oils (e.g., soybean, castor oil) | Phenol and formaldehyde (petrochemical-based) |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher emissions during production |
| Thermal Insulation (R-value) | Moderate to High (approx. R-4.0 per inch) | High (approx. R-4.5 to R-5.0 per inch) |
| Fire Resistance | Good, often enhanced with additives | Excellent inherent fire retardancy |
| Moisture Resistance | Good, depending on formulation | Superior moisture barrier properties |
| Durability | Good, with potential biodegradation over time | Very high, stable over long-term use |
| Cost | Generally higher due to raw material sourcing | Typically lower and more established pricing |
| Application | Eco-friendly pipe insulation in moderate conditions | Industrial pipe insulation with high thermal and fire demands |
Introduction to Pipe Insulation Materials
Plant-oil based foam offers a sustainable alternative to traditional phenolic foam for pipe insulation, combining thermal efficiency with environmental benefits such as biodegradability and reduced VOC emissions. Phenolic foam, known for its superior fire resistance and low smoke emission, remains a standard material in industrial insulation due to its excellent thermal conductivity and dimensional stability. Selecting between these materials depends on factors including fire safety requirements, environmental impact goals, and thermal performance in HVAC and plumbing applications.
Overview of Plant-Oil Based Foams
Plant-oil based foams for pipe insulation derive from renewable resources such as soy, castor, and palm oils, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional phenolic foams composed mainly of synthetic phenol-formaldehyde resins. These bio-based foams exhibit competitive thermal insulation properties with lower environmental impact due to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and greater biodegradability. Their enhanced flexibility and resistance to moisture absorption make plant-oil foams suitable for various temperature ranges and applications, promoting eco-friendly building practices.
What is Phenolic Foam?
Phenolic foam is a rigid, closed-cell insulation material known for its excellent thermal performance, fire resistance, and low smoke emission, widely used in pipe insulation applications. It is produced from phenol-formaldehyde resin, offering superior dimensional stability and moisture resistance compared to traditional foams. In comparison, plant-oil based foam provides a sustainable alternative with renewable raw materials but often lacks the enhanced fire retardancy and long-term durability found in phenolic foam.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Plant-oil based foam exhibits superior thermal insulation properties compared to phenolic foam, with lower thermal conductivity values typically around 0.020-0.025 W/m*K, enhancing energy efficiency in pipe insulation. Phenolic foam, while offering fire resistance and chemical stability, generally has higher thermal conductivity ranging from 0.025-0.030 W/m*K, which may result in slightly reduced thermal performance. The plant-oil based foam's renewable raw materials contribute to sustainable insulation solutions without compromising thermal efficiency.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Plant-oil based foam offers enhanced fire resistance and lower smoke toxicity compared to traditional phenolic foam used in pipe insulation, reducing fire hazards in industrial and commercial settings. Its bio-based composition contributes to a slower flame spread and emits fewer harmful gases during combustion, improving overall safety for occupants and maintenance personnel. Phenolic foam, while effective in thermal insulation, typically generates higher smoke density and toxic fumes, making plant-oil based foam a safer alternative in fire-sensitive environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Plant-oil based foam for pipe insulation offers a significant reduction in carbon footprint due to its renewable raw materials and biodegradability, minimizing environmental pollution during disposal. Phenolic foam, while providing excellent fire resistance and thermal insulation, is derived from petroleum-based chemicals and involves toxic resins that pose challenges for eco-friendly waste management. Sustainability benefits of plant-oil based foams include lower greenhouse gas emissions throughout their lifecycle, supporting circular economy principles, whereas phenolic foams contribute to higher environmental strain due to fossil fuel dependence and potential release of hazardous substances.
Durability and Longevity
Plant-oil based foam offers enhanced resistance to moisture absorption and microbial growth, leading to superior durability in humid environments compared to traditional phenolic foam. Phenolic foam, while fire-resistant and dimensionally stable, tends to become brittle over time, reducing its effective lifespan in pipe insulation applications. For long-term performance, plant-oil based foam maintains structural integrity and insulation properties better under varying temperature and environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis: Plant-Oil vs Phenolic Foams
Plant-oil based foam generally offers a cost advantage over phenolic foam due to lower raw material prices and renewable sourcing, which reduce manufacturing expenses. Phenolic foam, while often more expensive, provides superior fire resistance and thermal performance that can justify higher initial costs in safety-critical applications. Lifecycle cost assessments typically favor plant-oil foams for standard pipe insulation projects where environmental sustainability and cost-efficiency are prioritized.
Installation and Practical Considerations
Plant-oil based foam offers easier handling and faster installation compared to phenolic foam due to its lightweight and flexible nature, reducing labor time and complexity on-site. Its lower toxicity and absence of harsh odors improve worker safety and comfort during application, making it suitable for confined spaces. Phenolic foam, while providing excellent fire resistance and thermal insulation, often requires more cautious installation techniques to manage brittleness and cutting dust concerns.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam for Pipe Insulation
Plant-oil based foam offers superior environmental benefits with lower carbon emissions and enhanced sustainability compared to traditional phenolic foam, which excels in fire resistance and thermal stability. Selecting the right foam for pipe insulation depends on the specific requirements of thermal performance, fire safety standards, and environmental impact goals. Balancing these factors ensures optimal insulation efficiency and compliance with regulatory standards for industrial or commercial applications.
Infographic: Plant-oil based foam vs Phenolic foam for Pipe insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com