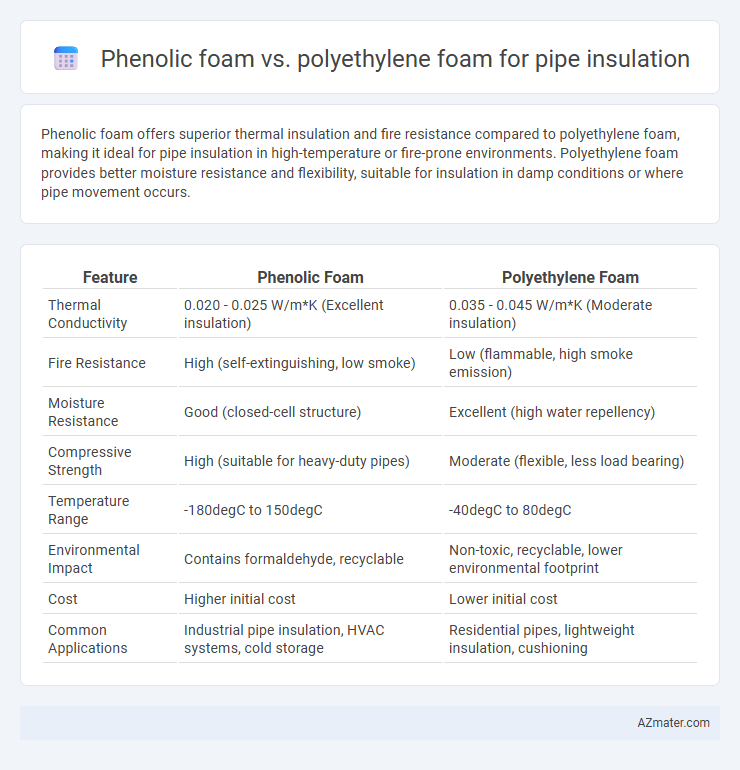
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation and fire resistance compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for pipe insulation in high-temperature or fire-prone environments. Polyethylene foam provides better moisture resistance and flexibility, suitable for insulation in damp conditions or where pipe movement occurs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Phenolic Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.020 - 0.025 W/m*K (Excellent insulation) | 0.035 - 0.045 W/m*K (Moderate insulation) |
| Fire Resistance | High (self-extinguishing, low smoke) | Low (flammable, high smoke emission) |
| Moisture Resistance | Good (closed-cell structure) | Excellent (high water repellency) |
| Compressive Strength | High (suitable for heavy-duty pipes) | Moderate (flexible, less load bearing) |
| Temperature Range | -180degC to 150degC | -40degC to 80degC |
| Environmental Impact | Contains formaldehyde, recyclable | Non-toxic, recyclable, lower environmental footprint |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Common Applications | Industrial pipe insulation, HVAC systems, cold storage | Residential pipes, lightweight insulation, cushioning |
Introduction to Pipe Insulation Materials
Pipe insulation materials like phenolic foam and polyethylene foam offer distinct thermal and mechanical properties essential for efficient energy conservation and system protection. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance and low thermal conductivity, making it ideal for high-temperature pipe insulation in commercial and industrial settings. Polyethylene foam offers excellent moisture resistance and flexibility, preferred for cold pipe applications and environments requiring impact protection.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a rigid, closed-cell insulation material known for its excellent thermal performance, fire resistance, and low smoke emission, making it ideal for pipe insulation in commercial and industrial applications. Its high compressive strength and dimensional stability provide long-term durability against compression and mechanical damage. Compared to polyethylene foam, phenolic foam offers superior insulation values with lower thermal conductivity, contributing to energy efficiency and enhanced fire safety standards.
Overview of Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell, flexible insulation material known for its excellent thermal resistance and moisture impermeability, making it highly suitable for pipe insulation in various temperature ranges. Its lightweight, durable composition provides effective cushioning and vibration dampening, while its resistance to chemicals and UV degradation extends the lifespan of insulated pipes. Compared to phenolic foam, polyethylene foam offers superior flexibility and ease of installation, especially in environments requiring resistance to water absorption and mechanical impact.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Phenolic foam exhibits superior thermal insulation performance compared to polyethylene foam due to its lower thermal conductivity, typically around 0.021-0.027 W/m*K versus polyethylene's 0.035-0.045 W/m*K. This significant difference allows phenolic foam to provide better energy efficiency and enhanced temperature retention in pipe insulation applications. The closed-cell structure of phenolic foam also offers greater resistance to moisture and fire, further improving its insulation reliability and longevity.
Fire Resistance and Safety Properties
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance compared to polyethylene foam due to its inherent low combustible nature and smoke suppressing characteristics, making it ideal for pipe insulation in fire-critical environments. Polyethylene foam, while providing good thermal insulation, is highly flammable and produces dense, toxic smoke when burned, posing significant safety risks. Phenolic foam's ability to self-extinguish and minimal smoke generation enhances overall safety, complying with stringent fire safety standards in industrial and commercial piping systems.
Moisture Resistance and Water Absorption
Phenolic foam exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to polyethylene foam, maintaining structural integrity even in high humidity environments due to its closed-cell structure and low water absorption rate below 1%. Polyethylene foam, while lightweight and flexible, tends to absorb more water over time, which can compromise its insulating properties and lead to potential pipe corrosion. For pipe insulation applications where moisture exposure is critical, phenolic foam provides enhanced durability and long-term thermal performance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Phenolic foam offers superior mechanical strength compared to polyethylene foam, providing excellent compression resistance and maintaining structural integrity under heavy loads for pipe insulation. Its closed-cell structure enhances durability by resisting moisture absorption and chemical degradation, ensuring long-term performance in harsh environments. In contrast, polyethylene foam has lower mechanical strength and may compress or degrade faster under similar conditions, making phenolic foam the preferred choice for applications requiring robust protection and longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Phenolic foam exhibits superior environmental performance with low global warming potential (GWP) and compliance with strict fire and smoke emissions standards, making it a sustainable choice for pipe insulation. Polyethylene foam, while offering good thermal insulation and moisture resistance, is derived from petrochemicals with a higher carbon footprint and limited recyclability, posing challenges to sustainability goals. Selecting phenolic foam supports reduced environmental impact due to its formaldehyde-free composition and longer service life, contributing to lower overall resource consumption and waste generation in insulation applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with an R-value of approximately 4.8 per inch, but its initial cost per square foot is typically 20-30% higher than polyethylene foam, which has an R-value around 3.9 per inch. Polyethylene foam is generally more cost-effective for projects with tight budgets due to lower material and installation expenses, despite shorter lifespan and reduced fire resistance compared to phenolic foam. Economic considerations must weigh the long-term energy savings and decreased maintenance costs of phenolic foam against the upfront affordability of polyethylene foam for pipe insulation.
Which Foam is Better for Pipe Insulation?
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity of about 0.021 W/m*K, making it highly effective for pipe insulation where energy efficiency is critical. Polyethylene foam, while more flexible and resistant to moisture and chemicals, has a higher thermal conductivity around 0.038 W/m*K, leading to less efficient insulation performance. For applications demanding excellent fire resistance and better insulation values, phenolic foam is generally the better choice, whereas polyethylene foam is preferred for pipes requiring greater flexibility and moisture resistance.
Infographic: Phenolic foam vs Polyethylene foam for Pipe insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com