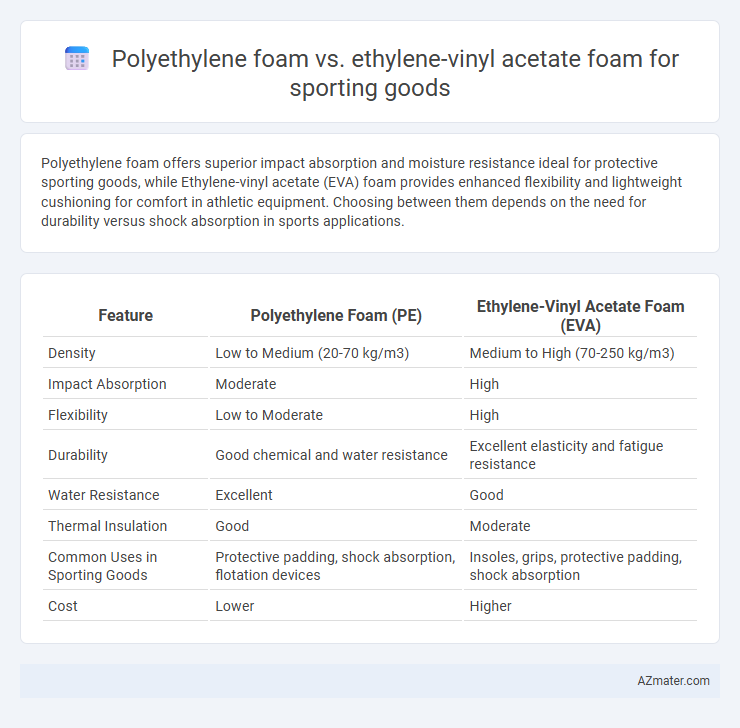
Polyethylene foam offers superior impact absorption and moisture resistance ideal for protective sporting goods, while Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides enhanced flexibility and lightweight cushioning for comfort in athletic equipment. Choosing between them depends on the need for durability versus shock absorption in sports applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyethylene Foam (PE) | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Foam (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low to Medium (20-70 kg/m3) | Medium to High (70-250 kg/m3) |
| Impact Absorption | Moderate | High |
| Flexibility | Low to Moderate | High |
| Durability | Good chemical and water resistance | Excellent elasticity and fatigue resistance |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Thermal Insulation | Good | Moderate |
| Common Uses in Sporting Goods | Protective padding, shock absorption, flotation devices | Insoles, grips, protective padding, shock absorption |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Polyethylene Foam and Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Foam
Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell, lightweight material known for its excellent impact absorption and water resistance, making it ideal for protective sports equipment and padding. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam features a softer, more flexible structure with superior shock absorption and durability, commonly used in insoles, helmets, and various athletic gear. Both foams offer unique cushioning properties, with polyethylene foam providing firmer support and EVA foam delivering enhanced comfort and energy return in sporting goods applications.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Polyethylene foam consists primarily of long chains of ethylene monomers, creating a highly durable, closed-cell structure that offers excellent cushioning and water resistance ideal for sporting goods like protective padding and insoles. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam incorporates vinyl acetate copolymers, resulting in a softer, more flexible material with enhanced shock absorption and energy return, often used in athletic footwear midsoles and impact protection. The chemical difference--polyethylene's pure hydrocarbon chain versus EVA's vinyl acetate units--directly influences their mechanical properties, making polyethylene foam more rigid and EVA foam more elastic and resilient under dynamic sports activities.
Key Physical Properties: Density, Flexibility, and Durability
Polyethylene foam offers higher density and excellent durability, making it suitable for impact protection and long-lasting performance in sporting goods. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides superior flexibility and cushioning, ideal for comfort and shock absorption in footwear and padding. Both materials balance density and resilience, but EVA is preferred where flexibility and softness are critical, while polyethylene foam excels in structural support and wear resistance.
Cushioning and Shock Absorption Capabilities
Polyethylene foam offers superior cushioning and shock absorption due to its closed-cell structure, making it highly effective in absorbing impacts in sporting goods such as helmets and padding. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides excellent flexibility and resilience, delivering enhanced energy return and comfort in footwear and protective gear. The choice between polyethylene foam and EVA foam depends on the required balance between impact attenuation and flexibility for specific sports applications.
Water and Moisture Resistance Features
Polyethylene foam exhibits superior water and moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, making it highly effective for sporting goods exposed to wet environments. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, while also resistant, tends to absorb more moisture over time because of its more open-cell formation, which can impact durability in prolonged moisture exposure. Choosing polyethylene foam ensures enhanced protection against water infiltration and better performance in aquatic or high-humidity sports applications.
Applications in Sporting Goods: A Side-by-Side Analysis
Polyethylene foam offers high impact absorption and flotation properties, making it ideal for protective sports gear such as helmets, knee pads, and swim training aids. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides superior flexibility, cushioning, and shock absorption, commonly used in shoe midsoles, yoga mats, and boxing gloves. Both materials enhance athlete safety and performance, with polyethylene foam favored for durability in water sports and EVA foam preferred for comfort and resilience in high-impact, land-based activities.
Comfort and Performance in Practical Use
Polyethylene foam offers excellent shock absorption and durability, making it ideal for high-impact sports equipment that requires firm support and long-lasting performance. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides superior cushioning and flexibility, enhancing comfort and movement fluidity in applications like shoe soles and protective gear. The choice between these foams depends on the balance between rigid support and softness needed, with EVA preferred for comfort-driven uses and polyethylene favored for structural resilience.
Weight and Portability Considerations
Polyethylene foam offers lightweight cushioning with excellent shock absorption, making it ideal for portable sporting goods that require easy handling and transport. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides a balance of lightweight construction and superior flexibility, enhancing portability while maintaining durability in sports equipment. Both foams contribute to reducing the overall weight of gear, but EVA foam often excels in applications where flexibility and comfort are prioritized alongside portability.
Cost Efficiency and Value for Money
Polyethylene foam offers cost efficiency due to its lower production expenses and durability, making it ideal for budget-conscious sporting goods manufacturers. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides superior shock absorption and flexibility, resulting in better performance and increased comfort, which enhances overall value for money despite its higher cost. Choosing between polyethylene foam and EVA foam depends on balancing upfront material costs against long-term product durability and user experience in sports applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Polyethylene foam, known for its low density and durable cushioning, is less biodegradable and presents challenges in recycling, impacting its sustainability profile negatively compared to Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) foam. EVA foam offers better environmental benefits with its partial biodegradability and potential for eco-friendly production processes, making it a preferred choice for sustainable sporting goods applications. Choosing EVA foam can reduce long-term environmental footprint due to lower greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing and improved recyclability in sports equipment.
Infographic: Polyethylene foam vs Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam for Sporting good
 azmater.com
azmater.com