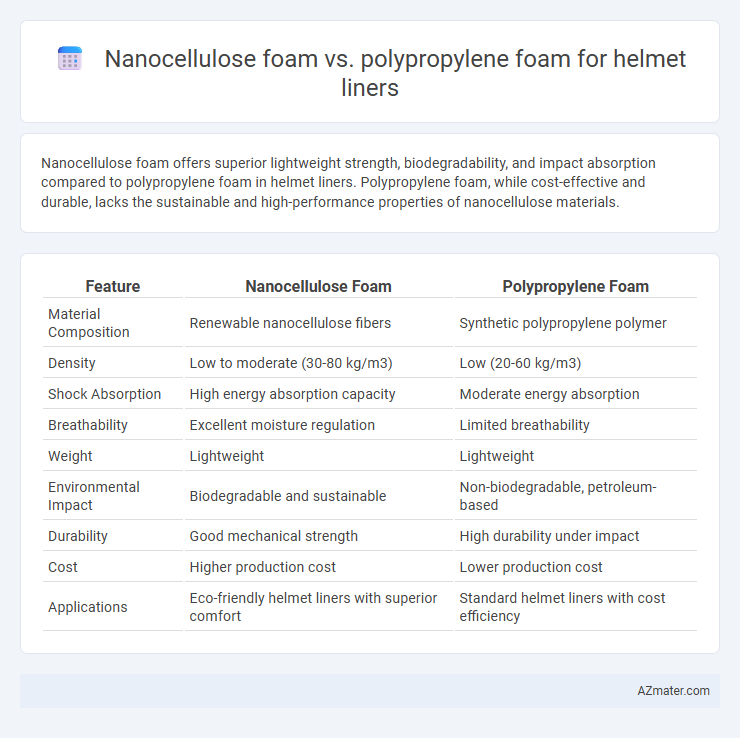
Nanocellulose foam offers superior lightweight strength, biodegradability, and impact absorption compared to polypropylene foam in helmet liners. Polypropylene foam, while cost-effective and durable, lacks the sustainable and high-performance properties of nanocellulose materials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nanocellulose Foam | Polypropylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Renewable nanocellulose fibers | Synthetic polypropylene polymer |
| Density | Low to moderate (30-80 kg/m3) | Low (20-60 kg/m3) |
| Shock Absorption | High energy absorption capacity | Moderate energy absorption |
| Breathability | Excellent moisture regulation | Limited breathability |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and sustainable | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength | High durability under impact |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
| Applications | Eco-friendly helmet liners with superior comfort | Standard helmet liners with cost efficiency |
Introduction to Helmet Liner Materials
Nanocellulose foam, derived from plant-based nanofibers, offers superior mechanical strength, lightweight properties, and enhanced cushioning compared to conventional polypropylene foam used in helmet liners. Polypropylene foam is widely favored for its cost-effectiveness, impact absorption, and ease of manufacturing, but it falls short in biodegradability and thermal stability. Advances in nanocellulose foam technology provide a sustainable alternative with improved breathability and moisture management, critical for enhanced comfort and safety in protective headgear.
Overview of Nanocellulose Foam
Nanocellulose foam offers a sustainable and lightweight alternative to traditional polypropylene foam for helmet liners, characterized by its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent energy absorption capabilities. Derived from renewable biomass, nanocellulose features a porous structure that provides superior impact resistance and enhanced breathability, improving wearer comfort. Its biodegradability and low environmental footprint position nanocellulose foam as a promising material for eco-friendly protective gear applications.
Overview of Polypropylene Foam
Polypropylene foam is a lightweight, durable material known for its excellent impact absorption and thermal insulation properties, making it a popular choice for helmet liners. Its closed-cell structure provides high resistance to water and chemicals, enhancing the helmet's lifespan and comfort during use. Cost-effective and easy to manufacture, polypropylene foam offers consistent cushioning performance, although it is less sustainable compared to nanocellulose foam.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Nanocellulose foam exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to polypropylene foam when used as a helmet liner, offering higher tensile strength and enhanced energy absorption capacity. The modulus of elasticity of nanocellulose foam is significantly greater, resulting in improved impact resistance and durability under repeated stress. Polypropylene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, generally demonstrates lower stiffness and less efficient shock absorption, making nanocellulose foam a more effective material for advanced helmet protection applications.
Impact Absorption and Safety Performance
Nanocellulose foam offers superior impact absorption compared to polypropylene foam due to its high energy dissipation and cellular structure, enhancing helmet liner safety performance. This bio-based material provides better shock attenuation and resilience, reducing the risk of head injuries during impacts. Polypropylene foam, while lightweight and economical, often exhibits lower energy absorption and diminished long-term durability under repeated impacts.
Environmental Sustainability and Biodegradability
Nanocellulose foam offers superior environmental sustainability compared to polypropylene foam due to its renewable origin from plant fibers and reduced carbon footprint during production. Unlike polypropylene foam, which is derived from non-renewable petroleum and contributes to microplastic pollution, nanocellulose foam is fully biodegradable and decomposes naturally within months in soil or compost conditions. The biodegradable property of nanocellulose foam significantly minimizes landfill waste and environmental toxin accumulation, making it a preferable eco-friendly alternative for helmet liner applications.
Manufacturing Processes and Scalability
Nanocellulose foam production involves a bio-based process including fibrillation of cellulose fibers followed by foam formation using freeze-drying or solvent exchange techniques, which can be energy-intensive and slower compared to polypropylene foam manufacturing. Polypropylene foam is produced through melt extrusion or chemical blowing agents, enabling high-speed, continuous production with established industrial scalability. Although nanocellulose foam offers superior biodegradability and mechanical properties for helmet liners, polypropylene foam currently dominates large-scale manufacturing due to easier process control and cost efficiency.
Weight and Comfort for Helmet Liners
Nanocellulose foam offers a significantly lower density compared to polypropylene foam, resulting in a lighter helmet liner that reduces overall helmet weight and enhances user comfort during prolonged wear. The superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties of nanocellulose foam improve ventilation, minimizing heat retention and skin irritation inside the helmet. Polypropylene foam, while durable, typically lacks the same level of comfort due to its higher weight and limited breathability, making nanocellulose foam a preferable choice for lightweight, comfortable helmet liners.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Nanocellulose foam offers superior cost efficiency due to its renewable sourcing and potential for biodegradability, reducing long-term environmental and disposal costs compared to polypropylene foam. Polypropylene foam remains widely available in the market, benefiting from established manufacturing processes and lower upfront material costs, making it a more immediate option for large-scale helmet liner production. The trade-off between higher initial expenses and sustainable lifecycle benefits positions nanocellulose foam as a strategic choice for eco-conscious brands, while polypropylene foam currently dominates due to market accessibility and proven performance.
Future Trends in Helmet Liner Technology
Nanocellulose foam is gaining significant attention in helmet liner technology due to its superior biodegradability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and excellent impact absorption compared to conventional polypropylene foam. Future trends indicate a shift towards sustainable materials like nanocellulose, which offer enhanced protection while reducing environmental impact during production and end-of-life disposal. Innovations will focus on integrating nanocellulose foam with smart sensors for real-time impact monitoring, promoting both safety and eco-friendliness in helmet design.
Infographic: Nanocellulose foam vs Polypropylene foam for Helmet liner
 azmater.com
azmater.com