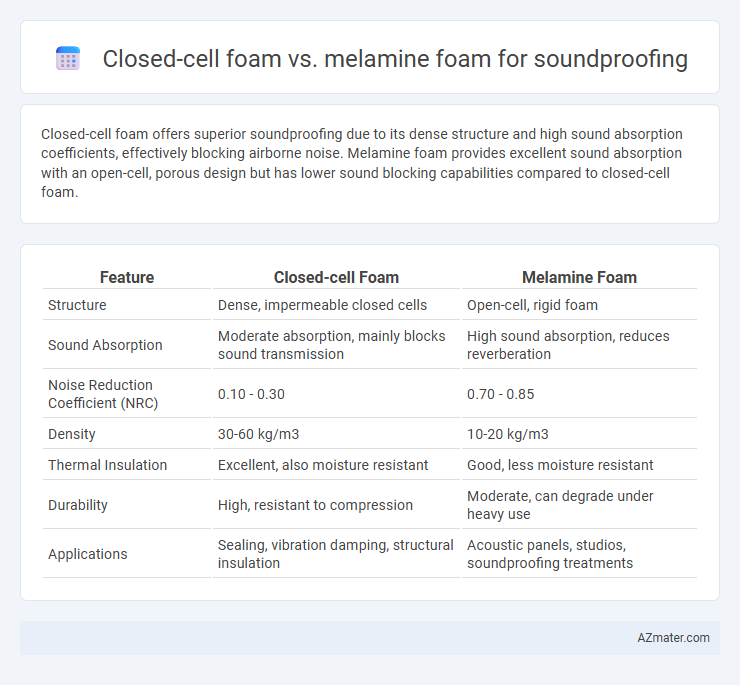
Closed-cell foam offers superior soundproofing due to its dense structure and high sound absorption coefficients, effectively blocking airborne noise. Melamine foam provides excellent sound absorption with an open-cell, porous design but has lower sound blocking capabilities compared to closed-cell foam.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Closed-cell Foam | Melamine Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Dense, impermeable closed cells | Open-cell, rigid foam |
| Sound Absorption | Moderate absorption, mainly blocks sound transmission | High sound absorption, reduces reverberation |
| Noise Reduction Coefficient (NRC) | 0.10 - 0.30 | 0.70 - 0.85 |
| Density | 30-60 kg/m3 | 10-20 kg/m3 |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, also moisture resistant | Good, less moisture resistant |
| Durability | High, resistant to compression | Moderate, can degrade under heavy use |
| Applications | Sealing, vibration damping, structural insulation | Acoustic panels, studios, soundproofing treatments |
Understanding Closed-Cell Foam: Composition and Properties
Closed-cell foam consists of tightly packed cells filled with gas, providing superior density and rigidity that significantly enhance soundproofing effectiveness by blocking airborne noise. Its composition includes materials such as polyethylene or polyurethane, which contribute to high moisture resistance and durability in acoustic applications. These properties make closed-cell foam ideal for environments requiring both thermal insulation and sound absorption, outperforming melamine foam in terms of structural integrity and noise reduction performance.
Introduction to Melamine Foam: Structure and Characteristics
Melamine foam is an open-cell, flexible material composed of thermoset melamine resin, renowned for its exceptional sound absorption properties due to its porous structure. Unlike closed-cell foam, melamine foam features a lightweight matrix of interconnected pores that trap sound waves, reducing noise through energy dissipation rather than reflection. Its high melting point, fire resistance, and thermal insulation capabilities make melamine foam a preferred choice in environments demanding both soundproofing and safety.
Sound Absorption Capabilities: Closed-Cell vs Melamine Foam
Closed-cell foam offers moderate sound absorption primarily by blocking airborne noise through its dense, impermeable structure, making it suitable for reducing sound transmission in insulation applications. Melamine foam excels in sound absorption due to its open-cell structure and high porosity, effectively trapping and dissipating sound waves across a broad frequency range, especially in mid to high frequencies. Acoustic performance tests demonstrate melamine foam's superior noise reduction coefficient (NRC), often exceeding 0.7, compared to closed-cell foam's lower NRC values around 0.3 to 0.5.
Acoustic Isolation Performance Compared
Closed-cell foam offers superior acoustic isolation with high density and rigidity, effectively blocking and absorbing low-frequency sound waves, making it ideal for soundproofing applications requiring strong noise reduction. Melamine foam, while lightweight and open-celled, excels in absorbing mid to high-frequency sounds but provides less effective isolation against low-frequency noise due to its porous structure. For comprehensive acoustic isolation, closed-cell foam outperforms melamine foam in blocking sound transmission, whereas melamine foam primarily enhances room acoustics by reducing reverberation and echoes.
Durability and Longevity of Both Foam Types
Closed-cell foam offers superior durability and longevity due to its dense, impermeable structure that resists moisture, compression, and wear, making it ideal for long-term soundproofing applications. Melamine foam, while effective for acoustic absorption, tends to be more fragile and prone to crumbling or degradation over time, especially in high-traffic or moist environments. For soundproofing solutions requiring extended lifespan and resilience, closed-cell foam is generally the more reliable choice.
Fire Resistance and Safety Features
Closed-cell foam offers superior fire resistance with higher ignition temperatures and less smoke generation compared to melamine foam, making it a safer choice for soundproofing in fire-prone environments. Melamine foam excels in thermal stability and self-extinguishing properties but tends to produce more toxic fumes during combustion, which raises safety concerns. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing fire safety standards and the specific building code requirements for fire resistance in acoustic insulation.
Ease of Installation and Versatility
Closed-cell foam offers straightforward installation due to its rigid, dense structure, making it easy to cut and fit into specific spaces, while its limited flexibility reduces adaptability to irregular surfaces. Melamine foam, known for its open-cell, lightweight, and flexible properties, provides greater versatility by conforming to complex shapes and irregular surfaces, though it may require adhesives or fasteners for secure placement. Both materials enhance soundproofing, but melamine foam's adaptability suits varied acoustic treatments, whereas closed-cell foam excels in stable, uniform applications.
Cost Analysis: Closed-Cell vs Melamine Foam
Closed-cell foam typically costs more per square foot than melamine foam, reflecting its higher density and superior insulation properties. Melamine foam offers a cost-effective solution for sound absorption with a lower material price but often requires thicker or additional layers to achieve similar acoustic performance. Evaluating long-term value, closed-cell foam's durability and moisture resistance can reduce replacement frequency, potentially offsetting its initial higher cost compared to melamine foam.
Best Use Cases for Each Soundproofing Material
Closed-cell foam excels in soundproofing applications requiring moisture resistance and durability, making it ideal for outdoor use, HVAC insulation, and areas exposed to humidity. Melamine foam offers superior sound absorption properties with lightweight and fire-retardant characteristics, best suited for indoor acoustic treatment such as recording studios, theaters, and office spaces. Choosing between them depends on environmental conditions and specific acoustic requirements, with closed-cell foam prioritizing structural sound blocking and melamine foam enhancing sound clarity and reduce reverberation.
Choosing the Right Foam for Optimal Soundproofing Results
Closed-cell foam provides superior soundproofing due to its dense structure that effectively blocks airborne noise and minimizes sound transmission. Melamine foam excels in absorbing mid-to-high frequency sounds thanks to its open-cell, flexible structure, making it ideal for reducing echo and reverberation within a room. Selecting the right foam depends on the specific soundproofing goals--closed-cell foam for insulation and noise blocking, melamine foam for acoustic treatment and sound absorption.
Infographic: Closed-cell foam vs Melamine foam for Soundproofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com